Demystifying Google Cloud Platform: A Beginner’s Guide
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services offered by Google. It allows individuals and businesses to access and use computing resources over the internet. Instead of owning and maintaining physical servers, users can leverage Google’s infrastructure for various needs. The purpose of Google Cloud Platform about is to provide scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for storing data, running applications, and more.
Cloud computing offers different service models. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides access to fundamental computing resources, such as virtual machines and storage. Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without the complexity of managing the underlying infrastructure. Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers ready-to-use applications over the internet. Google Cloud Platform about encompasses all three models, providing a comprehensive range of services to cater to diverse requirements. It’s important to know what google cloud platform about can offer to your business, depending on its size and goals.
GCP’s role in the cloud computing landscape is significant. It competes with other major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. Each platform has its own strengths and weaknesses, but Google Cloud Platform about is known for its innovation in areas like data analytics, machine learning, and containerization with Kubernetes. For startups to enterprises, Google Cloud Platform about enables organizations to build and deploy applications more efficiently, analyze vast amounts of data, and drive innovation through machine learning. Its global network of data centers ensures high availability and performance for users worldwide.
How to Navigate the Google Cloud Console: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Navigating the Google Cloud Console is essential for managing your Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources. This guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough to help new users become familiar with the interface. The Google Cloud Console is your central point for accessing and managing all google cloud platform about services. First, ensure you have a Google Cloud account. If you don’t, you’ll need to create one and set up a billing account. Once logged in, you’ll see the main dashboard. This dashboard provides an overview of your projects, resources, and recent activity. The left-hand navigation menu is key to accessing different services. Here, you’ll find categories like Compute Engine, Storage, Networking, and more. Clicking on a service will take you to its dedicated page, where you can create and manage resources.
To create a new project, click on the project selection dropdown at the top of the console. Then, select “New Project.” Enter a project name and ID. The project ID must be unique across all of Google Cloud. Once the project is created, you can start adding resources. For example, to create a Compute Engine instance, navigate to Compute Engine > VM instances. Click “Create Instance” and follow the prompts to configure your virtual machine. Pay close attention to the settings. These settings include machine type, operating system, and network configuration. Setting up billing is crucial to avoid service interruptions. To manage billing, go to the navigation menu and select “Billing.” Here, you can link a billing account to your project. You can also monitor your spending and set budgets. The Google Cloud console also offers tools for managing users and permissions using Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM allows you to control who has access to your resources and what they can do. This is essential for maintaining the security of your google cloud platform about environment.
Google Cloud console’s user interface (UI) has evolved over time. While the core functionality remains consistent, the appearance and organization of elements may vary slightly depending on the version you are using. Google periodically updates the console to improve user experience and introduce new features. The differences between versions are usually minor. Differences may involve changes in icon styles, menu placements, and the layout of dashboards. If you encounter discrepancies between this guide and your console view, refer to the official Google Cloud documentation for the most up-to-date information. Regular updates to the documentation ensure you have access to accurate instructions. The console also offers a search bar at the top. You can use it to quickly find specific services, resources, or documentation. Mastering the navigation of the Google Cloud Console is the first step toward effectively utilizing the power of google cloud platform about and its diverse offerings.
Exploring Core Google Cloud Services: Compute, Storage, and Networking
Google Cloud Platform offers a comprehensive suite of services, categorized into Compute, Storage, and Networking, that form the foundation for building and deploying various applications. These services provide the infrastructure and tools necessary to support a wide range of workloads, from simple websites to complex enterprise applications. Understanding these core services is crucial for effectively leveraging the power of the google cloud platform about.
In the Compute category, Google Cloud Platform provides several options to meet diverse needs. Compute Engine allows users to create and manage virtual machines with customizable configurations. App Engine offers a platform-as-a-service (PaaS) environment for building and deploying web applications. Kubernetes Engine (GKE) provides a managed Kubernetes service for orchestrating containerized applications. Each of these services serves different use cases: Compute Engine for infrastructure control, App Engine for rapid application development, and Kubernetes Engine for container orchestration. Choosing the right compute service depends on the specific requirements of the application and the level of control needed. These compute options of the google cloud platform about, are integral to application development.
The Storage options within Google Cloud Platform encompass various solutions for storing and managing data. Cloud Storage provides scalable and durable object storage for unstructured data, such as images, videos, and backups. Cloud SQL offers fully managed relational databases based on MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. Cloud Spanner is a globally distributed, scalable, and strongly consistent database service. Regarding Networking, Google Cloud Platform offers Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create isolated networks, Cloud Load Balancing to distribute traffic across multiple instances, and Cloud DNS to manage domain name systems. These storage solutions within the google cloud platform about, ensure data is managed effectively. Each networking service plays a critical role in building secure and reliable network infrastructure in the cloud.
