Why Specify an AWS Region for CLI Operations?
Configuring an AWS region when using the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is crucial for directing your commands to the appropriate geographical location of your AWS resources. The AWS region acts as a context, informing the CLI which data center to interact with. Specifying the correct region ensures that you are managing the resources you intend to manage and prevents unintended actions on resources in other regions. Understanding how to set aws region in cli is the first step to properly manage your AWS account.
Proximity to your resources directly impacts latency. By selecting a region close to your physical location or the location of your users, you can significantly reduce response times and improve the overall performance of your AWS operations. For example, if your primary user base is located in Europe, configuring the AWS CLI to use a European region (e.g., eu-west-1) will generally result in faster command execution compared to using a region in North America. Therefore, it is important to understand how to set aws region in cli.
If an AWS region is not explicitly configured, the AWS CLI attempts to use a default region. This default region is often defined in the AWS configuration file or through an environment variable. However, relying on the default region without explicitly setting it can lead to unpredictable behavior, especially when working with multiple AWS accounts or environments. It’s a best practice to always define the region to ensure commands are executed in the intended location. Learning how to set aws region in cli properly avoids a lot of issues. Failing to do so could inadvertently create, modify, or delete resources in the wrong region, potentially causing service disruptions or incurring unexpected costs. Therefore, a clear understanding of how to set aws region in cli is paramount for efficient and secure AWS management.
A Straightforward Way to Configure Your AWS CLI Region
To effectively interact with AWS services via the command line, knowing how to set AWS region in CLI is crucial. The simplest method involves using the `aws configure` command. This command prompts you for essential information, including your AWS Access Key ID, Secret Access Key, the desired default AWS region, and your preferred output format. By providing this information, the AWS CLI knows which region to target for your requests. Configuring the AWS region ensures your commands are executed in the intended geographical location, impacting resource creation, access, and overall performance.
The `aws configure` command offers an interactive way to configure the AWS CLI. Once executed, the CLI will step-by-step ask for the necessary credentials and configurations. It’s important to select the region closest to your resources or users to minimize latency and optimize performance. This streamlined process makes it easy to set the AWS region in CLI and begin managing your AWS resources efficiently. This is the primary and most used way on how to set AWS region in CLI.
Choosing the correct region is vital for several reasons. Data residency requirements might dictate that your data resides within a specific geographic boundary. Also, service availability can vary between regions, so choosing a region where all necessary services are available is essential. Understanding how to set AWS region in CLI correctly using `aws configure` is therefore a fundamental skill for any AWS user. This simple command ensures that all subsequent CLI operations are directed to the appropriate AWS environment, preventing errors and streamlining your workflow. You’ll avoid any issues related to submitting resources to the wrong location, or facing permission errors because you are trying to reach them on a non-existent AWS region for your user.
Using the ‘aws configure’ Command: A Detailed Walkthrough
The `aws configure` command is the most common way to set the AWS region in CLI. It’s an interactive process that guides you through the necessary settings. This method is straightforward and stores your configurations in a profile, making it easy to manage different AWS environments. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use it:
First, open your terminal or command prompt. Then, type `aws configure` and press Enter. The CLI will then prompt you for four pieces of information, one at a time. The first prompt is for your Access Key ID. This is a unique identifier for your AWS account. It allows the CLI to authenticate your requests. Enter your Access Key ID and press Enter. The next prompt asks for your Secret Access Key. Treat this like a password and keep it secure. Enter your Secret Access Key and press Enter. Now, you will be prompted for the Default region name. This is where you specify the AWS Region you want to work with, such as `us-west-2` or `eu-central-1`. Understanding how to set aws region in cli is key. This ensures your commands target the correct geographical location. Enter your desired AWS Region and press Enter. Finally, the CLI asks for your preferred output format. This determines how the CLI displays the results of your commands. Common options are `json`, `text`, and `table`. Choose your preferred format (e.g., `json`) and press Enter. An example set of inputs might look like this:
`AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE`
`AWS Secret Access Key [None]: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY`
`Default region name [None]: us-west-2`
`Default output format [None]: json`
After entering these details, the AWS CLI is configured to use the specified region and credentials for subsequent commands. This detailed walkthrough demonstrates how to set aws region in cli effectively.
