Why Database Backup is Essential for Oracle Environments
In Oracle environments, the importance of a robust oracle backup database strategy cannot be overstated. Data is the lifeblood of any organization, and its protection is paramount. Several threats can compromise the integrity and availability of your oracle backup database. Hardware failures, such as disk crashes or server malfunctions, can lead to data loss if backups are not in place. Data corruption, whether caused by software bugs or human error, can render your oracle backup database unusable. Human error, ranging from accidental data deletion to incorrect updates, remains a significant risk. Cyberattacks, including ransomware and data breaches, are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent, posing a serious threat to valuable data assets. An effective oracle backup database approach is the primary defense against these challenges.
The role of oracle backup database procedures extends beyond simple data preservation. They are integral to business continuity and disaster recovery planning. In the event of a disaster, such as a fire, flood, or cyberattack, backups enable organizations to restore their oracle backup database and resume operations with minimal downtime. Without proper backups, businesses risk significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities. A well-defined oracle backup database strategy ensures that data can be recovered quickly and efficiently, allowing organizations to maintain essential services and meet regulatory requirements.
Therefore, investing in a comprehensive oracle backup database solution is not merely an IT expense; it is a strategic investment in the long-term survival and success of the organization. Proactive measures, including regular backups, thorough validation, and robust security protocols, are essential to safeguarding valuable data assets and ensuring business resilience. Ignoring the importance of oracle backup database is a gamble that no organization can afford to take in today’s data-driven world. The ability to recover quickly from unforeseen events is what separates thriving businesses from those that struggle or fail.
Crafting a Robust Oracle Database Backup Plan
Creating a comprehensive oracle backup database plan is paramount for safeguarding critical data and ensuring business continuity. The initial step involves identifying all oracle backup database instances within the environment, categorizing them based on their importance to business operations. This categorization informs the prioritization of backup efforts and resource allocation. A clear understanding of the data’s sensitivity and its role in essential processes is crucial.
Defining Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) is another critical step. RPO determines the acceptable data loss in the event of an outage, influencing the frequency of backups. For instance, a near-zero RPO necessitates more frequent backups. RTO, on the other hand, dictates the maximum allowable time to restore database functionality. These objectives must align with business needs and be realistically achievable given the available resources and technology. The selection of appropriate oracle backup database methods follows RPO and RTO definition. This includes choosing between logical and physical backups, considering incremental backups for efficiency, and leveraging RMAN’s capabilities for streamlined management. Each method offers distinct advantages and disadvantages concerning speed, storage requirements, and recovery complexity.
Establishing a rigorous oracle backup database schedule is essential for consistent data protection. This schedule should consider peak and off-peak hours to minimize the impact on database performance. Automating the backup process through tools like cron or Oracle Scheduler ensures reliability and reduces the risk of human error. Regular review and adjustment of the backup plan are necessary to adapt to changing business requirements, data growth, and evolving threat landscapes. Documentation of the entire backup process, including procedures, schedules, and responsibilities, is vital for maintaining consistency and facilitating efficient recovery efforts. The oracle backup database plan must also incorporate regular testing and validation to ensure its effectiveness and identify potential weaknesses before a real disaster strikes.
Oracle Backup Techniques: A Detailed Overview
Several techniques exist for creating an oracle backup database, each offering different advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods is crucial for designing an effective oracle backup database strategy. Logical backups involve extracting data from the database into a separate file. Data Pump (expdp) and the original export utility (exp) are commonly used tools for this purpose. The portability and ability to selectively back up specific data are advantages of logical backups. However, they generally require longer restore times and might lead to data loss during the export process if not carefully managed. Therefore, consider these factors when choosing logical backups for your oracle backup database.
Physical backups, on the other hand, create copies of the actual datafiles, control files, and redo logs. This approach provides a more complete oracle backup database solution. Cold backups require shutting down the database before taking a copy, ensuring consistency. Hot backups, facilitated by RMAN (Recovery Manager), allow backups to be performed while the database remains online. Incremental backups offer a compromise by backing up only the data blocks that have changed since the last full or incremental backup. This results in faster backup times and reduced storage space requirements. Differential incremental backups capture all changes since the last full backup, while cumulative incremental backups include all changes since the last incremental backup. While efficient, incremental backups can complicate the restore process.
Image copies create direct, identical copies of datafiles, streamlining the recovery process as no restoration is needed. RMAN (Recovery Manager) is Oracle’s comprehensive tool for managing oracle backup database and recovery operations. It is particularly vital for physical backups, offering features like backup scheduling, compression, and validation. A basic understanding of RMAN’s core functionalities, such as configuring backup destinations, defining retention policies, and initiating backup jobs, is essential for any Oracle DBA. By using RMAN effectively, you can ensure a reliable and efficient oracle backup database and recovery process.
