Cloud Computing: A Double-Edged Sword
Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative technology, enabling businesses and individuals to access and manage data and applications over the internet. Its growing popularity can be attributed to the myriad benefits it offers, such as cost savings, scalability, and flexibility. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential downsides associated with cloud computing, as understanding these challenges can help users make informed decisions and ensure a secure and productive experience.
Advantages of Cloud Computing: A Quick Recap
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals manage and access data and applications. Some of the primary advantages include:
- Cost savings: Cloud computing eliminates the need for investing in expensive hardware, maintenance, and upgrades, allowing organizations to reduce their IT infrastructure costs significantly.
- Scalability: Cloud services enable users to easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and resource allocation without unnecessary expenditures.
- Flexibility: Cloud computing allows users to access their data and applications from any location and device with an internet connection, promoting remote work and collaboration.
- Disaster recovery: Cloud providers often offer robust disaster recovery solutions, ensuring data protection and business continuity in the event of unforeseen circumstances or catastrophes.
- Automatic updates: Cloud service providers handle software and security updates, freeing up users’ time and resources for other important tasks.
Although cloud computing offers numerous benefits, it is essential to be aware of the potential downsides to make informed decisions and ensure a secure and productive experience.
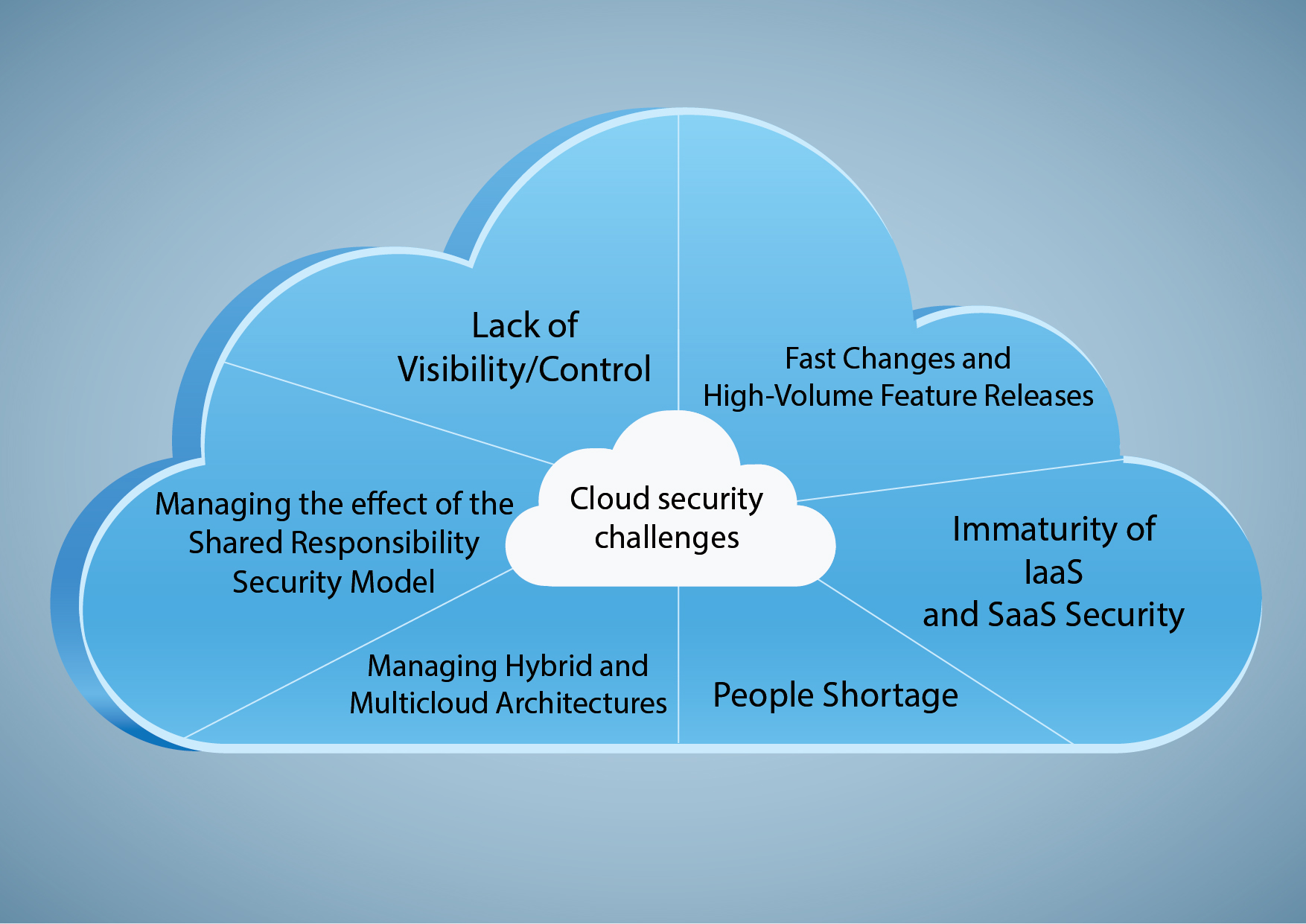
Disadvantage 1: Security and Privacy Concerns
Cloud computing, while offering numerous benefits, is not without its challenges. One of the most significant concerns is the potential for security breaches and privacy issues. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on cloud services to store and manage sensitive data, the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats becomes more pronounced.
