Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud: Key Cloud Computing Deployment Models
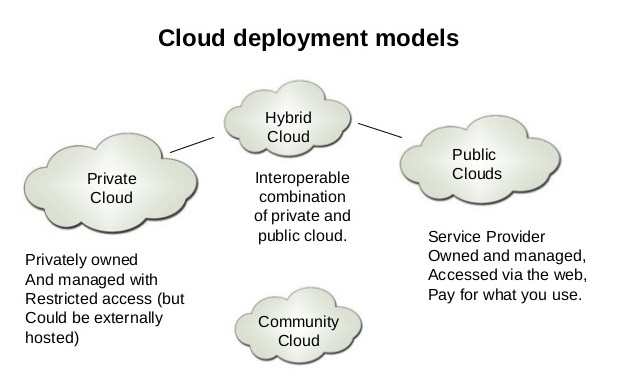
Cloud computing deployment models describe the various methods for implementing and managing cloud services, infrastructure, and platforms. These models cater to diverse business needs and regulatory requirements, offering flexibility and control over resources. The three primary cloud computing deployment models are public, private, and hybrid clouds. Each model has unique characteristics and benefits that make it suitable for specific use cases.
Public Cloud: Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
The public cloud deployment model is a multi-tenant environment where cloud providers offer resources, such as applications, storage, and computing power, available to the general public over the internet. This model is highly scalable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for businesses with fluctuating workload demands or limited IT resources.
Public clouds are managed and maintained by third-party service providers, which eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and manage their own infrastructure. This arrangement allows companies to focus on their core operations while benefiting from the economies of scale provided by the cloud provider.
Key advantages of the public cloud deployment model include:
- Cost savings: Public clouds operate on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which means businesses only pay for the resources they consume. This setup reduces capital expenditures and operational costs associated with maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
- Scalability: Public clouds offer near-infinite scalability, enabling businesses to quickly and easily increase or decrease resources as needed. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for companies with seasonal workload fluctuations or those experiencing rapid growth.
- Reliability and availability: Public cloud providers typically offer service level agreements (SLAs) that guarantee uptime and availability. This commitment ensures that businesses can rely on their cloud services for critical operations and applications.
- Easy access and collaboration: Public clouds can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easy for remote and distributed teams to collaborate on projects and share resources.
Despite the numerous benefits, the public cloud deployment model may not be suitable for all businesses or workloads. Businesses should carefully evaluate their specific needs, regulatory requirements, and security considerations before choosing a cloud computing deployment model.
Private Cloud: Security and Compliance
A private cloud deployment model is a single-tenant environment where cloud services, infrastructure, and platforms are dedicated to a single organization. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises, in a third-party data center, or through a cloud provider’s infrastructure. This model offers enhanced security, data privacy, and regulatory compliance features, making it an ideal choice for businesses with stringent data protection requirements.
Key advantages of the private cloud deployment model include:
- Security and control: Private clouds provide businesses with complete control over their cloud infrastructure, including security policies, access management, and data protection measures. This setup reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Data privacy and compliance: Private clouds offer robust data privacy features that help businesses meet regulatory compliance requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This model is particularly suitable for industries that handle sensitive data, such as healthcare, finance, and government.
- Customization and flexibility: Private clouds can be customized to meet specific business needs and workload requirements. Businesses can tailor their cloud infrastructure to optimize performance, cost, and resource allocation.
- Predictable costs: While private clouds may have higher upfront costs compared to public clouds, they offer predictable ongoing costs through capital expenditures. This arrangement can be more cost-effective for businesses with consistent workload demands.
However, private clouds also have some limitations. They may require more resources and expertise to manage and maintain compared to public clouds. Additionally, private clouds may not offer the same level of scalability and cost-effectiveness as public clouds.