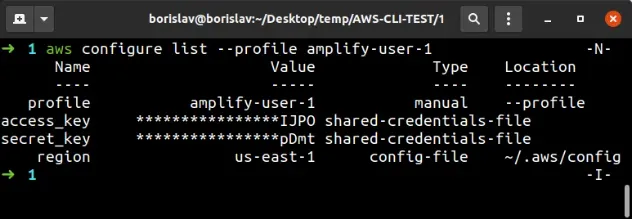
Once configured, the AWS CLI stores these settings in the `~/.aws/credentials` and `~/.aws/config` files. These files contain your Access Key ID, Secret Access Key, default region, and output format. You can manually edit these files if needed, but it’s generally recommended to use the `aws configure` command for managing your settings. To ensure proper functionality, understanding how to set aws region in cli and verifying the configuration is vital. The `aws configure` command offers a user-friendly way to manage AWS credentials and regional settings, facilitating smooth interaction with AWS services.
Setting the AWS Region Through Environment Variables
An alternative method for configuring the AWS region involves leveraging environment variables. This approach offers advantages in terms of portability and facilitates automation through scripts. The primary environment variables used are `AWS_REGION` and `AWS_DEFAULT_REGION`. Both serve the same purpose: specifying the AWS Region for CLI operations. Setting the AWS Region using environment variables provides a flexible way to manage configurations, especially in dynamic environments or when dealing with multiple AWS accounts. This is another way on how to set aws region in cli.
To set the AWS Region using environment variables, you’ll need to define these variables in your operating system. On Linux or macOS, you can typically achieve this by adding the following lines to your shell configuration file (e.g., `.bashrc`, `.zshrc`):
`export AWS_REGION=your_desired_region`
or
`export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=your_desired_region`
Replace `your_desired_region` with the appropriate AWS Region code (e.g., `us-west-2`, `eu-central-1`, `ap-southeast-1`). After modifying the configuration file, remember to source it (e.g., `source ~/.bashrc`) to apply the changes to your current shell session. On Windows, you can set environment variables through the System Properties dialog box.
It’s important to understand the precedence rules when multiple methods for setting the AWS Region are employed. Environment variables take precedence over the region specified in the AWS CLI configuration file (created using `aws configure`). However, the `–region` option, when used directly with a command, overrides both environment variables and the configuration file. This hierarchy allows for granular control over the region targeted by specific AWS CLI commands. If you are using a script it is very useful on how to set aws region in cli. Properly leveraging environment variables can streamline your AWS CLI workflow and enhance the manageability of your configurations. Setting up AWS Region is one of the first thing a user needs to do. Knowing how to set aws region in cli will save you time.
Leveraging the `–region` Option for Single Commands
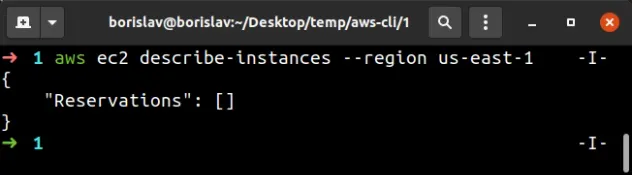
There’s another way on how to set aws region in cli and that is through the `–region` option. The AWS CLI allows specifying the target AWS Region directly within individual commands. This approach offers flexibility when interacting with resources across multiple regions or when a temporary override of the default region configuration is needed. Using the `–region` option doesn’t alter your configured settings; it applies only to that specific command execution.
To utilize this option, append `–region
The `–region` option proves invaluable in scenarios where you need to interact with multiple AWS Regions frequently. Instead of constantly reconfiguring the AWS CLI with `aws configure` or modifying environment variables, you can specify the region on a per-command basis. This approach streamlines workflows and reduces the risk of errors associated with managing multiple configurations. Moreover, when scripting AWS CLI commands, incorporating the `–region` option enhances the script’s readability and maintainability. It explicitly states the target region for each command, making the script’s purpose clearer to others and reducing potential ambiguities.
When deciding how to set aws region in cli, consider the frequency and scope of your region-specific operations. If you consistently work within a single region, setting the default region using `aws configure` or environment variables may be more efficient. However, for occasional tasks or when dealing with multiple regions, the `–region` option provides a convenient and targeted solution. It’s a versatile tool in the AWS CLI arsenal that empowers users to manage their resources effectively across different AWS Regions.
Verifying Your AWS CLI Region Configuration
After configuring the AWS CLI, it’s crucial to verify that the settings are correct and the CLI is targeting the intended AWS Region. This ensures that subsequent commands are executed in the correct geographical location and against the appropriate resources. Several methods can be employed to confirm your AWS CLI region configuration and to understand how to set aws region in cli properly.
One straightforward approach is to execute a simple AWS CLI command that interacts with a specific AWS service. A commonly used command for this purpose is `aws s3 ls`. This command lists the S3 buckets in your AWS account. Execute the command in your terminal. If the command executes successfully and lists the buckets associated with your account in the configured region, it indicates that the AWS CLI is properly configured. If you encounter errors, such as authentication failures or region-related issues, it suggests that the configuration needs to be reviewed. The output of this command will implicitly reveal which region the CLI is targeting, as S3 bucket names are globally unique within a region. Learning how to set aws region in cli correctly ensures you are managing resources in the intended geographic area.
