Understanding the “Not Recognized as a Cmdlet” Error
Cmdlets are the commands you use within Windows PowerShell. They’re essentially the building blocks for automating tasks and managing your system. Seeing the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error means PowerShell can’t find the command you’re trying to run. This is frustrating, especially when dealing with a command you expect to work, like trying to manage files or network settings. Imagine trying to copy a file using a command you found online, only to be met with this error. This article will help you troubleshoot and resolve this issue. The error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” often stems from simple mistakes, but can also indicate more serious underlying problems. Let’s explore the common causes and solutions.
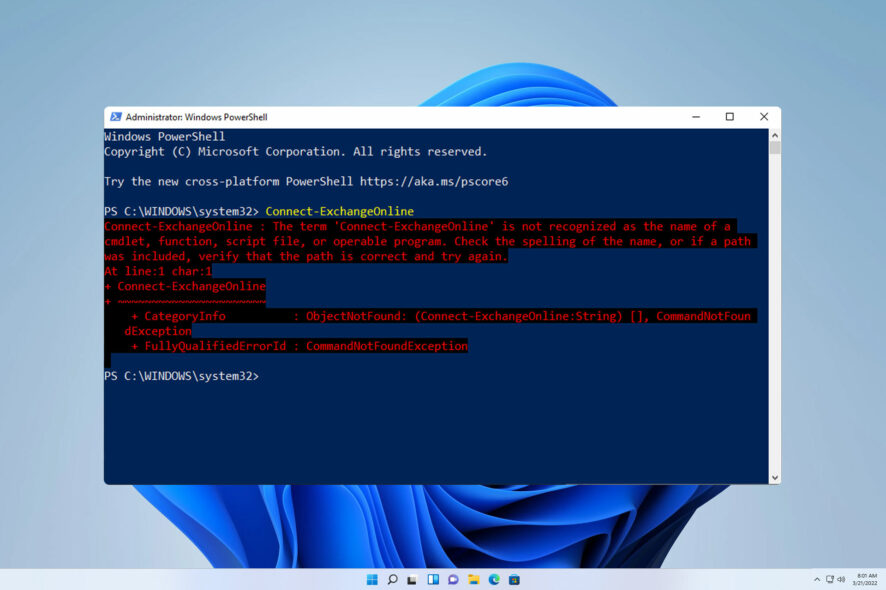
The “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error frequently arises when attempting to execute commands within the PowerShell environment. It signals that the specified command is unavailable to the system. This could be due to a variety of factors, ranging from simple typographical errors to more complex system configuration issues. For example, if you intend to use the `Get-Process` cmdlet but accidentally type `Get-Proceess`, the error message will appear. This prevents you from completing desired actions and can be highly problematic, particularly for users who are less familiar with PowerShell’s command-line structure. Addressing this effectively requires a systematic approach, starting with the most straightforward potential causes. Effective troubleshooting often involves examining spelling, checking for the presence of the cmdlet, and investigating associated system settings.
Many users encounter the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error when working with PowerShell. This usually indicates a problem locating or executing the requested command. Understanding the reasons behind this error is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Sometimes, the problem is a simple typo. Other times, it involves more complex issues with your system’s configuration. This guide will show you how to identify the root cause and implement appropriate solutions. Learning to resolve this common error will save you time and frustration. Mastering these troubleshooting steps will enhance your proficiency in using Windows PowerShell.
Common Causes of the “Cmdlet Not Found” Message
The “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error frequently stems from simple mistakes. Typos are a common culprit. Double-check the command’s spelling and ensure accurate capitalization, as PowerShell is case-sensitive. For example, “Get-Process” is different from “get-process”. This oversight often leads to the frustrating “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error message.
Another frequent cause is the cmdlet’s absence from your system. PowerShell cmdlets are often part of specific modules or features. If the necessary module isn’t installed, the command will fail. This can happen with cmdlets related to networking, storage management, or specialized applications. The error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” signals this missing component. Incorrectly configured environment variables can also prevent PowerShell from finding the cmdlet. Environment variables, such as the PATH variable, tell PowerShell where to look for executables. If the location of a cmdlet’s executable is not listed, the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error appears. PowerShell itself may also be the source of the problem. Outdated or corrupted PowerShell installations can cause various errors, including the failure to recognize cmdlets. Consider updating or reinstalling PowerShell.