Hybrid Cloud: Balancing Cost and Performance
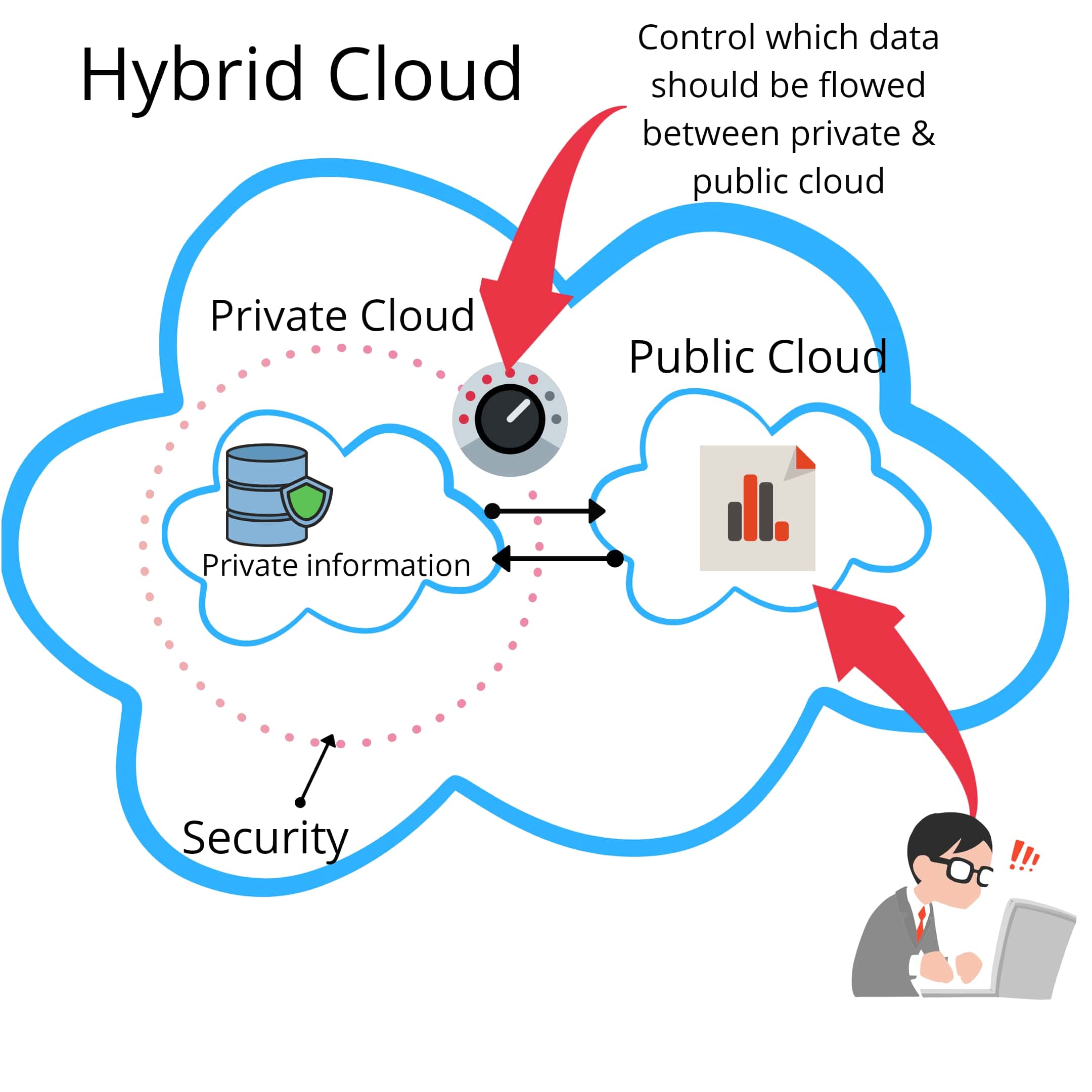
A hybrid cloud deployment model combines public and private clouds, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of both environments. This model enables organizations to optimize cost, performance, and flexibility by using the most appropriate cloud infrastructure for each workload. Hybrid clouds are particularly suitable for businesses with fluctuating workload demands, data protection requirements, or specific regulatory constraints.
Key advantages of the hybrid cloud deployment model include:
- Cost optimization: Hybrid clouds enable businesses to balance capital and operational expenses by using public clouds for variable workloads and private clouds for consistent workloads. This arrangement allows companies to minimize costs while maintaining performance and security.
- Scalability and flexibility: Hybrid clouds offer the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds for variable workloads, along with the security and control of private clouds for sensitive data and applications. This setup enables businesses to adapt to changing workload demands and regulatory requirements.
- Data protection and disaster recovery: Hybrid clouds can be used for data protection and disaster recovery purposes. Businesses can store critical data in a private cloud and replicate it to a public cloud for backup and recovery purposes. This setup ensures data availability and business continuity in the event of a disaster or outage.
- Regulatory compliance: Hybrid clouds allow businesses to store and process sensitive data in a private cloud while using a public cloud for less sensitive workloads. This arrangement helps companies meet regulatory compliance requirements and data protection standards.
However, hybrid clouds also have some challenges. They require robust integration and orchestration between public and private clouds to ensure seamless workload migration and data synchronization. Additionally, managing and maintaining a hybrid cloud infrastructure can be more complex compared to a single cloud environment.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Computing Deployment Model
Selecting the most appropriate cloud computing deployment model is crucial for businesses to optimize costs, performance, and security. By following a step-by-step approach, organizations can make informed decisions based on their unique needs, workload requirements, and budget constraints.
