The Advantages of Migrating Active Directory to the Cloud
Migrating Active Directory to the cloud can bring about numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes. One of the primary advantages is cost savings. By moving Active Directory to the cloud, businesses can eliminate the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure and the associated maintenance costs. Additionally, cloud-based Active Directory often operates on a consumption-based pricing model, allowing businesses to only pay for the resources they use.
Another benefit of Active Directory in the cloud is increased scalability. Cloud-based solutions can easily be scaled up or down to meet the changing needs of an organization. This is particularly beneficial for businesses that experience spikes in demand during certain times of the year, as they can quickly and easily increase their resources to meet the demand without the need for additional infrastructure.
Improved security is another key advantage of Active Directory in the cloud. Cloud service providers often have robust security measures in place, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security updates. This can help to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, cloud-based Active Directory can be easily integrated with other cloud-based security solutions, providing an additional layer of protection.
In conclusion, migrating Active Directory to the cloud can bring about numerous benefits for organizations, including cost savings, increased scalability, and improved security. By carefully considering the various cloud-based Active Directory options available and following best practices for migration, businesses can successfully make the transition to the cloud and begin reaping the benefits it has to offer.
Understanding Cloud-Based Active Directory Solutions
When it comes to cloud-based Active Directory, businesses have several options to choose from. Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a popular choice, offering features such as single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, and device management. Azure AD can also be integrated with other Microsoft cloud services, such as Office 365 and Dynamics 365, providing a seamless user experience.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Directory Service is another option for cloud-based Active Directory. It allows businesses to set up and manage a directory in the AWS cloud, and can be integrated with on-premises Active Directory. AWS Directory Service also supports popular directory features, such as trust relationships and group policies.
Google Cloud Directory Sync is a tool that allows businesses to synchronize their on-premises Active Directory with Google Cloud. This enables users to access Google Cloud services, such as Gmail and Google Drive, using their Active Directory credentials. Google Cloud Directory Sync also supports features such as password synchronization and one-way synchronization.
In conclusion, when it comes to cloud-based Active Directory, businesses have several options to choose from, including Microsoft Azure AD, AWS Directory Service, and Google Cloud Directory Sync. By carefully evaluating the features and capabilities of each option, businesses can select the solution that best meets their needs and begin reaping the benefits of cloud-based Active Directory.
How to Successfully Migrate Active Directory to the Cloud
Migrating Active Directory to the cloud can be a complex process, but careful planning and execution can ensure a smooth transition. The first step is to assess the current on-premises Active Directory environment and identify any potential issues that may need to be addressed. This includes evaluating the current Active Directory infrastructure, identifying any customizations or third-party tools in use, and determining the number of users and devices that will be migrated.
Once the current environment has been assessed, the next step is to select a cloud-based Active Directory solution. Businesses have several options to choose from, including Microsoft Azure AD, Amazon Web Services (AWS) Directory Service, and Google Cloud Directory Sync. Each solution has its own unique features and capabilities, so it is important to carefully evaluate each option and select the one that best meets the needs of the business.
After a solution has been selected, the next step is to prepare the on-premises environment for migration. This includes ensuring that all systems and applications are up to date, and that any necessary updates or upgrades have been performed. It is also important to ensure that all user and device data is backed up and that a rollback plan is in place in case any issues arise during the migration.
The next step is to perform the migration. This typically involves synchronizing the on-premises Active Directory with the cloud-based solution, and then gradually migrating users and devices to the cloud. It is important to monitor the migration process closely and to address any issues that may arise as soon as they are identified.
Once the migration is complete, it is important to thoroughly test the new cloud-based Active Directory environment to ensure that it is functioning properly. This includes testing user authentication, access to applications and resources, and any other critical functions.
In conclusion, migrating Active Directory to the cloud can bring about numerous benefits for businesses, but it is important to carefully plan the migration and to follow best practices to ensure a smooth transition. By assessing the current environment, selecting a cloud-based solution, preparing for the migration, and thoroughly testing the new environment, businesses can successfully migrate Active Directory to the cloud and begin reaping the benefits it has to offer.
Securing Cloud-Based Active Directory
As with any cloud-based solution, security should be a top priority when implementing Active Directory in the cloud. There are several steps that businesses can take to properly secure their cloud-based Active Directory environment.
First and foremost, it is important to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users. MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification before being granted access to the system. This can include something they know, such as a password, something they have, such as a security token, or something they are, such as a fingerprint.
Another important security measure is to regularly monitor for suspicious activity. This includes monitoring login attempts, changes to user accounts, and other potentially suspicious behavior. By regularly reviewing these logs, businesses can quickly identify and address any potential security threats.
