Understanding the Role of a System Administrator
System administrators are the unsung heroes of the digital world. They ensure that computer systems run smoothly and efficiently. Their responsibilities are incredibly diverse. They manage servers, networks, and databases. They also provide crucial user support and maintain system security. A significant portion of their work involves proactive maintenance, preventing issues before they arise. This involves anticipating potential problems and implementing preventative measures. System administrators must possess a wide range of technical skills and a keen ability to solve problems. The role is critical for any organization that relies on technology, making them invaluable assets. Effective system administration is about ensuring uptime and optimal performance, which, in turn, allows businesses and organizations to function effectively. Many times, the role of an iam admin involves being the first responder in a technical crisis.
The iam admin role requires a unique blend of technical expertise and soft skills. Strong problem-solving abilities are essential. System administrators constantly face unexpected challenges. They must quickly diagnose and resolve issues, often under pressure. Effective communication is also key. They need to explain complex technical problems to non-technical users, both within their organization and possibly externally. Collaboration is another vital skill. System administrators often work as part of a team, coordinating with other IT professionals and stakeholders. This collaborative approach can resolve issues more effectively and build a stronger sense of shared responsibility for the IT infrastructure. Proactive monitoring and maintenance is a key component of a successful system administrator’s routine, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing downtime. The role of an iam admin is a continuous learning process. The field of technology is constantly evolving, so ongoing professional development is necessary to stay current with the latest advancements.
In essence, a system administrator acts as a guardian of the organization’s digital infrastructure. They ensure the reliability, security, and efficiency of computer systems. The skills needed go beyond mere technical proficiency. They need to be adaptable, resourceful, and able to work independently and as part of a larger team. The iam admin’s influence extends throughout the organization, impacting all aspects of technology. Their work enables others to achieve their tasks efficiently and securely, making them an integral part of the technological backbone of any organization. Effective system administrators are crucial for the overall success of any business or organization that utilizes technology. They are the architects and protectors of the digital realm, ensuring the smooth operation of the organization’s technological infrastructure.
Essential Skills for System Administrators
Becoming a successful system administrator requires a diverse skillset. Proficiency in operating systems is paramount. This includes a deep understanding of both Linux distributions (like Ubuntu, CentOS, or Red Hat) and Windows Server environments. A strong grasp of networking protocols, such as TCP/IP and DNS, is also essential for managing and troubleshooting network infrastructure. Many system administration tasks involve scripting. Therefore, fluency in scripting languages like Bash (for Linux) and PowerShell (for Windows) is highly beneficial. These skills enable automation, which is crucial for efficiency. Database management skills are also increasingly important, particularly for administrators managing applications that rely on databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server. The role of an iam admin frequently involves managing cloud technologies. Therefore familiarity with at least one major cloud provider like AWS, Azure, or GCP is highly valuable. These platforms offer scalability and flexibility, but effective management demands specific knowledge. Finally, cybersecurity best practices are critical. System administrators are responsible for implementing and maintaining security measures to protect systems and data from threats. This includes understanding firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists. A skilled iam admin understands and applies these security measures daily. Proactive security is a key component of effective system administration.
In addition to technical skills, effective system administration necessitates strong problem-solving abilities. Administrators frequently encounter unexpected issues that require quick and effective solutions. They must be able to analyze problems, identify root causes, and implement solutions efficiently. Proactive maintenance is another key aspect. Regular system monitoring, software updates, and preventative measures help avoid larger issues down the line. An iam admin who excels in proactive maintenance minimizes disruptions and ensures optimal system performance. Furthermore, strong communication skills are necessary. System administrators often interact with users, developers, and other IT staff, requiring clear and concise communication. Effective communication prevents misunderstandings and facilitates collaboration. These soft skills are just as important as technical skills for a successful iam admin.
The modern iam admin must also be adaptable and a continuous learner. Technology constantly evolves, requiring administrators to stay up-to-date with new tools, techniques, and best practices. Keeping abreast of industry trends and emerging technologies helps maintain efficiency and effectiveness. The role of an iam admin is multifaceted and demands a combination of technical skills, problem-solving capabilities, communication skills, and a commitment to continuous learning. This commitment ensures that the administrator remains a valuable asset to any organization. These skills, combined with experience and a passion for technology, create a highly effective system administrator.
How to Troubleshoot Common System Issues
Troubleshooting is a crucial skill for any iam admin. Network connectivity problems frequently plague systems. First, check the physical cables. Are they securely connected? Then, verify network settings on the affected machine. Is the IP address correct? Is the subnet mask properly configured? Ping the default gateway and other known hosts to test connectivity. If you are an iam admin and these steps don’t resolve the issue, inspect firewall rules. Are they blocking necessary ports? Examine any recent configuration changes. Sometimes, a simple reboot resolves seemingly intractable problems. Remember, documenting each step aids in future troubleshooting and helps other iam admins.