-
Assess your business needs and objectives: Identify your organization’s short- and long-term goals, regulatory requirements, and security considerations. Understanding your business needs will help you determine the most suitable cloud deployment model.
-
Evaluate workload requirements: Analyze your workloads to determine their resource demands, scalability, and performance requirements. Different workloads may be better suited for specific cloud deployment models.
-
Consider budget constraints: Determine the total cost of ownership (TCO) and return on investment (ROI) for each cloud deployment model. Public clouds typically offer lower upfront costs, while private and hybrid clouds may have higher capital expenditures but lower ongoing costs.
-
Review security and compliance requirements: Assess your data protection and regulatory compliance needs. Private and hybrid clouds often provide enhanced security and compliance features, while public clouds offer scalability and cost-effectiveness.
-
Test and validate your chosen deployment model: Before fully committing to a cloud deployment model, test it in a pilot environment to ensure it meets your business needs, workload requirements, and budget constraints. This step will help you identify any potential issues and make adjustments as needed.
By carefully evaluating your organization’s unique needs and constraints, you can choose the most appropriate cloud computing deployment model from the three major options: public, private, or hybrid clouds. Remember that the best choice will depend on your specific situation and may change over time as your business needs and technology evolve.
Real-World Examples of Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Numerous companies have successfully implemented the three major cloud computing deployment models to optimize their IT infrastructure and achieve their business objectives. Here are some real-world examples:
Public Cloud: Netflix
Netflix, a leading entertainment streaming service, leverages the public cloud deployment model using Amazon Web Services (AWS). By utilizing AWS’s scalability and cost-effectiveness, Netflix can handle millions of concurrent users and quickly adapt to fluctuating workload demands.
Private Cloud: Bank of America
Bank of America, one of the largest financial institutions globally, utilizes a private cloud deployment model to ensure enhanced security, data privacy, and regulatory compliance. By maintaining control over their cloud infrastructure, Bank of America can protect sensitive financial data and meet stringent regulatory requirements.
Hybrid Cloud: DHL
DHL, a multinational logistics company, uses a hybrid cloud deployment model to balance cost and performance. By utilizing public clouds for variable workloads and private clouds for consistent workloads, DHL can optimize costs while maintaining security and performance standards.
These real-world examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of the three major cloud computing deployment models in addressing diverse business needs and regulatory requirements. By carefully evaluating their unique needs and constraints, organizations can choose the most appropriate cloud deployment model and successfully implement it to achieve their objectives.
Emerging Cloud Computing Deployment Models
In addition to the traditional public, private, and hybrid cloud computing deployment models, new approaches are emerging to address evolving business needs and technological advancements. Two such models are multi-cloud and edge computing.
Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud refers to the use of multiple cloud computing services from different providers. This approach allows organizations to leverage the unique strengths and features of each cloud provider, ensuring optimal performance, cost, and flexibility. Multi-cloud environments can be used for various purposes, such as load balancing, disaster recovery, and workload optimization.
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data and running applications on distributed devices located at the “edge” of the network, close to the source of data generation. By reducing the need for data transfer to centralized cloud servers, edge computing can improve latency, bandwidth utilization, and data security. This approach is particularly useful for IoT (Internet of Things) devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities, where real-time processing and data privacy are critical.
As technology continues to advance, it is essential for businesses to stay informed about emerging cloud computing deployment models and evaluate their potential benefits and applications. Adapting to new trends and technologies can help organizations maintain a competitive edge and achieve their strategic objectives.
Navigating the Future of Cloud Computing Deployment Models
As technology continues to advance, cloud computing deployment models will evolve to meet the changing needs of businesses and society. Staying informed about these developments and adapting to new trends is crucial for organizations to maintain a competitive edge and achieve their strategic objectives.
In the future, we can expect to see further refinements and innovations in public, private, and hybrid cloud computing deployment models. For instance, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics will likely drive the development of more sophisticated cloud services and platforms. Additionally, the increasing adoption of IoT devices and edge computing will necessitate new approaches to data processing, storage, and security.
Moreover, the ongoing convergence of telecommunications and cloud computing will lead to the emergence of new deployment models, such as telco cloud and 5G-enabled cloud services. These developments will provide businesses with even greater flexibility, scalability, and performance, enabling them to support increasingly complex and data-intensive workloads.
In conclusion, the future of cloud computing deployment models is promising and dynamic. By staying informed and embracing new trends and technologies, organizations can harness the full potential of cloud computing to drive innovation, enhance productivity, and achieve sustainable growth.