Delving into Google’s Cloud Solutions: Big Data and Machine Learning Capabilities
Google Cloud Platform distinguishes itself with robust Big Data and Machine Learning capabilities, offering a suite of services designed to handle vast datasets and complex analytical tasks. These services empower businesses to extract valuable insights, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions. Google’s offerings in this area are particularly attractive due to their scalability, integration, and ease of use. Google cloud platform about helps customers process the data in a secure environment.
Key services in Google Cloud’s Big Data and Machine Learning arsenal include BigQuery, a fully-managed, serverless data warehouse that enables rapid analysis of large datasets using SQL. Dataflow provides a unified stream and batch data processing service, ideal for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines and real-time analytics. Dataproc is a managed Hadoop and Spark service, simplifying the deployment and management of these open-source big data frameworks. The Cloud AI Platform offers a comprehensive environment for building, training, and deploying machine learning models, supporting various frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn. When we talk about ‘managed services’ in the context of these data tools, it signifies that Google handles the underlying infrastructure, patching, scaling, and maintenance, allowing users to focus on data analysis and model development rather than operational complexities. Google cloud platform about is a managed service that requires very little maintenance by the end user. This approach significantly reduces the overhead associated with managing big data and machine learning infrastructure, making these powerful tools accessible to a wider range of users.
For example, BigQuery can be employed to analyze customer behavior, identify trends, and personalize marketing campaigns. Dataflow can process real-time sensor data from IoT devices to detect anomalies and optimize operations. Dataproc can be used to process large volumes of log data for security analysis and threat detection. The Cloud AI Platform facilitates the development of predictive models for fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer churn prediction. These Google cloud platform about services provide a complete toolkit for organizations looking to harness the power of data to drive innovation and gain a competitive edge. Google’s investment in AI and data analytics positions it as a leader in providing cutting-edge solutions for businesses seeking to unlock the value of their data.
Google Cloud vs. Competitors: A Comparative Analysis
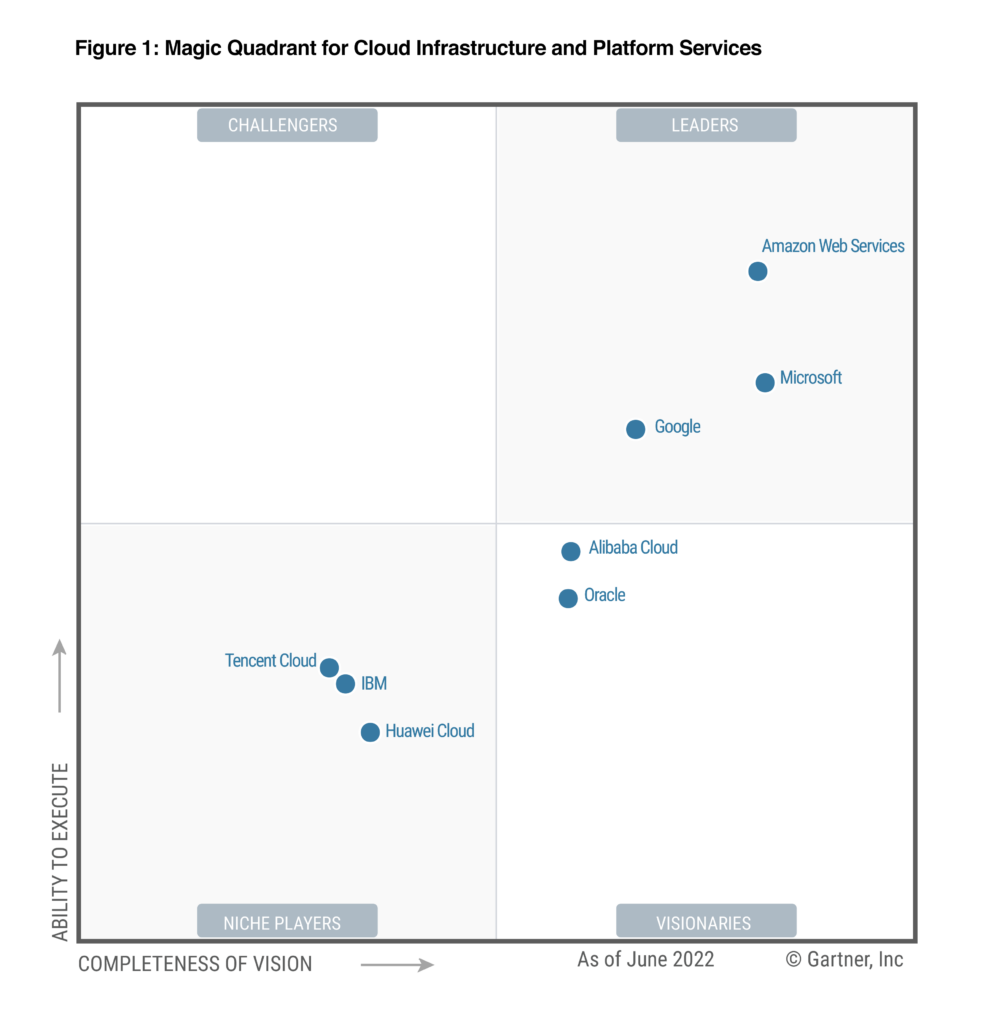
The google cloud platform about market is dominated by three major players: Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure. Each platform offers a wide array of cloud computing services, but they differ in pricing models, service offerings, geographic availability, and overall user experience. Understanding these differences is crucial for organizations when choosing the right cloud provider for their specific needs. AWS, being the first to market, holds a significant market share and a mature ecosystem. They offer a vast selection of services, catering to almost every conceivable use case. Azure, deeply integrated with Microsoft’s enterprise solutions, is a strong contender, particularly for organizations heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. The google cloud platform about offerings stand out with its innovative solutions and strengths in data analytics, machine learning, and containerization.
