Demystifying the Cloud: A Primer for Agile Teams
Cloud computing has revolutionized software development, offering unprecedented scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. For agile teams, understanding the cloud’s core benefits is crucial for maximizing efficiency and innovation. Unlike traditional on-premise infrastructure, the cloud provides on-demand access to computing resources, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. This agility allows development teams to rapidly provision and de-provision resources as needed, adapting quickly to changing project requirements. The shift to devops and cloud empowers teams to focus on building and deploying applications, rather than managing complex infrastructure.
Scalability is a key advantage of cloud computing. Applications can be designed to automatically scale up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance even during peak usage periods. This elasticity is particularly valuable for agile teams working on projects with fluctuating workloads. Cost-effectiveness is another significant benefit. Cloud providers offer various pricing models, allowing teams to pay only for the resources they consume. This pay-as-you-go approach can significantly reduce infrastructure costs compared to traditional on-premise deployments. Furthermore, the cloud’s inherent flexibility enables agile teams to experiment with new technologies and approaches without the risk of large capital expenditures. The synergy between devops and cloud allows for faster experimentation and iteration, crucial elements of the agile methodology.
The cloud offers a wide range of services that can streamline the development process. From virtual machines and container orchestration platforms to serverless computing and managed databases, cloud providers offer tools that simplify application deployment and management. This enables agile teams to focus on delivering value to customers, rather than getting bogged down in infrastructure management tasks. Cloud-native architectures, such as microservices and containerization, are well-suited for cloud environments, enabling teams to build and deploy applications independently and at scale. Embracing devops and cloud principles empowers agile teams to deliver high-quality software faster, more efficiently, and with greater flexibility. Understanding these core benefits allows teams to leverage the cloud’s full potential and drive business agility.
How to Architect Scalable Applications in the Cloud
Designing scalable applications in the cloud requires a shift in mindset compared to traditional on-premise environments. The cloud offers unparalleled opportunities for elasticity and responsiveness, but these benefits must be architected into the application from the outset. Several key architectural patterns are essential for achieving optimal scalability. Microservices, for example, involve breaking down a large application into smaller, independent services that can be deployed and scaled independently. This allows teams to focus on specific functionalities and release updates without impacting the entire system. Containerization, often used in conjunction with microservices, packages each service with its dependencies, ensuring consistency across different environments. Docker and Kubernetes are popular tools for managing containers and orchestrating their deployment. Serverless computing represents another paradigm shift, where developers focus solely on writing code without managing the underlying infrastructure. Cloud providers handle the scaling and resource allocation automatically, making it ideal for event-driven applications and workloads with fluctuating demands. These architectural choices are critical for devops and cloud success.
Effective resource utilization is paramount for scalable applications. Cloud services like AWS Auto Scaling and Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets automatically adjust the number of instances based on predefined metrics, such as CPU utilization or request volume. This ensures that the application can handle peak loads without over-provisioning resources during periods of low activity. Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple instances, preventing any single instance from becoming a bottleneck. Caching mechanisms, such as content delivery networks (CDNs) and in-memory caches, can further improve performance by reducing latency and offloading traffic from the application servers. Choosing the right database is also crucial. NoSQL databases, like Cassandra and MongoDB, are often preferred for their scalability and ability to handle unstructured data, making them ideal for applications with high write volumes and diverse data requirements. Proper database selection is vital for successful devops and cloud implementations.
Beyond the choice of architectural patterns and cloud services, careful consideration must be given to application design. Applications should be stateless whenever possible, meaning that they do not store any session-specific data on the server. This allows requests to be routed to any available instance without affecting the user experience. Asynchronous communication, using message queues or event buses, can decouple different components of the application and improve resilience. Monitoring and logging are essential for identifying performance bottlenecks and proactively addressing issues. A well-designed application that leverages the power of the cloud can achieve unparalleled scalability and responsiveness, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing market demands. Embracing these concepts enables optimized devops and cloud deployments, fostering efficiency and innovation. These architectural choices are critical for devops and cloud success.