It is also important to keep the cloud-based Active Directory environment up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This includes applying security updates to the operating system, as well as to any applications or services that are running on the system.
In addition to these security measures, businesses should also consider implementing a robust backup and disaster recovery plan. This will ensure that in the event of a security breach or other disaster, the business can quickly and easily restore its Active Directory environment.
In conclusion, security should be a top priority when implementing Active Directory in the cloud. By implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly monitoring for suspicious activity, keeping the environment up to date with the latest security patches, and implementing a robust backup and disaster recovery plan, businesses can properly secure their cloud-based Active Directory environment and protect their sensitive data.
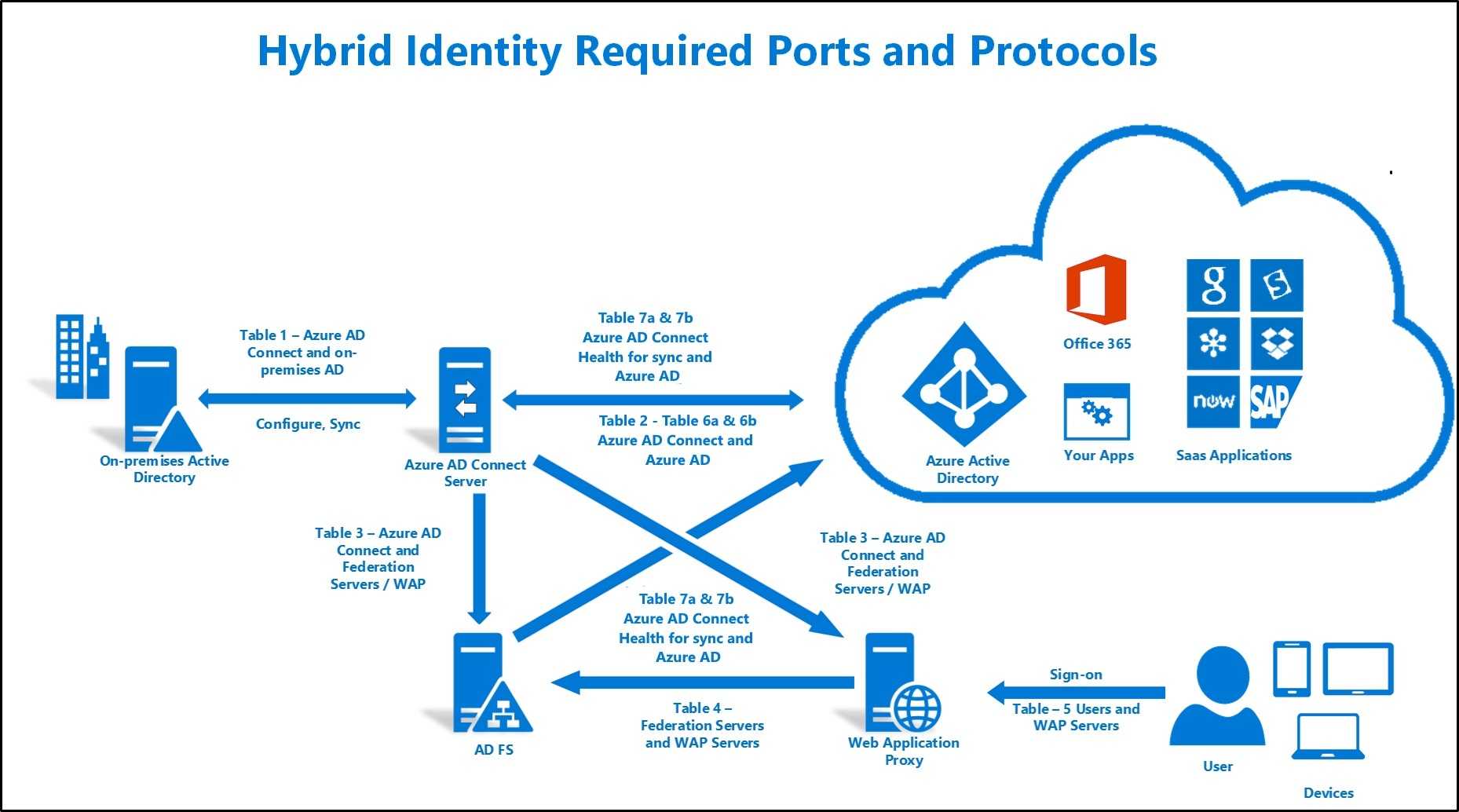
Integrating Cloud-Based Active Directory with On-Premises Directory Services
For many businesses, the move to cloud-based Active Directory does not mean abandoning their on-premises directory services entirely. Instead, they may choose to integrate the two, allowing for a hybrid approach that offers the best of both worlds.