Server downtime is a serious issue. An iam admin must swiftly diagnose and rectify such situations. Check the server’s logs for error messages. These provide valuable clues. Monitor system resources like CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk space. High resource utilization often indicates a problem. Check the server’s status page, if available. It may show alerts or errors. Restarting services or the entire server may be necessary if an application crashes or a critical service fails. If the problem persists, a system reboot may be needed. For persistent problems, consider hardware failure as a possibility. An iam admin needs to know when to escalate to a hardware specialist.
User account issues are common. If a user can’t log in, verify their username and password. Has the account been locked due to too many failed login attempts? Check that the account is enabled and hasn’t been accidentally deleted. If a user lacks access to certain files or applications, review their permissions. The iam admin should ensure appropriate access rights are assigned. If a user reports application errors, collect information. Check application logs for specific error messages. They provide insight. Also, verify the application’s configuration and its dependencies. Update the software if a bug is causing the problem. Remember, proactive system management prevents many issues. Regular backups and updates reduce the impact of problems. A well-maintained system is less prone to issues. An experienced iam admin employs preventative measures to minimize disruptions.
Securing Your Systems: Best Practices and Tools
System security is paramount for any iam admin. Robust security measures protect sensitive data and ensure system uptime. Firewalls act as the first line of defense, controlling network traffic and blocking unauthorized access. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor network activity for malicious behavior, alerting administrators to potential threats. Access control lists (ACLs) restrict access to sensitive resources based on user roles and permissions. Regular security audits identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies. Implementing strong password policies and using multi-factor authentication (MFA) further enhances security. The iam admin should also regularly update software and operating systems to patch known vulnerabilities.
Beyond fundamental security practices, proactive monitoring is crucial. Real-time monitoring tools provide insights into system activity, enabling the iam admin to quickly identify and respond to security incidents. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of security events. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability scanning help identify weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. Employing a layered security approach, combining multiple security tools and techniques, is essential for a robust defense. This layered approach is particularly important given the ever-evolving threat landscape. An iam admin must stay updated on the latest security threats and best practices to mitigate risks effectively. Regular training and professional development are essential to maintain a high level of security expertise.
Specific security tools vary depending on the system’s needs and infrastructure. However, widely used examples include open-source tools like Fail2ban (for blocking brute-force attacks) and Snort (for intrusion detection), as well as commercial solutions like CrowdStrike Falcon (for endpoint protection) and Splunk (for SIEM). The selection of tools depends on factors such as budget, system complexity, and the organization’s security posture. Regardless of the specific tools used, the iam admin must ensure that all security measures are regularly reviewed and updated to maintain optimal protection. Proactive security management is not just a technical task; it’s a continuous process requiring vigilance and adaptation. A skilled iam admin understands this, proactively updating security measures and staying informed about the latest threats. This ensures the ongoing protection of the organization’s valuable data and systems.
Efficient System Monitoring and Maintenance
Proactive system monitoring and maintenance are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing outages. A well-maintained system is a secure system. Ignoring this aspect can lead to significant problems. System administrators employ various tools and techniques to track key metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network traffic. These tools provide real-time insights into system health. Regular monitoring allows for the early detection of potential issues, enabling timely intervention and preventing costly downtime. For example, if disk space is nearing capacity, an alert can trigger an investigation and prompt actions such as removing unnecessary files or expanding storage. Effective monitoring is a cornerstone of efficient system administration. An iam admin uses these tools to ensure everything runs smoothly. This proactive approach saves time and resources in the long run.
Regular maintenance tasks are equally important. These tasks might include software updates, security patching, log file analysis, and database backups. Scheduling these tasks ensures consistent system stability and minimizes vulnerabilities. Automated scripts can greatly simplify these maintenance procedures. An iam admin regularly reviews system logs to identify and address potential problems. For instance, frequent error messages can pinpoint issues with applications or services. Log analysis helps in identifying and resolving such issues before they escalate into larger problems. Through diligent monitoring and regular maintenance, system administrators guarantee reliable and secure IT infrastructure. The efficiency and reliability of IT infrastructure directly affects business operations. Efficient maintenance is not just a technical skill; it is a crucial managerial skill that an iam admin possesses.
Choosing the right monitoring tools is essential. Many options are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some popular tools provide comprehensive dashboards, offering a centralized view of system health. Others specialize in specific areas, such as network monitoring or application performance. The best choice depends on the size and complexity of the system being managed, as well as the specific needs of the organization. An iam admin must carefully evaluate different options to select the best tools for their environment. This includes considering factors such as cost, ease of use, and scalability. System monitoring and maintenance are ongoing processes. Regular review and adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal performance and security. Proactive system administration contributes significantly to the overall efficiency and reliability of the entire IT infrastructure. This is why proactive system maintenance is so critical for preventing problems and ensuring business continuity. An iam admin understands and utilizes these strategies for success.