DevOps Principles: Fostering Collaboration and Automation in Cloud Environments
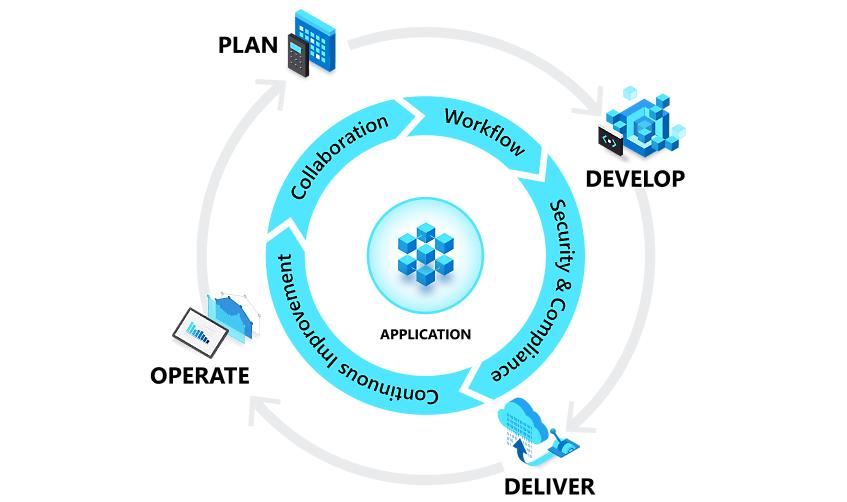
DevOps principles are fundamental for maximizing the benefits of cloud computing. DevOps and cloud environments thrive on collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement. These principles bridge the gap between development and operations teams, fostering a culture of shared responsibility and efficiency. By embracing DevOps, organizations can accelerate software delivery, enhance application quality, and optimize resource utilization in the cloud.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) are cornerstones of DevOps and cloud practices. CI/CD pipelines automate the software release process, from code integration to deployment. This automation reduces manual errors, accelerates feedback loops, and enables faster time-to-market. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) further enhances automation by allowing teams to manage cloud infrastructure in a programmatic and repeatable manner. With IaC, infrastructure changes can be version controlled, tested, and deployed automatically, ensuring consistency and reliability across different environments. DevOps and cloud together empowers businesses to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands.
Collaboration is at the heart of successful DevOps and cloud implementations. Breaking down silos between development, operations, and security teams is essential for streamlining workflows and improving communication. Shared tools, collaborative platforms, and cross-functional teams enable faster problem resolution, better decision-making, and a more cohesive approach to software delivery. DevOps and cloud security should be integrated throughout the entire development lifecycle, not treated as an afterthought. By embedding security into the CI/CD pipeline and fostering a culture of shared responsibility, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure the security of their cloud-native applications. Ultimately, the synergy between devops and cloud practices drives innovation, efficiency, and agility, enabling businesses to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Implementing CI/CD Pipelines for Cloud-Native Applications
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are essential for modern software development, particularly for applications deployed in the cloud. They automate the software release process, enabling faster delivery, improved quality, and reduced risk. A well-designed CI/CD pipeline is fundamental for organizations embracing devops and cloud principles. The synergy between devops and cloud is amplified through automated pipelines, streamlining deployments and fostering agility.
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline for cloud-native applications involves several key stages. First, code changes are integrated into a shared repository, triggering an automated build process. This process includes compiling the code, running unit tests, and performing static analysis. Next, the built artifact is packaged into a deployable format, such as a Docker container. Subsequently, automated tests, including integration and end-to-end tests, are executed to ensure the application meets quality standards. Popular tools for building CI/CD pipelines include Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, and cloud-native services like AWS CodePipeline and Azure DevOps. These tools offer features such as pipeline orchestration, automated testing, and integration with various cloud platforms. Leveraging devops and cloud infrastructure in tandem allows for dynamic resource allocation during pipeline execution, optimizing cost and performance.
The final stage of the CI/CD pipeline involves deploying the application to the cloud environment. This can be achieved through various deployment strategies, such as blue-green deployments, canary releases, or rolling updates. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or CloudFormation can be integrated into the pipeline to automate infrastructure provisioning and configuration. Monitoring and logging are crucial components of a successful CI/CD pipeline. Real-time insights into application performance and infrastructure health enable rapid identification and resolution of issues. Effective CI/CD pipelines require close collaboration between development, operations, and security teams, fostering a DevSecOps culture. Automating the delivery process via CI/CD is key to fully capitalizing on devops and cloud, allowing for faster iteration and innovation. Proper implementation of devops and cloud principles provides a framework for a CI/CD pipeline that improves the application development lifecycle.