How to Implement Oracle Database Backup Using RMAN
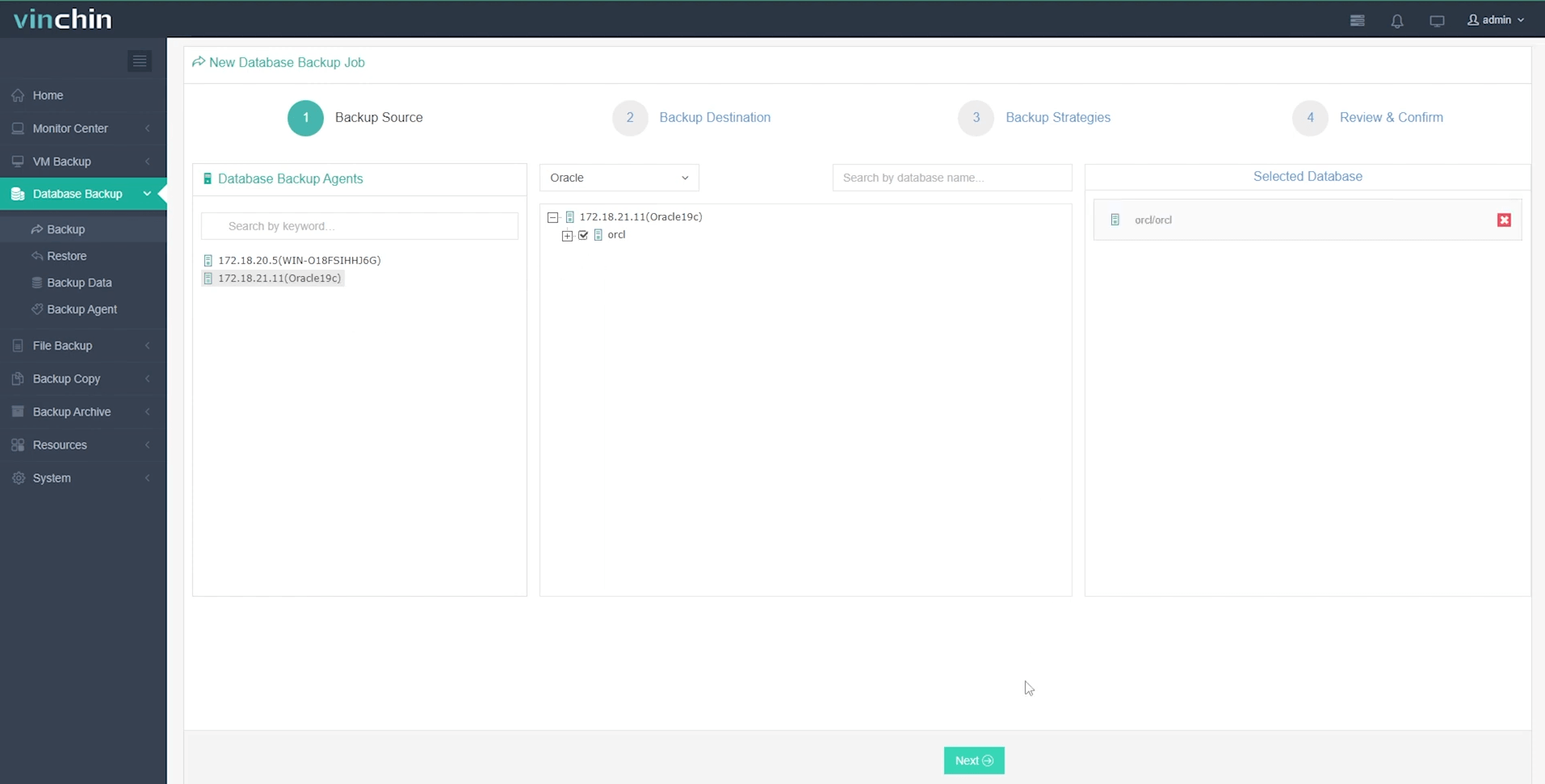
Implementing Oracle database backup using Recovery Manager (RMAN) offers a robust and efficient method for safeguarding your data. RMAN provides a centralized framework for managing all aspects of the backup and recovery process. This guide will walk you through the essential steps for configuring RMAN and performing various types of backups. Before starting, ensure that your Oracle environment is properly configured and that you have the necessary privileges to execute RMAN commands. A well-planned oracle backup database strategy is key.