Automating Administrative Tasks for Increased Efficiency
System administrators often face repetitive tasks. These can consume valuable time and resources. Automation offers a powerful solution. By automating routine processes, iam admin teams can significantly increase efficiency and reduce the risk of human error. Scripting languages like Bash and PowerShell are invaluable tools for this purpose. They allow administrators to create custom scripts to automate tasks such as user account creation, software updates, and system backups. Effective automation streamlines workflows. It allows iam admin personnel to focus on more complex and strategic initiatives.
Numerous automation tools are available to further enhance efficiency. Configuration management tools, like Ansible and Puppet, enable administrators to manage and configure systems across large networks. These tools automate the deployment and configuration of software and applications. They ensure consistency across all managed systems. This simplifies complex deployments and reduces manual intervention. Implementing automation strategies requires careful planning and consideration of potential challenges. However, the long-term benefits in terms of increased efficiency and reduced workload for the iam admin team are substantial.
Consider automating tasks like log analysis and monitoring. This can provide proactive insights into system health and performance. Automated reporting features alert administrators to potential issues before they escalate. The iam admin can then take proactive steps to address them. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and improves overall system stability. Automating routine tasks frees up the iam admin to concentrate on more strategic activities. This includes improving security measures and optimizing system performance. The result is a more resilient and efficient IT infrastructure. Ultimately, automation empowers the iam admin to manage increasingly complex systems effectively.
Managing User Accounts and Permissions: A System Administrator’s Guide
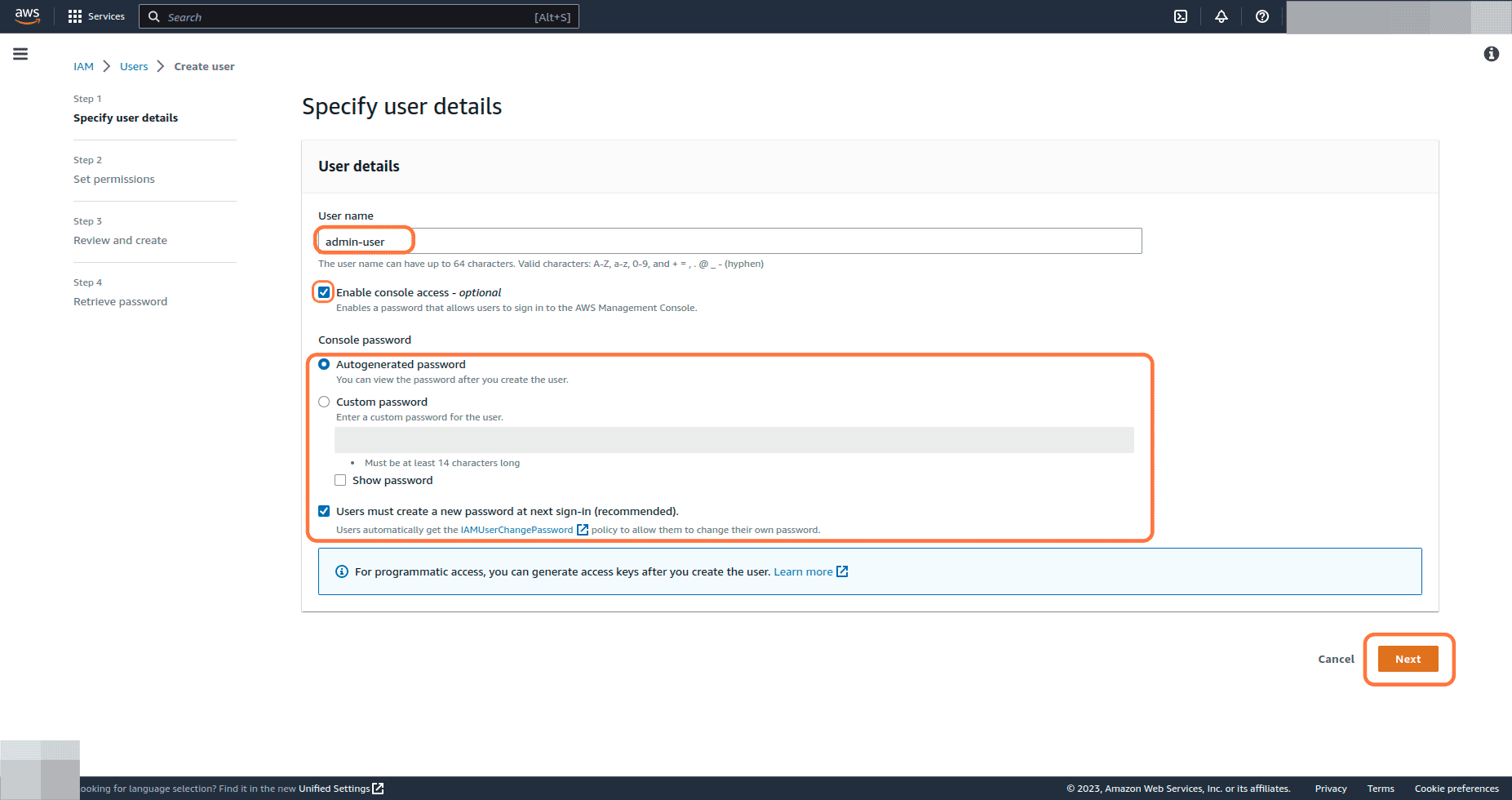
Efficient user account management is crucial for any organization. System administrators, or iam admins, play a vital role in this process. They are responsible for creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts. This involves careful consideration of each user’s role and responsibilities. Appropriate permissions and access levels must be assigned to maintain system security and data integrity. An iam admin must understand the implications of granting excessive access, which could lead to security vulnerabilities. Regular audits of user accounts are also essential to identify any unauthorized access or dormant accounts that should be removed. Strong password policies should be enforced, along with multi-factor authentication where possible. These measures minimize the risk of unauthorized access and protect sensitive data. For an iam admin, proper account management is not merely a task; it’s a cornerstone of a robust security posture. The iam admin also handles account lockout procedures, ensuring compliance with security policies and helping to recover from password-related issues. Account management processes must be documented thoroughly, allowing consistent application of standards across the organization. This ensures efficiency and reduces the risk of human error.