Problems with PowerShell’s execution policy can also prevent cmdlets from running. The execution policy determines what scripts PowerShell can run. A restrictive policy might prevent the execution of a cmdlet, even if it’s correctly installed. Finally, permissions can be a factor. Attempting to run a cmdlet without the necessary administrative privileges often results in the error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet”. Running PowerShell as an administrator can often resolve this issue. These factors commonly contribute to the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. Addressing these points will usually resolve the problem.
How to Fix the “Is Not Recognized as a Cmdlet” Error
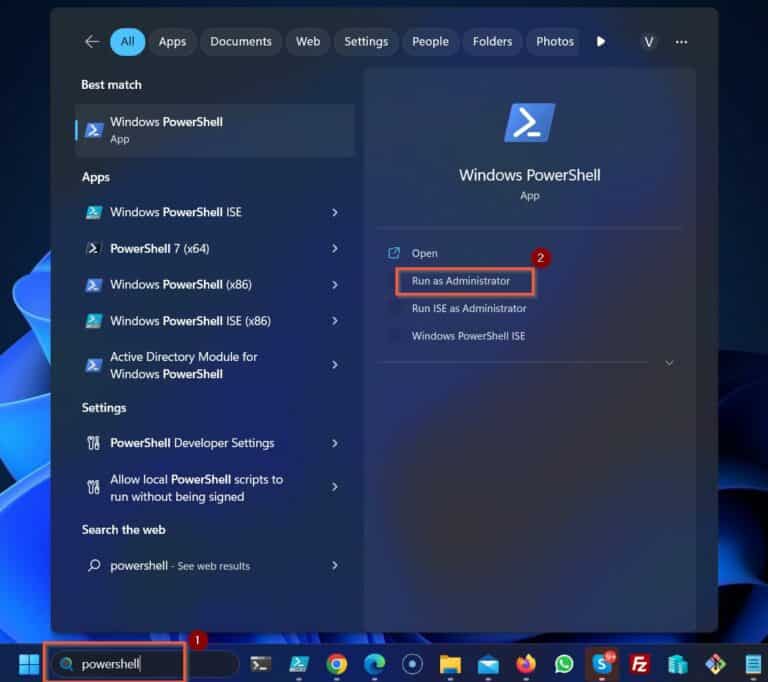
Troubleshooting the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error begins with the simplest checks. First, meticulously review the command you entered. Typos are a frequent culprit. Double-check the spelling and capitalization of the cmdlet name. PowerShell is case-sensitive; even a minor error can prevent the command from running. For example, if the correct command is `Get-Process`, `get-process` or `GET-PROCESS` will produce the error. Correcting the spelling and capitalization is often the quickest fix. If the problem persists, proceed to the next steps.
Next, consider the possibility that the cmdlet itself might not be installed on your system. Many cmdlets are part of specific modules. If you’re using a cmdlet that isn’t a core PowerShell component, it needs to be installed before you can use it. Check the documentation for the specific cmdlet or software to determine if it requires installation of an additional module. If so, use the `Install-Module` cmdlet to install the necessary module. Remember to run PowerShell as administrator to ensure you have the required permissions for installation. Some cmdlets might also have dependencies on other modules or components, so installing those could resolve the issue. If you continue to receive the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” message after ensuring correct spelling and module installation, explore other potential solutions. Check your system’s environment variables. This error often occurs if the system cannot locate the executable file for the cmdlet.
Another potential cause is an issue with your system’s environment variables, particularly the PATH variable. This variable tells Windows where to look for executable files. If the directory containing the cmdlet is not included in the PATH, the system cannot locate the command, resulting in the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” message. Access the environment variable settings (search for “environment variables” in the Windows search bar) to verify that the necessary paths are included. Correcting or adding these paths can resolve the problem. Updating Windows or reinstalling PowerShell are more advanced solutions. Windows updates often include critical patches that can fix underlying system issues. Reinstalling PowerShell is a last resort; ensure you back up any important data before attempting this action. Remember to run any troubleshooting steps as an administrator, to guarantee sufficient privileges. Incorrect path configurations are a common cause of the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. If none of these steps resolve the error, more advanced troubleshooting may be required.