First, configure RMAN to connect to your target database. This involves setting up the environment variables and establishing a connection using the RMAN command-line interface. For instance, to connect to a database named ‘ORCL’, you would use a command similar to: rman target / (if connecting locally with OS authentication). Alternatively, you can specify the connection string: rman target sys/password@ORCL. Once connected, configure the backup settings. This includes specifying the backup destination, the number of backup copies, and the retention policy. Here’s an example RMAN script for creating a full backup:
CONFIGURE RETENTION POLICY TO RECOVERY WINDOW OF 7 DAYS;
CONFIGURE BACKUP OPTIMIZATION ON;
CONFIGURE DEFAULT DEVICE TYPE TO DISK;
CONFIGURE CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP ON;
CONFIGURE CONTROLFILE AUTOBACKUP FORMAT FOR DEVICE TYPE DISK TO '/backup/controlfile/%F';
BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
This script configures the retention policy to keep backups for 7 days, enables backup optimization, sets the default device type to disk, and enables control file autobackup. The BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG; command initiates a full database backup including the archived redo logs.
For incremental backups, which are essential for an efficient oracle backup database strategy, you can specify the level of incremental backup (level 0 for full, level 1 for incremental). Here’s an example:
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 0 DATABASE;
BACKUP INCREMENTAL LEVEL 1 DATABASE;
Level 0 creates a full backup (similar to a full backup), while level 1 backs up only the blocks that have changed since the last level 0 backup. Regularly validate your backups using the VALIDATE DATABASE; command within RMAN. This command checks for physical and logical corruption in the backup sets. It is also a good security practice to secure your RMAN repository. Implement access controls and regularly audit RMAN activities to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of your oracle backup database operations.
Validating Oracle Backups: Ensuring Data Integrity
Validating oracle backup database integrity is crucial for ensuring data recoverability. Without proper validation, backups may be corrupt, rendering them useless during a disaster. Regular validation provides confidence that the oracle backup database strategy is effective and reliable. Several methods exist to validate oracle backup database integrity, each offering a different level of assurance.
One key method is using the RMAN VALIDATE command. This command checks for physical and logical corruption within backup sets and datafiles. RMAN VALIDATE can detect corrupt blocks, missing files, and other inconsistencies that could prevent a successful restore. It is a best practice to schedule RMAN VALIDATE regularly as part of the oracle backup database maintenance plan. Restore testing is another critical validation method. This involves performing regular test restores to a separate environment. The goal is to verify the oracle backup database process and ensure that data can be recovered within the required Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Setting up a test environment that mirrors the production environment is essential for accurate restore testing. The testing process should include restoring different types of backups, such as full, incremental, and archive logs.
DBVERIFY is a command-line utility that can be used to detect data block corruption in online or offline datafiles. While RMAN VALIDATE focuses on backup sets, DBVERIFY directly examines the datafiles themselves. Running DBVERIFY regularly can help identify corruption issues before they impact the oracle backup database process. Combining these validation methods provides a comprehensive approach to ensuring oracle backup database integrity. Consistent validation, coupled with proactive monitoring, is essential for maintaining a robust and reliable oracle backup database strategy.
Optimizing Oracle Backup Performance: Strategies for Efficiency
Efficient oracle backup database operations are vital for minimizing downtime and resource consumption. Several strategies can significantly enhance the performance of oracle backup database processes. Parallelism, for instance, involves using multiple channels to simultaneously read data and write backups. This approach can dramatically reduce the overall backup time, especially for large databases. The degree of parallelism should be carefully tuned based on the available hardware resources, such as CPU cores, memory, and disk I/O capacity. Insufficient resources can lead to contention and diminished returns. Furthermore, consider the impact of parallelism on other database operations and schedule backups accordingly.
Compression is another crucial technique for optimizing oracle backup database performance. By compressing backup sets, the storage space required for backups is reduced, leading to lower storage costs. Compression also decreases the amount of data that needs to be transferred over the network, which can significantly speed up backup and restore operations, especially in environments with limited bandwidth. RMAN offers various compression algorithms that can be configured based on the desired balance between compression ratio and CPU usage. It’s important to test different compression levels to determine the optimal setting for a specific environment. In addition, RMAN’s backup optimization feature can be enabled to skip backing up unchanged data blocks, further reducing the size of backups and the time required to complete them. This optimization is particularly effective for databases with a high percentage of static data.
