Understanding Your AWS Networking Needs
To effectively leverage Amazon Web Services (AWS), a solid grasp of its networking fundamentals is crucial. This includes Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), subnets, and the gateways that connect these networks to the outside world. VPCs function as isolated sections of the AWS cloud, providing enhanced security and control. Subnets further divide the VPC into smaller logical networks. Public subnets have direct internet access, while private subnets do not. Choosing the right gateway—the aws nat gateway vs internet gateway—is paramount for enabling appropriate external connectivity for your applications and resources. The Internet Gateway provides a connection to the public internet, while the NAT Gateway allows private instances to access the internet without public IP exposure. This crucial difference significantly impacts security and cost considerations. Understanding this distinction is key to designing a secure and efficient AWS architecture.
The selection between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway depends heavily on the intended use of your resources. Publicly accessible applications, such as web servers, require an Internet Gateway for direct internet connectivity. This allows inbound and outbound traffic to reach and leave your server. Conversely, private instances, such as databases or internal applications, benefit from a NAT Gateway. This gateway translates private IP addresses to public ones, allowing outbound internet access while keeping the instances hidden from the public internet. This approach enhances security by reducing the attack surface. This decision directly impacts your network design, resource allocation, and overall security posture. A well-informed choice optimizes network performance and minimizes costs.
Effective AWS networking hinges on understanding the interplay between VPCs, subnets, and gateways. Resources residing in public subnets connect directly to the internet through the Internet Gateway. This direct connection offers high performance but compromises security. In contrast, resources in private subnets rely on the NAT Gateway for internet access. This translates private IPs to public IPs for outbound connections, shielding the private instances from direct internet exposure. The choice between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway should consider factors such as security needs, cost, and application requirements. Careful planning ensures a secure, scalable, and cost-effective AWS infrastructure. Understanding these concepts provides a foundation for designing robust and reliable cloud-based systems.
Introducing the Amazon Internet Gateway
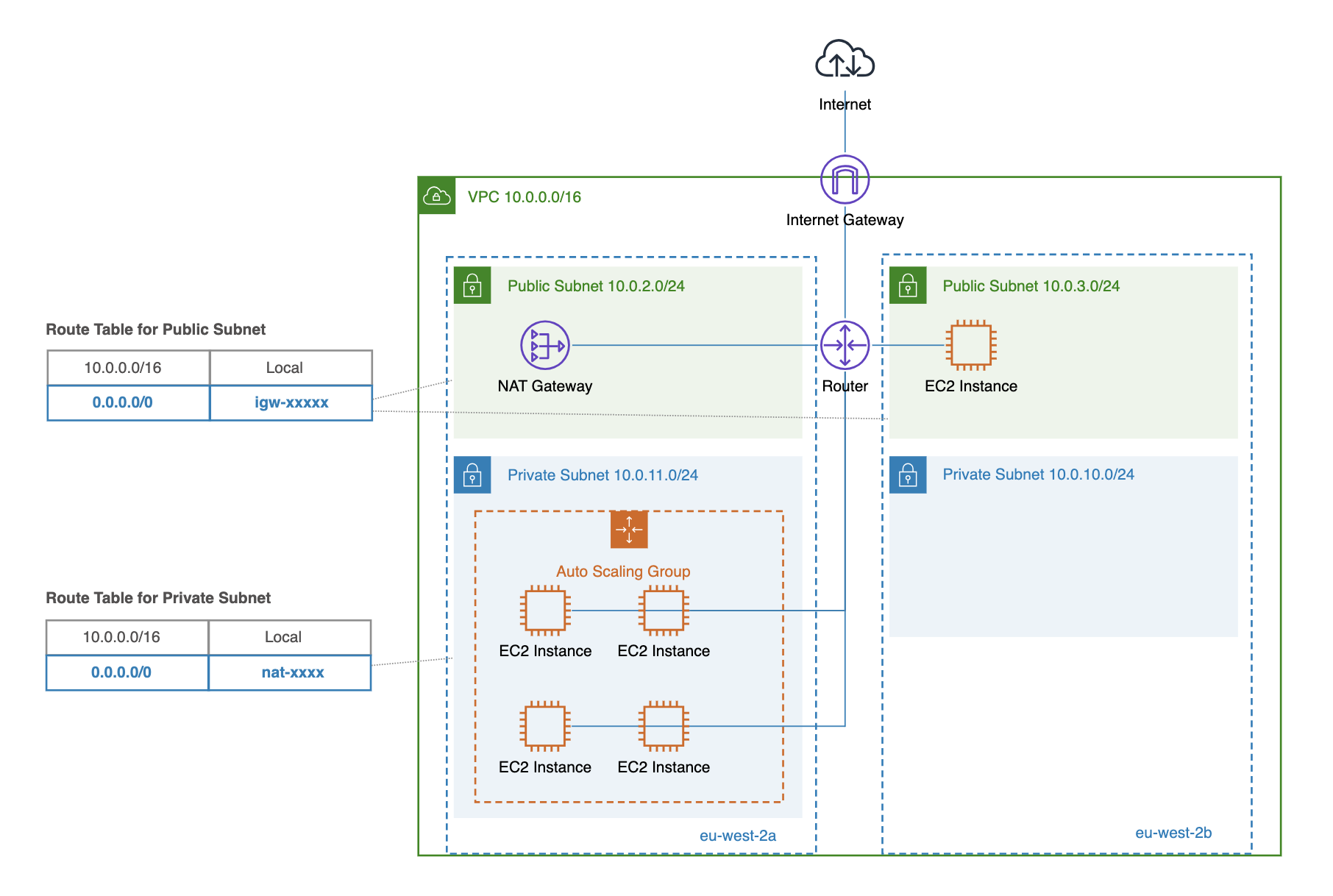