Checking Your PowerShell Version and Updates
Keeping your PowerShell version up-to-date is crucial. Outdated versions may lack cmdlets or have bugs causing the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. To check your PowerShell version, open PowerShell (search for it in the Start menu). Then, type $PSVersionTable and press Enter. This displays detailed information, including the major and minor version numbers. Note the version number for reference. An outdated version might be the root cause of the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error.
PowerShell updates often include new cmdlets and bug fixes, improving stability and functionality. To update PowerShell, use Windows Update. Open the Settings app (Windows key + I), select “Update & Security,” then “Windows Update.” Check for updates and install any available. Restart your computer after the update completes. This simple step often resolves the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” issue, particularly if the problem stems from missing or outdated cmdlets. Regular updates prevent compatibility problems and keep your system secure. Remember, prompt updates can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering the frustrating “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error.
If Windows Update doesn’t find a PowerShell update, or if you suspect a more serious problem, consider manually checking for updates from the Microsoft website. Microsoft frequently releases updates and patches. Directly searching for and installing the latest version can sometimes resolve problems where the automatic update process fails. This is especially helpful when troubleshooting the persistent “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. Always download updates from official sources to prevent malware infections. After the manual installation and system restart, try the cmdlet again. If the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error persists, explore other troubleshooting steps.
Verifying Environment Variables: A Troubleshooting Step for “Cmdlet Not Found” Errors
Environment variables act like a roadmap for Windows. They tell the system where to find programs and commands. The PATH variable is particularly crucial. It lists directories where Windows searches for executable files, including PowerShell cmdlets. If a cmdlet’s location isn’t listed in the PATH, the error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” will appear. This is a common reason why the command is not found.
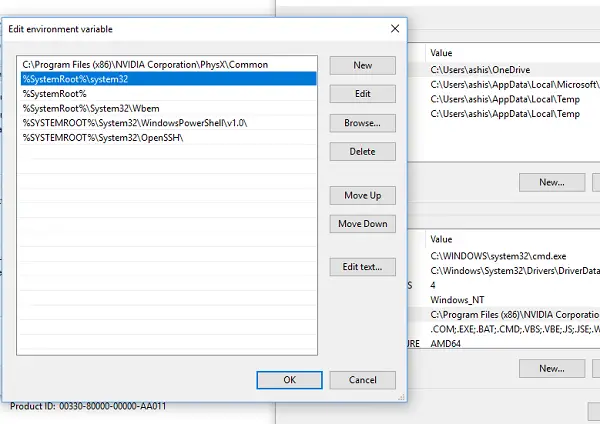
To check your PATH variable, search for “environment variables” in the Windows search bar. Select “Edit the system environment variables.” Click “Environment Variables…” In the “System variables” section, find the variable named “Path” and select it. Click “Edit…” You’ll see a list of directories. Make sure the directories containing your PowerShell cmdlets are included. If they’re missing, you’ll need to add them. This involves clicking “New,” then entering the correct directory path. Remember to restart your system after making changes to environment variables for them to take effect. Incorrectly modifying these variables can cause other problems, so proceed cautiously. If the problem persists after correctly setting the PATH variable, the issue may lie elsewhere.
Sometimes, the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error arises because the system cannot locate the correct PowerShell module. Verifying that the necessary modules are installed and correctly configured is crucial. Use the `Get-Module` cmdlet to list installed modules and check if the required one is present. If it’s missing, you may need to reinstall or repair PowerShell, or potentially download specific modules, depending on the commands you are attempting to use. Remember that a missing or incorrectly configured module can also lead to this error, even if the PATH variable is correctly set. Pay close attention to any error messages that may provide additional clues about the source of the problem. This detailed examination of environment variables will frequently resolve instances of “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet”.
Reinstalling PowerShell or Related Components
Reinstalling PowerShell can resolve many issues causing the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. This process involves uninstalling and then reinstalling the PowerShell module. Begin by opening the Windows Control Panel. Navigate to “Programs and Features.” Locate “Windows PowerShell” in the list of installed programs. Select it and click “Uninstall.” Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the uninstallation. After successfully uninstalling, restart your computer. This ensures all related processes are terminated before reinstalling. Once restarted, open Windows Update to search for and install any available updates. This step is crucial because it often includes the latest version of PowerShell, ensuring the latest features and bug fixes. Failure to update might lead to the same “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error recurring.