For instance, in 2020, the Capital One data breach exposed the personal information of over 100 million individuals, highlighting the vulnerabilities associated with cloud-based systems. Additionally, insider threats, such as rogue employees or contractors with access to sensitive data, can pose a significant risk to organizations using cloud services.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial for businesses and individuals to carefully evaluate cloud providers’ security measures, including encryption, access controls, and monitoring capabilities. Furthermore, implementing robust security policies and procedures, regularly updating and patching systems, and raising awareness about potential threats can help protect against security and privacy issues in cloud computing.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JlCezVM1KA
Disadvantage 2: Downtime and Dependence on Internet Connectivity
Cloud computing services can be affected by downtime, which may result in a significant loss of productivity and access to critical data. This risk is particularly relevant for businesses and individuals who rely heavily on cloud-based applications and services for their day-to-day operations.
For example, in 2017, Amazon Web Services (AWS) experienced an outage that affected numerous high-profile websites and applications, causing disruptions and financial losses for many businesses.
Moreover, cloud computing services require a stable and reliable internet connection to function optimally. In regions with limited or unreliable internet access, users may experience difficulties in accessing their data and applications, leading to potential productivity losses and frustration.
To mitigate these challenges, businesses and individuals should consider implementing redundancy and failover strategies, such as using multiple cloud providers or maintaining local backups. Additionally, ensuring a reliable internet connection through service provider diversification or alternative connectivity options can help minimize the impact of downtime and improve overall cloud computing experience.
Disadvantage 3: Limited Control and Customization Options
When using cloud computing services, businesses and organizations may face limitations in terms of control and customization. Cloud providers often offer standardized configurations and settings, which may not cater to the unique needs of every user. This lack of flexibility can impact organizations that require specific configurations or settings to optimize their operations.
For instance, certain industries have stringent compliance requirements or unique workload characteristics that may not align with the offerings of mainstream cloud providers. In such cases, users may need to adapt their processes or invest in additional tools and services to meet their specific needs, which can lead to increased costs and complexity.
To overcome these limitations, users should carefully evaluate cloud providers’ offerings and ensure that they align with their unique requirements. Engaging in open dialogues with potential cloud providers and negotiating customized solutions can help address some of these concerns. Additionally, exploring multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies can provide users with the flexibility and control they need while still leveraging the benefits of cloud computing.
Disadvantage 4: Vendor Lock-In and Data Portability Issues
Vendor lock-in and data portability are significant challenges associated with cloud computing. Businesses and individuals may find it difficult to migrate their data and applications to alternative service providers due to proprietary technologies, data formats, and contractual obligations. This lack of interoperability can lead to potential vendor lock-in situations, making it challenging for users to switch providers or negotiate better terms.
Data portability is another concern, as users may struggle to extract their data from cloud services in a usable format. This issue can hinder competition and innovation, as it may discourage users from exploring alternative solutions or taking advantage of new services.
To address these challenges, users should carefully review cloud providers’ contract terms, focusing on data ownership, portability, and exit strategies. Engaging in open dialogues with potential cloud providers and negotiating favorable contract terms can help mitigate some of these concerns. Additionally, exploring multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies can provide users with the flexibility and control they need to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure data portability.
Disadvantage 5: Potential for Increased Costs Over Time
The dynamic nature of cloud computing services can lead to potential cost increases over time. Users may encounter unexpected charges or fees due to changes in usage patterns, storage requirements, or performance demands. This unpredictability can make it challenging for businesses and individuals to budget and manage their cloud computing expenses effectively.
For example, a sudden surge in user traffic or data storage needs can result in significant additional costs if not properly managed or anticipated. Additionally, some cloud providers may charge hidden fees or penalties for exceeding specific usage thresholds, further exacerbating the financial impact.
To mitigate these cost challenges, users should carefully monitor their cloud computing usage and regularly review their bills for accuracy. Implementing cost optimization strategies, such as rightsizing instances, using reserved or spot instances, and leveraging automation tools to manage resources can help control costs and minimize unexpected charges. Furthermore, engaging in open dialogues with cloud providers and negotiating favorable pricing structures can also help mitigate some of these concerns.
Navigating the Disadvantages: Strategies for Successful Cloud Computing Adoption
To ensure a successful and secure cloud computing experience, businesses and individuals should consider the following strategies:
- Thoroughly research and evaluate potential cloud providers, focusing on security, privacy, control, customization, and cost management features.
- Develop a comprehensive cloud computing strategy that aligns with unique business or personal needs and objectives.
- Negotiate favorable contract terms and service level agreements (SLAs) that address security, data portability, and cost management concerns.
- Regularly monitor cloud computing usage, performance, and costs to ensure optimal resource allocation and financial management.
- Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls, to protect sensitive data and applications.
- Establish a comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity plan to minimize the impact of downtime and data loss.
- Continuously review and update cloud computing strategies to adapt to evolving business needs, technological advancements, and regulatory requirements.