The Amazon Internet Gateway (IGW) serves as the essential connection point between your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and the public internet. It’s the only gateway capable of routing traffic directly to and from the internet. This makes it crucial for any VPC needing public web access. Use cases include hosting publicly accessible web servers, databases, or applications that require direct internet connectivity. The IGW uses public IP addresses assigned by AWS. It handles both inbound and outbound internet traffic seamlessly, providing a straightforward path to global connectivity. When choosing between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway, consider the need for public accessibility.
An IGW’s simplicity is a key advantage. It requires minimal configuration and management. You attach it to your VPC, and it automatically handles routing. This ease of use contrasts with the more complex configuration of a NAT Gateway, making it a preferable option for workloads needing straightforward public access. However, this simplicity comes at the cost of increased security risk, as instances directly connected via an IGW are exposed to the public internet. This necessitates robust security measures on those instances to mitigate potential vulnerabilities. A simple diagram would show the IGW sitting at the edge of the VPC, routing traffic to and from the internet. The decision of aws nat gateway vs internet gateway hinges on your security priorities and application needs.
Understanding the role of the IGW within the broader context of aws nat gateway vs internet gateway is vital. While a NAT Gateway provides internet access for private instances, the IGW provides the foundational connection to the internet for the entire VPC. Without an IGW, no internet connectivity is possible, regardless of the use of NAT Gateways. Therefore, an IGW is always a necessary component of any VPC that requires internet access, even when utilizing NAT Gateways for enhanced security of specific resources. Choosing between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway depends on whether your resources require direct public exposure or not.
Deep Dive into the AWS NAT Gateway
The AWS NAT Gateway is a fully managed service that enables instances in private subnets to connect to the internet or other AWS services without requiring public IP addresses. This is a key differentiator in the aws nat gateway vs internet gateway discussion. Unlike instances connected via an Internet Gateway, instances using a NAT Gateway remain shielded from direct internet exposure, enhancing security. The NAT Gateway acts as an intermediary, translating private IP addresses of instances within a private subnet to public IP addresses for outbound connections. This translation process masks the private IP addresses, preventing them from being directly accessible from the internet. This architecture is crucial for improving the security posture of your VPC, making it a powerful tool when comparing aws nat gateway vs internet gateway options.