Storage considerations play a critical role in oracle backup database performance. Selecting appropriate storage devices for backups based on performance and cost requirements is essential. High-performance storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), can significantly accelerate backup and restore operations, but they typically come at a higher cost. Traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) offer a lower cost per terabyte but may be slower, especially for random I/O operations. Network-attached storage (NAS) and storage area networks (SANs) provide shared storage solutions that can be accessed by multiple servers, but their performance can vary depending on network congestion and other factors. Cloud storage services offer a scalable and cost-effective option for long-term backup retention, but data transfer speeds and security considerations should be carefully evaluated. Regularly monitoring backup performance and adjusting storage configurations as needed is crucial for maintaining optimal efficiency and ensuring that backups can be completed within the required timeframes. Properly configured oracle backup database parameters are key to a successful strategy.
Automating Oracle Backups: Scheduling and Monitoring
Automating the oracle backup database process is crucial for ensuring consistent data protection and minimizing the risk of data loss. Scheduling tools and robust monitoring systems are essential components of a reliable oracle backup database strategy. This automation reduces the need for manual intervention, freeing up database administrators to focus on other critical tasks.
Several scheduling tools can be used to automate oracle backup database operations. Cron, a widely used job scheduler in Unix-like operating systems, is a viable option. The Oracle Scheduler, a built-in feature of the Oracle database, offers more advanced scheduling capabilities. With Oracle Scheduler, database administrators can define complex schedules, dependencies, and event-based triggers to initiate oracle backup database procedures. Jobs can be configured to run daily, weekly, monthly, or at custom intervals. Proper configuration of these scheduling tools is vital for ensuring that oracle backup database operations are executed as planned. Detailed documentation should be maintained to track scheduling configurations and changes.
Monitoring is just as important as scheduling. Implementing a monitoring solution that provides real-time alerts about backup failures is crucial. Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) offers comprehensive monitoring capabilities for Oracle environments, including oracle backup database processes. Alternatively, custom scripts can be developed to check the status of backup jobs and send notifications via email or other alerting mechanisms. Regular review of backup logs is essential for identifying potential issues and ensuring the integrity of the oracle backup database. Proper logging and auditing of backup activities are also vital for compliance and security purposes. Audit trails provide a record of all backup-related operations, making it easier to track changes and identify potential security breaches. This thorough approach ensures the reliability and recoverability of the oracle backup database, safeguarding critical business data.
Selecting the Right Oracle Backup Solution: On-Premise vs. Cloud
Choosing the right Oracle backup database solution is a critical decision, requiring careful consideration of both on-premise and cloud-based options. Each approach presents distinct advantages and disadvantages, impacting cost, scalability, security, and management complexity. Organizations must evaluate their specific needs and constraints to make an informed choice. Understanding the nuances of each deployment model is essential for a robust oracle backup database strategy.
On-premise oracle backup database solutions involve maintaining the backup infrastructure within the organization’s own data center. This provides greater control over data security and compliance, as the data never leaves the organization’s premises. However, on-premise solutions require significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and personnel. Scalability can also be a challenge, as expanding storage capacity requires purchasing and installing additional equipment. Management complexity is another factor, as the organization is responsible for all aspects of backup and recovery, including configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting. An effective on-premise oracle backup database strategy needs skilled staff. The total cost of ownership for on-premise solutions can be substantial, encompassing hardware maintenance, software upgrades, and ongoing operational expenses. Despite the challenges, some organizations prefer the control and security offered by on-premise deployments for their oracle backup database needs.
Cloud-based oracle backup database solutions offer a compelling alternative, leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud. Cloud providers offer various backup services that integrate seamlessly with Oracle databases, simplifying the backup and recovery process. Advantages of cloud backups include reduced capital expenditure, as organizations pay only for the storage and bandwidth they consume. Scalability is also a major benefit, as storage capacity can be easily increased or decreased as needed. Management complexity is reduced, as the cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure and maintenance. However, cloud backups also introduce potential security concerns, as data is stored on a third-party’s infrastructure. Organizations must carefully evaluate the security policies and compliance certifications of cloud providers to ensure that their data is adequately protected. Network bandwidth can also be a limiting factor, especially for large databases. Restore times may be longer compared to on-premise solutions, depending on the network connection and the size of the data. Cost considerations should include egress fees for retrieving data from the cloud. Reputable cloud backup solutions compatible with Oracle databases include offerings from Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Each offers various services that can form the basis of a comprehensive oracle backup database strategy. When considering a cloud based oracle backup database solution, organizations should perform due diligence when examining recovery options and security capabilities.