There are several tools and solutions available for integrating cloud-based Active Directory with on-premises directory services. One option is to use synchronization tools, which can automatically synchronize user accounts, groups, and other data between the cloud-based and on-premises environments. This ensures that user information is always up to date and consistent across both environments.
Another option is to use single sign-on (SSO) solutions, which allow users to access both cloud-based and on-premises resources using a single set of credentials. This can simplify the login process for users and reduce the administrative burden of managing multiple sets of credentials.
When integrating cloud-based Active Directory with on-premises directory services, it is important to carefully plan the integration and to consider the potential challenges. This includes ensuring that the necessary infrastructure is in place, such as a secure connection between the cloud and on-premises environments. It is also important to consider the impact on user experience, as well as the potential security implications.
In conclusion, integrating cloud-based Active Directory with on-premises directory services can offer a number of benefits for businesses, including a hybrid approach that combines the best of both worlds. By carefully planning the integration and considering the potential challenges, businesses can successfully integrate their cloud-based and on-premises directory services and provide a seamless user experience.
Cost Considerations for Cloud-Based Active Directory
When considering a move to cloud-based Active Directory, cost is often a major factor for businesses. While there are potential cost savings to be had, it is important to carefully consider the financial implications of using cloud-based Active Directory.
One of the key benefits of cloud-based Active Directory is the use of consumption-based pricing. This means that businesses only pay for the resources they use, rather than having to pay for a fixed amount of resources upfront. This can result in significant cost savings, particularly for businesses with fluctuating needs.
However, it is important to carefully monitor usage to avoid unexpected charges. This includes tracking the number of users, the amount of data stored, and the amount of computing resources being used. By regularly reviewing usage and making adjustments as needed, businesses can ensure that they are not overspending on their cloud-based Active Directory environment.
Another cost consideration for cloud-based Active Directory is the potential need for additional infrastructure and support. This may include the need for additional servers, storage, and networking equipment, as well as the need for additional IT staff to manage and maintain the environment.
In conclusion, cost is an important consideration when implementing cloud-based Active Directory. By carefully considering the financial implications, monitoring usage, and planning for any additional infrastructure and support needs, businesses can ensure that they are making the most of their investment in cloud-based Active Directory.
Real-World Examples of Active Directory in the Cloud
Many businesses have successfully implemented Active Directory in the cloud and have experienced numerous benefits as a result.
For example, a large retail company with multiple locations was able to improve the efficiency and security of its user authentication process by moving its Active Directory environment to the cloud. By using cloud-based Active Directory, the company was able to eliminate the need for manual user account management and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Another example is a healthcare organization that used cloud-based Active Directory to improve the accessibility and availability of its directory services. By implementing a hybrid cloud model, the organization was able to provide its users with seamless access to both cloud-based and on-premises resources, while also ensuring the security and compliance of its directory data.
These are just a few examples of the many businesses that have successfully implemented Active Directory in the cloud. By carefully considering the benefits and potential challenges, businesses can ensure a smooth and successful migration to cloud-based Active Directory.
Future Trends in Cloud-Based Active Directory
As more and more businesses move their operations to the cloud, the use of cloud-based Active Directory is expected to continue to grow. There are several trends that are likely to shape the future of cloud-based Active Directory, including:
Increasing adoption of hybrid cloud models: Many businesses are choosing to adopt a hybrid cloud model, in which they maintain some directory services on-premises and move others to the cloud. This allows them to take advantage of the benefits of both environments, while also ensuring the security and compliance of their directory data.
Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies: Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are becoming increasingly prevalent in the world of cloud-based Active Directory. These technologies can be used to automate tasks, improve security, and enhance the user experience.
Improved scalability and performance: As cloud-based technologies continue to evolve, we can expect to see improvements in the scalability and performance of cloud-based Active Directory. This will allow businesses to support more users and devices, and to do so more efficiently.
Greater focus on security: With the increasing adoption of cloud-based Active Directory, there is also a growing focus on security. Businesses are looking for ways to protect their directory data and ensure the privacy and security of their users. This is likely to result in the development of new security features and capabilities in cloud-based Active Directory.
In conclusion, the future of cloud-based Active Directory is bright, with a number of exciting trends and developments on the horizon. By staying up-to-date with these trends and considering the needs of their users, businesses can ensure a successful implementation of cloud-based Active Directory.