One of the primary benefits of a NAT Gateway is its simplified network management. Administrators don’t need to manage individual NAT instances or public IP addresses for each instance requiring internet access. The NAT Gateway handles this automatically, scaling resources as needed to accommodate the traffic load. This scalability is a significant advantage over managing individual NAT instances, particularly in dynamic environments. This ease of management is a factor to consider when choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway solution. Furthermore, the NAT Gateway’s inherent security benefits minimize the attack surface compared to instances with public IP addresses, which are directly exposed to potential threats. The simplified management and improved security offered by the NAT Gateway contribute to a more robust and efficient network infrastructure.
The AWS NAT Gateway uses a combination of network address translation (NAT) and elastic IP addresses to provide outbound connectivity. When an instance in a private subnet needs to access the internet, its traffic is routed through the NAT Gateway. The NAT Gateway then translates the private IP address of the instance to one of its own elastic IP addresses before sending the traffic to the internet. The response traffic follows the reverse path, with the NAT Gateway translating the public IP address back to the private IP address of the instance. This process ensures that instances in private subnets can access the internet securely and without having their private IP addresses exposed. The selection between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway depends heavily on these security and management considerations. Remember to consider the implications for your specific network architecture when making your choice.
Choosing Between AWS Internet Gateway and NAT Gateway: A Decision-Making Guide
Selecting the right gateway for your AWS architecture is crucial. The choice between an AWS Internet Gateway and a NAT Gateway hinges on your specific networking needs and security priorities. This section clarifies the decision-making process for choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway. A key factor is whether your instances require direct public internet access. An Internet Gateway provides this direct access, making it suitable for publicly accessible applications like web servers. However, this direct exposure increases your security risks. Conversely, a NAT Gateway allows instances in private subnets to access the internet without public IP addresses, enhancing security. This makes it ideal for internal applications that require internet connectivity but shouldn’t be directly exposed to the public web. The decision often comes down to balancing cost, security, and management simplicity. Understanding the trade-offs is vital for efficient and secure cloud infrastructure management.
The following table summarizes the key differences between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway to aid in your decision-making process. When deciding between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway, consider the security implications. Directly exposing instances to the internet (Internet Gateway) increases vulnerability. NAT Gateways mitigate this by masking private IP addresses. Management complexity also differs; Internet Gateways are simpler to manage, while NAT Gateways require configuring the NAT translation process. Cost is another significant factor. Internet Gateways have a minimal fixed cost, while NAT Gateways incur an hourly charge based on usage. Bandwidth consumption significantly impacts NAT Gateway costs. High-bandwidth applications might make NAT Gateways more expensive than initially anticipated. Therefore, carefully consider your application’s bandwidth requirements when choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway. The choice between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway is not a simple one-size-fits-all solution.
Consider these use cases: A web application needing public access necessitates an Internet Gateway. In contrast, a database server needing internet access for updates but not public exposure is a perfect use case for a NAT Gateway. For applications requiring high availability and redundancy, deploying multiple NAT Gateways across different Availability Zones is recommended. This ensures continuous internet access even in case of an AZ failure. This decision, therefore, requires a careful evaluation of your application’s requirements, security needs, and budget constraints. Remember, the optimal choice for aws nat gateway vs internet gateway depends entirely on the specific needs of your application and infrastructure. Effective planning and understanding of the capabilities and limitations of each gateway are essential for building a robust and secure AWS environment. Choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway depends on your needs. The right choice directly influences security and cost-effectiveness.