If the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error persists after updating, consider a more thorough reinstall. One method is to use the Windows repair tool. This tool can detect and fix corrupted system files, including those related to PowerShell. Use the search function in the Start Menu to find and run the Windows repair tool. Follow the prompts to diagnose and repair any found errors. Once this is complete, restart your computer again. If the repair tool cannot resolve the error, you may need to perform a clean installation of the operating system. This is a more advanced procedure and should be done only if other methods fail. Remember to back up important data before undertaking a clean install. Improperly performed clean installations may lead to data loss.
Sometimes, the problem isn’t with PowerShell itself, but with specific modules or cmdlets. If you’re receiving the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error for a particular command, check if that specific module is properly installed. Many modules can be installed through PowerShellGet. Use the `Get-Module` cmdlet to list installed modules. If the required module is missing, use `Install-Module` to install it. Always refer to the official documentation of the software or module in question for specific installation instructions. Incorrect installation processes for specific modules are a common cause of the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. Remember to run PowerShell as administrator when installing modules. This ensures the necessary permissions to add modules to your system.
Troubleshooting Specific Cmdlets: Common Examples and Solutions
Users frequently encounter the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error with cmdlets related to network management. For example, attempting to use the `Get-NetIPAddress` cmdlet might result in this error if the NetworkManagement module isn’t installed. To resolve this, open PowerShell as an administrator and run `Install-Module NetworkManagement`. This installs the necessary module, allowing the `Get-NetIPAddress` cmdlet to function correctly. Always verify the cmdlet’s module before troubleshooting. If the error persists after installation, check your PowerShell version and environment variables as previously discussed. Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve temporary issues. The error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” highlights the importance of proper module installation.
Another common scenario involves cmdlets associated with specific software applications. Consider a situation where a user installs a custom PowerShell module for managing a database system. If the module installation is incomplete or the environment variables are not configured correctly, commands provided within that module may return the dreaded “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” message. Before troubleshooting, ensure the software is properly installed. Check the software’s documentation for instructions on installing any necessary PowerShell modules. Verify the module’s path is included in your system’s PATH environment variable. Incorrectly configured PATH variables frequently cause the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. This error message might appear even for cmdlets included within standard Windows PowerShell installations if there’s a problem with PATH.
Troubleshooting cmdlets related to Active Directory often presents similar challenges. Cmdlets like `Get-ADUser` or `Set-ADGroupMember` rely on the Active Directory module for Windows PowerShell. The error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” can occur if this module is missing or corrupted. To fix this, ensure Active Directory is properly configured. Then, reinstall the RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) feature pack from Windows Features, which includes the necessary Active Directory modules. Remember to always run PowerShell as administrator when working with Active Directory. If the problem persists after reinstalling, verify the environment variables, focusing on paths related to Active Directory modules. The error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” should not be a persistent problem after addressing these points. Thoroughly checking the module’s installation is key to preventing this error.
When to Seek Further Assistance
While this guide offers solutions for many common “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” errors, some problems require more advanced troubleshooting. If you’ve checked spelling, ensured PowerShell is updated, verified environment variables, and still encounter the error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet,” consider seeking additional support. Exploring Microsoft’s official documentation and support channels can provide valuable insights.
Community forums dedicated to Windows PowerShell often have users facing similar challenges. Their collective experience and shared solutions can prove invaluable. Remember, seeking assistance is not a sign of failure; it’s a proactive step toward resolving complex technical issues. The error “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” can be frustrating, but with persistence and the right resources, a solution is often within reach. Reviewing the steps above, particularly checking spelling and capitalization, and ensuring the correct PowerShell version is installed, often resolve many instances of this error.
Remember to restart your system after making significant changes, such as updating PowerShell or adjusting environment variables. This ensures the changes take effect correctly. If the issue persists despite trying all troubleshooting steps, consider seeking professional IT support for assistance with the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error. Detailed error messages, along with screenshots, can greatly aid in diagnosing the problem effectively. Proactive troubleshooting will help you efficiently resolve the “is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet” error and maintain a smoothly running system. Many instances of this error stem from simple oversights, so a careful review of each step can save significant time and effort.