The process of assigning permissions often involves utilizing a Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) system. This approach defines roles with specific permissions, streamlining account management and improving security. Instead of assigning permissions individually to each user, iam admins assign roles, granting users the necessary privileges for their job functions. This approach simplifies administration, reduces errors, and enhances security by limiting access to only what is necessary. An iam admin must carefully design these roles to ensure that they accurately reflect the responsibilities of each position within the organization. Regular reviews of these roles ensure that permissions remain relevant and appropriate as job duties or organizational structures change. The iam admin must be familiar with the underlying operating system’s security mechanisms to leverage these RBAC systems effectively. Understanding group policies, permissions inheritance, and access control lists is fundamental to maintaining a secure environment. This deep understanding allows the iam admin to quickly react to and mitigate any potential security issues.
Effective user account management goes beyond simply adding or removing users. It includes regular reviews and audits. These audits can be automated using scripting and monitoring tools to identify inactive or suspicious accounts. This proactive approach is vital for detecting and preventing potential threats before they cause significant damage. The iam admin may also use these tools to monitor login attempts and unusual activities, providing further insights into potential security breaches. A comprehensive logging system is crucial to track all changes made to user accounts and permissions, enabling effective auditing and accountability. Properly managed user accounts are a strong defense against various cyber threats, and the iam admin plays an integral role in maintaining that defense. By carefully managing user accounts and permissions, an iam admin ensures the organization’s security and data integrity, while simultaneously promoting efficient system administration.
Advanced System Administration Techniques
High availability setups are critical for ensuring continuous service. System administrators employ techniques like clustering and load balancing to distribute workloads across multiple servers. Redundancy is key. This minimizes downtime in case of server failure. An iam admin must understand these concepts. Implementing failover mechanisms is essential. These mechanisms automatically switch to a backup server. This ensures uninterrupted operation. Regular testing of these systems is crucial to verify their effectiveness. A proactive approach to maintaining high availability is paramount. Ignoring this can lead to significant service disruptions.
Disaster recovery planning is another crucial area for experienced system administrators. This involves developing strategies to mitigate the impact of unforeseen events. These events can range from natural disasters to cyberattacks. A comprehensive plan includes data backups, recovery procedures, and alternative infrastructure. Regular drills and testing help ensure the plan’s effectiveness. Understanding data replication techniques and cloud-based backup solutions is important. The ability to quickly restore systems and data minimizes disruption. An iam admin needs to understand these considerations. They should consider the business impact analysis when developing their disaster recovery plans.
Virtualization technologies play a significant role in modern system administration. Virtual machines (VMs) allow administrators to create and manage multiple isolated operating systems on a single physical server. This improves resource utilization and simplifies server management. This also allows for easier testing and deployment of new applications. Hypervisors, such as VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM, are essential tools. Understanding the nuances of VM management, resource allocation, and network configuration is key. An iam admin skilled in virtualization can optimize resource utilization. They can easily manage complex server environments. They can leverage the benefits of cloud computing platforms.