Infrastructure as Code: Managing Cloud Resources Efficiently
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) represents a fundamental shift in how cloud infrastructure is managed. It moves away from manual configuration to programmatic and repeatable processes. With IaC, developers and operations teams define and manage infrastructure using code, treating it like any other software application. This approach brings numerous benefits, including increased speed, consistency, and reliability. IaC allows for version control of infrastructure configurations, enabling easy rollback to previous states if needed. It also promotes collaboration between development and operations teams, fostering a true devops and cloud environment.
Several powerful tools are available to implement IaC, each with its own strengths and features. Terraform, developed by HashiCorp, is a popular open-source tool that supports multiple cloud providers. It uses a declarative language to define the desired state of the infrastructure. AWS CloudFormation is a native AWS service that allows users to define and provision AWS resources using JSON or YAML templates. Azure Resource Manager is Microsoft Azure’s IaC service, enabling the deployment and management of Azure resources through declarative templates. These tools streamline infrastructure provisioning, configuration, and management, significantly reducing manual effort and the risk of human error. Leveraging such tools becomes indispensable when embracing devops and cloud principles.
The advantages of IaC extend beyond simple automation. It empowers organizations to create consistent and reproducible environments, which is essential for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. By defining infrastructure as code, teams can easily spin up development, testing, and production environments that are identical, minimizing inconsistencies and ensuring smooth deployments. Furthermore, IaC facilitates compliance and auditing by providing a clear record of all infrastructure changes. It enables organizations to track who made what changes and when, simplifying the process of demonstrating adherence to regulatory requirements. Ultimately, IaC is a cornerstone of modern devops and cloud practices, enabling organizations to achieve greater agility, efficiency, and control over their cloud infrastructure. Therefore, IaC is a crucial component for any company looking to optimize devops and cloud performance.
Security Considerations for DevOps in the Cloud
Securing DevOps and cloud environments requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses vulnerabilities at every stage of the software development lifecycle. A fundamental aspect of cloud security is Identity and Access Management (IAM). IAM ensures that only authorized users and services can access specific cloud resources. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), is critical to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data. Regular audits of IAM policies are necessary to maintain a secure configuration and minimize potential security breaches. The integration of security into the entire DevOps lifecycle, known as DevSecOps, is crucial for building secure cloud-native applications. This proactive approach embeds security considerations early in the development process, rather than treating it as an afterthought. By incorporating security testing and vulnerability scanning into the CI/CD pipeline, development teams can identify and remediate security issues before they reach production.
Vulnerability scanning plays a vital role in identifying potential weaknesses in cloud infrastructure and applications. Automated vulnerability scanners can detect known vulnerabilities in operating systems, software libraries, and application code. These scans should be performed regularly and integrated into the CI/CD pipeline to ensure that new code is checked for vulnerabilities before deployment. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) are essential for monitoring cloud environments for malicious activity. These systems analyze network traffic and system logs to detect suspicious patterns and potential security threats. When a threat is detected, the IDS/IPS can alert security teams or automatically take action to mitigate the threat. Data encryption is a cornerstone of cloud security. Encrypting data at rest and in transit protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. Cloud providers offer various encryption options, including server-side encryption, client-side encryption, and encryption using customer-managed keys. Choosing the appropriate encryption method depends on the sensitivity of the data and the specific security requirements of the application. A key aspect of devops and cloud security involves consistent monitoring, using sophisticated tools to detect anomalies.
DevSecOps emphasizes the importance of collaboration between development, operations, and security teams. By fostering a culture of shared responsibility, organizations can create a more secure and resilient cloud environment. Security training for all team members is essential to raise awareness of potential security threats and best practices. Regular security reviews and penetration testing can help identify weaknesses in security controls and validate the effectiveness of security measures. Compliance with industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive data in the cloud. Implementing appropriate security controls and policies can help ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties. Effective security practices in devops and cloud computing are not a one-time effort but a continuous process of assessment, improvement, and adaptation to the evolving threat landscape. Continuous monitoring and logging provide visibility into application performance and security events, enabling proactive problem resolution and improved user experience. Regular backups and disaster recovery planning are essential for protecting against data loss and ensuring business continuity in the event of a security incident or system failure. Applying these security considerations in your devops and cloud strategy ensures secure and scalable infrastructure, mitigating risks effectively.