Another way to verify the configuration is by directly examining the AWS CLI configuration files. These files are typically located in the `~/.aws/` directory. The two primary files are `config` and `credentials`. The `config` file contains the default region setting, along with other configuration options. Open the `config` file using a text editor. Look for the `region` parameter under the `[default]` profile or any named profiles you have configured. Ensure that the value of the `region` parameter matches the intended AWS Region. For example, it might say `region = us-west-2` for the US West (Oregon) region. Remember that knowing how to set aws region in cli and confirming the setting are crucial steps. Similarly, you can check environment variables like `AWS_REGION` or `AWS_DEFAULT_REGION` to ensure they are not overriding the region specified in the configuration file. By combining these verification methods, you can confidently confirm that your AWS CLI is correctly configured and that you understand how to set aws region in cli for seamless interaction with AWS services.
Troubleshooting Common Region Configuration Issues
When learning how to set aws region in cli, users sometimes encounter problems. One frequent issue is typing the region name incorrectly. For example, writing “us-west-2” as “uswest2” will cause errors. Always double-check the region code against the official AWS documentation. Another common mistake involves incorrect environment variable settings. Ensure that the `AWS_REGION` or `AWS_DEFAULT_REGION` variables are defined correctly and that your system recognizes them. Use the `echo $AWS_REGION` command (or the equivalent for your operating system) to verify the variable’s value.
Conflicting configurations can also lead to problems when you want to know how to set aws region in cli. The AWS CLI prioritizes the region specified using the `–region` option on the command line, followed by environment variables, and then the setting in the configuration file (set via `aws configure`). If you’re experiencing unexpected behavior, check for conflicting settings in each of these locations. If a command consistently targets the wrong region, examine your shell’s startup scripts (e.g., `.bashrc`, `.zshrc`) for potentially overriding environment variables. Also, inspect the `~/.aws/config` file to make sure the default region and the profile regions are configured correctly.
If you’re still facing difficulties to understand how to set aws region in cli, try these debugging tips. First, run `aws configure get region` to see the region the CLI is currently using, according to its configuration file. If that returns the wrong region or nothing at all, it indicates an issue with your configuration file or profile setup. You can also use the `–debug` option with your AWS CLI commands to get more verbose output, which can help identify where the CLI is getting its region information. Ensure your AWS CLI version is up to date, as older versions might have compatibility issues or bugs related to region handling. Consider creating a new AWS profile using `aws configure –profile
Best Practices for Managing AWS Region Configuration
Effective management of AWS region configurations within the CLI is crucial for maintaining consistency, enhancing security, and promoting automation. Several best practices can streamline your workflow and minimize potential issues when determining how to set aws region in cli. Adhering to these guidelines ensures a more robust and manageable AWS environment.
One fundamental practice is to prioritize consistency across your infrastructure. Standardize the way you define the AWS region, whether through environment variables or the `aws configure` command. In dynamic environments, leveraging environment variables such as `AWS_REGION` or `AWS_DEFAULT_REGION` offers significant advantages. These variables allow you to dynamically set the AWS region based on the specific environment or deployment stage. This approach greatly simplifies automation through scripts and configuration management tools, ensuring that the correct region is always targeted. Remember that environment variables generally take precedence over settings defined via `aws configure`, providing a convenient way to override the default region when needed. Another key security best practice is to avoid hardcoding AWS credentials, including the region, directly into scripts or configuration files. Instead, utilize IAM roles and profiles to grant necessary permissions to your resources. This reduces the risk of accidentally exposing sensitive information and simplifies credential management. Regularly review and update your IAM policies to adhere to the principle of least privilege, granting only the minimum necessary permissions to each role. Carefully consider how to set aws region in cli for different applications and environments, ensuring that each application is configured to use the appropriate region based on its requirements and the location of its resources. It is also important to document your AWS region configuration strategy clearly, outlining the methods used to set the region and the precedence rules that apply. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for team members and helps to ensure consistency across the organization.
Furthermore, adopting infrastructure-as-code (IaC) principles can significantly enhance the management of AWS region configurations. Tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation allow you to define your infrastructure, including region settings, in a declarative manner. This ensures that your infrastructure is consistently deployed across different environments and that any changes to the region configuration are tracked and version controlled. In summary, by embracing these best practices – prioritizing consistency, utilizing environment variables, avoiding hardcoding credentials, and adopting IaC principles – you can effectively manage AWS region configurations within the CLI. This results in a more secure, automated, and manageable AWS environment. Understanding how to set aws region in cli correctly will save valuable time.