When comparing pricing, each provider employs complex models with various options for on-demand, reserved instances, and committed use discounts. AWS is known for its granular pricing structure, offering flexibility but potentially leading to complexity in cost management. Azure often provides competitive pricing, especially for organizations already using Microsoft products. Google cloud platform about often presents sustained use discounts and committed use discounts, which can result in substantial savings for workloads that run predictably. Service availability varies across regions for each provider. AWS has the broadest global reach, with numerous availability zones worldwide. Azure follows closely behind, expanding its global infrastructure rapidly. The google cloud platform about global presence is also growing, focusing on strategic regions to serve key markets. The user experience also differs, with AWS offering a mature but sometimes overwhelming interface. Azure provides a seamless integration with Microsoft tools. Navigating the Google Cloud Console can be intuitive, especially for those familiar with Google’s design principles.
One of the unique features of the google cloud platform about is its commitment to open source technologies and containerization. Google was the birthplace of Kubernetes, now a leading container orchestration platform, and actively contributes to various open-source projects. This focus benefits organizations that value flexibility and portability in their cloud deployments. AWS and Azure also support open-source technologies and offer their own container services, but Google’s deep roots in this area provide a distinct advantage. Ultimately, the best cloud platform depends on an organization’s specific requirements and priorities. Each offers a compelling set of services and benefits. A thorough evaluation of pricing, service offerings, geographic availability, and ease of use is essential for making an informed decision about google cloud platform about.
Optimizing Google Cloud Costs: Strategies for Efficient Resource Management
Managing costs effectively within the google cloud platform about is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Neglecting cost optimization can lead to unexpected expenses and hinder the return on investment. Several strategies can be implemented to ensure efficient resource management and minimize unnecessary spending on the google cloud platform about. Right-sizing instances is a fundamental step. This involves selecting the appropriate instance type and size based on actual workload requirements. Over-provisioning resources results in wasted capacity and higher costs. Regularly monitor resource utilization using Google Cloud’s monitoring tools to identify underutilized instances that can be scaled down or eliminated. Using Committed Use Discounts (CUDs) offers significant cost savings for predictable workloads. By committing to use specific resources for a one- or three-year term, organizations can receive substantial discounts compared to pay-as-you-go pricing on the google cloud platform about. Preemptible VMs (also known as Spot VMs) provide another cost-effective option for fault-tolerant workloads. These VMs are available at a lower price but can be terminated with a 24-hour notice. Leveraging preemptible VMs for non-critical tasks can significantly reduce compute costs.
Cost management tools play a vital role in monitoring and controlling cloud spending. Google Cloud provides tools such as Cloud Billing and the Cost Management dashboard, which offer detailed insights into resource consumption and associated costs. These tools enable users to track spending trends, identify cost drivers, and set budgets and alerts to prevent overspending on the google cloud platform about. Implementing proper tagging and labeling conventions is essential for cost allocation and accountability. By tagging resources with relevant metadata, organizations can accurately track costs across different projects, departments, or applications. This allows for better cost visibility and facilitates chargeback mechanisms. It’s also important to understand the cost differences between running workloads on the google cloud platform about versus on-premises servers. On-premises infrastructure involves upfront capital expenditures, ongoing maintenance costs, and operational overhead. Cloud computing eliminates these expenses, offering a pay-as-you-go model that aligns costs with actual resource consumption. For example, calculating the total cost of ownership (TCO) for an on-premises server includes hardware costs, software licenses, power and cooling, and IT staff salaries. In contrast, the cost of running a similar workload on the google cloud platform about can be estimated based on instance type, storage usage, and network traffic.