Monitoring and Logging: Gaining Visibility into Cloud Application Performance
Monitoring and logging are vital for maintaining the health and performance of cloud-native applications. Effective monitoring provides real-time insights into application behavior, allowing for proactive problem resolution and an improved user experience. A robust monitoring strategy is a cornerstone of successful devops and cloud deployments.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools are essential for tracking key metrics such as response time, error rates, and resource utilization. These tools provide a detailed view of application performance, enabling devops and cloud teams to identify bottlenecks and optimize code. Log aggregation is another critical aspect of monitoring. Centralizing logs from various sources allows for efficient troubleshooting and analysis. Tools like Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana (ELK stack) are commonly used for log aggregation and analysis in devops and cloud environments. Anomaly detection algorithms can be applied to monitoring data to automatically identify unusual patterns or deviations from expected behavior. This helps in detecting and resolving issues before they impact users. Integrating monitoring and logging into the CI/CD pipeline ensures that performance is continuously assessed throughout the development lifecycle. This is a key aspect of devops and cloud best practices. Proper monitoring and logging is a critical component of devops and cloud solutions.
Several tools and techniques are available to monitor and log cloud applications effectively. Cloud provider services like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Monitoring offer comprehensive monitoring capabilities. Open-source solutions like Prometheus and Grafana provide flexible and customizable monitoring options. Implementing a comprehensive monitoring and logging strategy requires careful planning and execution. It is essential to define clear monitoring goals, select appropriate tools, and establish alerting thresholds. Regular review and optimization of the monitoring setup are crucial to ensure its continued effectiveness. By gaining comprehensive visibility into application performance through effective monitoring and logging practices, devops and cloud teams can ensure the reliability, scalability, and cost-efficiency of their cloud-native applications. Investing in robust monitoring and logging capabilities is an investment in the long-term success of devops and cloud initiatives. A strong emphasis on these practices fosters a proactive approach to issue resolution and continuous improvement. Integrating monitoring and logging into the devops and cloud lifecycle is a core principle of modern software development.
Optimizing Cloud Costs with DevOps Practices
DevOps practices offer a pathway to significant cloud cost optimization. Businesses leveraging devops and cloud strategies often find themselves able to dramatically reduce expenditure. This is achieved through a combination of strategies focused on efficiency and waste reduction. The synergy between devops and cloud, when properly managed, leads to a leaner, more cost-effective IT infrastructure.
One key area is rightsizing instances. Many organizations over-provision resources, leading to unnecessary costs. DevOps and cloud enable continuous monitoring of resource utilization. This data allows teams to identify underutilized instances and adjust their size accordingly. Automation plays a crucial role here. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows for quick and easy resizing of instances based on real-time needs. Automating resource scaling is another effective technique. Cloud platforms offer auto-scaling capabilities. These can be integrated into devops and cloud workflows. This ensures resources are automatically scaled up or down based on demand. This prevents overspending during periods of low activity. Identifying and eliminating waste is also vital. DevOps and cloud provide tools for analyzing resource consumption. This helps identify idle resources, orphaned storage volumes, and other forms of waste. By regularly reviewing and eliminating these inefficiencies, businesses can significantly reduce their cloud bills.
Cloud providers offer cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Cost Management. These tools provide detailed insights into cloud spending. They allow teams to track costs, identify trends, and forecast future expenses. Integrating these tools into devops and cloud dashboards provides a centralized view of cost data. Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential for long-term cost efficiency. DevOps and cloud workflows should include regular cost reviews. These reviews should focus on identifying new opportunities for optimization. This includes exploring different pricing models, such as reserved instances or spot instances. It also involves evaluating the cost-effectiveness of different cloud services. By embracing a culture of continuous cost optimization, organizations can maximize the value of their cloud investments when using devops and cloud principles. This approach not only saves money but also improves the overall efficiency and agility of the business.