| Feature | Internet Gateway | NAT Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Connects VPC to the internet | Enables private subnet instances to access the internet |
| IP Address Requirement | Requires public IP addresses | Uses Elastic IP addresses (EIP) |
| Security | Higher risk due to direct internet exposure | Enhanced security due to private IP address usage |
| Cost | Minimal fixed cost | Hourly charge based on usage |
| Management Complexity | Relatively simple | Requires configuration of NAT translation |
| Use Cases | Publicly accessible web servers, load balancers | Internal applications requiring internet access |
Security Implications: A Comparative Analysis of aws nat gateway vs internet gateway
When comparing aws nat gateway vs internet gateway, security is a paramount concern. An Internet Gateway directly exposes instances to the public internet. This creates a larger attack surface, increasing vulnerability to various threats. Malicious actors can directly target instances with public IP addresses. Effective security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, are crucial but cannot fully mitigate the inherent risks. Understanding the potential consequences of this direct exposure is vital for network security planning. The choice between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway significantly impacts your overall security posture.
In contrast, a NAT Gateway enhances security by shielding private subnet instances from the public internet. These instances do not possess public IP addresses. Outbound internet access is facilitated through the NAT Gateway’s translation of private to public IPs. This significantly reduces the attack surface, making it more difficult for malicious actors to directly target internal systems. This indirect connection offers a critical layer of defense, improving the overall security of the VPC. The decision of aws nat gateway vs internet gateway should strongly consider the varying security implications.
The benefits of a NAT Gateway extend beyond simply hiding private IPs. It provides better control over outbound traffic. Network administrators can implement stricter access controls and monitor traffic flow more effectively. This granular control contributes to improved security posture and minimizes the risk of unauthorized data egress. By comparing aws nat gateway vs internet gateway, organizations can choose the solution that best aligns with their security requirements and risk tolerance. Careful consideration of the security aspects is essential for a robust and protected cloud infrastructure.
Cost Considerations: Internet Gateway vs. NAT Gateway
Understanding the cost implications of choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway is crucial for efficient AWS resource management. The Internet Gateway, a fundamental component of any VPC, carries a minimal, often negligible, cost. Its pricing model is typically included within the overall cost of the VPC and associated services. This means that while there is a cost associated with the underlying infrastructure, it is not usually a significant factor in budgetary considerations when compared to other AWS services. The primary cost driver with the Internet Gateway is the underlying data transfer costs, which are charged based on the volume of data transmitted in and out of your VPC. Efficient bandwidth management practices are key to controlling expenses.
In contrast, the aws nat gateway vs internet gateway cost comparison highlights a key difference: NAT Gateways incur an hourly charge. This charge is based on the size of the NAT Gateway, which is scalable to meet your needs. Larger NAT Gateways, capable of handling greater bandwidth, naturally result in higher hourly costs. Therefore, efficient sizing of your NAT Gateway is crucial to cost optimization. Data transfer costs, similar to the Internet Gateway, also apply to NAT Gateways and will impact the overall expenditure. The cost of a NAT Gateway can be significantly higher than an Internet Gateway if not managed effectively. This is because the hourly charge accumulates continuously. Choosing the right size for your needs and accurately predicting your bandwidth requirements will minimize these costs. Factors such as the number of instances accessing the internet via the NAT Gateway and their average data transfer volume directly affect expenses. Consider these aspects during your aws nat gateway vs internet gateway analysis to gain better control over costs.
In summary, when comparing aws nat gateway vs internet gateway from a cost perspective, the Internet Gateway offers a more predictable and often negligible fixed cost, primarily driven by data transfer. The NAT Gateway introduces an hourly charge that scales with its size and bandwidth usage. Careful planning, efficient sizing, and monitoring of bandwidth consumption are paramount to optimize costs when using a NAT Gateway. A thorough understanding of your application’s internet usage patterns is crucial in choosing between these gateways and effectively managing associated expenses. Proper analysis of your aws nat gateway vs internet gateway options and the associated costs will ensure that your AWS infrastructure remains cost-effective and optimized for your needs.