To illustrate cost optimization, consider a scenario where a company is running a web application on Compute Engine. By analyzing resource utilization, they discover that the instances are consistently underutilized during off-peak hours. They can implement a scaling policy to automatically reduce the number of instances during these periods, saving on compute costs. Additionally, they can leverage Cloud Storage for storing infrequently accessed data, as it offers lower storage costs compared to persistent disks. Regularly reviewing and optimizing cloud resources is an ongoing process. Organizations should continuously monitor their spending, identify areas for improvement, and implement best practices to ensure efficient resource management and minimize costs on the google cloud platform about. Following these strategies, organizations can maximize the value of their cloud investments and achieve significant cost savings.
Securing Your Data in Google Cloud: Best Practices and Security Features
Securing data in the google cloud platform about is paramount. Robust security measures are not just an option; they are a necessity. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a comprehensive suite of tools and features to protect sensitive information. Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a foundational element. It allows administrators to control who has access to specific Google Cloud resources. IAM enables granular permission management, ensuring that users only have the access they need. This principle of least privilege minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Encryption is another critical component of Google Cloud security. GCP provides encryption at rest and in transit, safeguarding data from unauthorized interception or access. Encryption keys can be managed by Google or by the customer, offering flexibility and control. Network security is also crucial. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows users to create isolated networks within Google Cloud, controlling network traffic and access. Firewalls and network policies can be configured to restrict traffic and prevent unauthorized connections. Compliance certifications demonstrate Google’s commitment to security and regulatory requirements. GCP adheres to industry standards such as SOC, ISO, and PCI DSS, providing assurance that data is handled securely and in compliance with relevant regulations. These features allow you to configure the google cloud platform about your needs.
Implementing security best practices is essential for maintaining a secure Google Cloud environment. Regularly review and update IAM policies to ensure that users have appropriate access levels. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security to user accounts. Monitor network traffic and security logs to detect and respond to potential threats. Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and address security weaknesses. Stay informed about the latest security threats and vulnerabilities, and apply security patches and updates promptly. The google cloud platform about security is continuously evolving, so it is important to stay up to date with the latest security best practices. Google’s shared responsibility model defines the security responsibilities between Google and the customer. Google is responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure. Customers are responsible for securing what they put in the cloud. This includes managing access, configuring security settings, and protecting data.
Understanding the shared responsibility model is critical for maintaining a secure Google Cloud environment. Customers must take ownership of their security responsibilities. By following security guidelines and implementing appropriate security measures, organizations can mitigate risks and protect their data in Google Cloud. For example, properly configuring Cloud Storage bucket permissions is a key aspect of data security. Ensuring that buckets are not publicly accessible and that access is granted only to authorized users is crucial. Regularly auditing and monitoring these configurations is essential to prevent data leaks. Similarly, implementing proper security measures for Compute Engine instances, such as using firewall rules and intrusion detection systems, is vital for protecting against attacks. The google cloud platform about data security provides a robust and secure environment, but it requires a proactive and diligent approach from users to ensure that their data is protected.
Real-World Applications of Google Cloud: Case Studies and Examples
The Google Cloud Platform about solving problems and achieving goals is showcased through real-world examples across diverse industries. Businesses leverage the versatility of Google Cloud Platform about innovation. These applications demonstrate the tangible benefits and transformative power of cloud technology.
One example involves a major retailer using Google Cloud Platform about data analytics capabilities to personalize customer experiences. By analyzing vast datasets with BigQuery, they gain insights into customer preferences and shopping patterns. This enables targeted marketing campaigns and optimized product recommendations, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty. Another case involves a healthcare provider utilizing Google Cloud Platform about secure data storage and processing for electronic health records. By leveraging Cloud Storage and Compute Engine, they ensure compliance with regulatory requirements while improving the efficiency of patient care. These applications demonstrate how the Google Cloud Platform about services empower organizations to optimize operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive innovation.
A global media company migrated its video streaming platform to Google Cloud Platform about content delivery network. This transition resulted in reduced latency, improved video quality, and enhanced user experience for millions of viewers worldwide. Another example features a financial services firm employing Google Cloud Platform about machine learning tools to detect fraudulent transactions. By training models on historical data with Cloud AI Platform, they identify suspicious activities in real-time, minimizing financial losses and protecting customers. These case studies exemplify how Google Cloud Platform about solutions enable businesses to achieve scalability, reliability, and security while unlocking new opportunities for growth and innovation. Documented success stories highlight the transformative impact of Google Cloud Platform about a wide range of applications.