Practical Scenarios: Real-World Use Cases of AWS NAT Gateway vs Internet Gateway
Choosing between an AWS NAT Gateway and an Internet Gateway depends heavily on the specific needs of your application. Consider a scenario where you have a web server requiring direct public access. This application demands an Internet Gateway, allowing inbound and outbound internet traffic. In contrast, a database server might only require access to external services for updates, not direct public access. This is an ideal use case for an AWS NAT Gateway. The NAT Gateway provides the necessary internet connectivity for the database server without exposing it directly to the internet, enhancing security. This illustrates the key difference: an Internet Gateway exposes resources publicly, while a NAT Gateway keeps resources private yet internet-capable. The choice between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway hinges on this critical distinction of public versus private subnet accessibility.
Another practical example highlights the cost-effectiveness of a NAT Gateway. Imagine a large-scale application with numerous internal servers requiring internet access for updates or internal communication. Using individual Internet Gateways for each server would be exorbitantly expensive and highly complex to manage. A far more efficient and cost-effective approach involves deploying a single or multiple NAT Gateways to handle outbound traffic from all private subnets. This approach simplifies management, enhances security by reducing the exposed attack surface, and significantly minimizes costs associated with public IP addresses. The selection between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway in this case is clear: the NAT Gateway provides a superior solution for cost optimization and security.
Finally, consider a microservices architecture. Individual services might have different connectivity needs. Some services may require public accessibility, necessitating an Internet Gateway, while others might benefit from the security and cost-efficiency of a NAT Gateway. This scenario highlights the flexibility offered by both gateway types and the importance of careful planning to align connectivity requirements with the appropriate gateway type. Properly choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway in such diverse environments requires a nuanced understanding of your application’s architecture and security posture. Understanding these scenarios is vital for effective AWS networking design.
Implementing and Managing Your Chosen Gateway
Creating and managing both Internet Gateways and AWS NAT Gateways within the AWS Management Console is a straightforward process. For an Internet Gateway, users navigate to the VPC section, select “Internet Gateways,” and then choose “Create Internet Gateway.” The process involves attaching the gateway to the VPC. Monitoring involves checking for connectivity issues and ensuring sufficient bandwidth. Troubleshooting might involve examining route tables and network ACLs. In contrast, setting up an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway requires specifying the subnet, allocation type, and desired bandwidth. AWS manages the underlying infrastructure. Monitoring focuses on performance metrics, such as latency and packet loss. Troubleshooting involves checking for NAT Gateway availability and ensuring sufficient capacity. The decision of aws nat gateway vs internet gateway hinges on specific networking needs.
When comparing aws nat gateway vs internet gateway, understanding their management differences is crucial. Internet Gateways require minimal ongoing management, primarily focusing on ensuring proper attachment to the VPC and monitoring for connectivity issues. NAT Gateways, however, necessitate monitoring resource utilization, especially during peak traffic periods. Scaling NAT Gateways involves creating additional instances to handle increased traffic demands. Efficient scaling prevents performance bottlenecks and ensures optimal network performance. Regular monitoring of metrics, such as latency and throughput, provides valuable insights into gateway performance and helps identify potential issues proactively. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and maintains optimal network functionality. Choosing between an aws nat gateway vs internet gateway impacts the management complexity.
Effective management of either gateway requires a robust monitoring strategy. AWS provides various monitoring tools, including CloudWatch, to track key performance indicators (KPIs). These tools provide real-time visibility into gateway health and performance. By setting up appropriate alarms and notifications, administrators can proactively address potential issues before they impact network operations. Understanding the limitations and capabilities of each gateway is critical for proper management. For example, while an Internet Gateway provides direct public access, it also increases the security risk. In contrast, a NAT Gateway offers enhanced security but introduces complexities related to network address translation and potential performance limitations. The choice between aws nat gateway vs internet gateway impacts ongoing management needs.