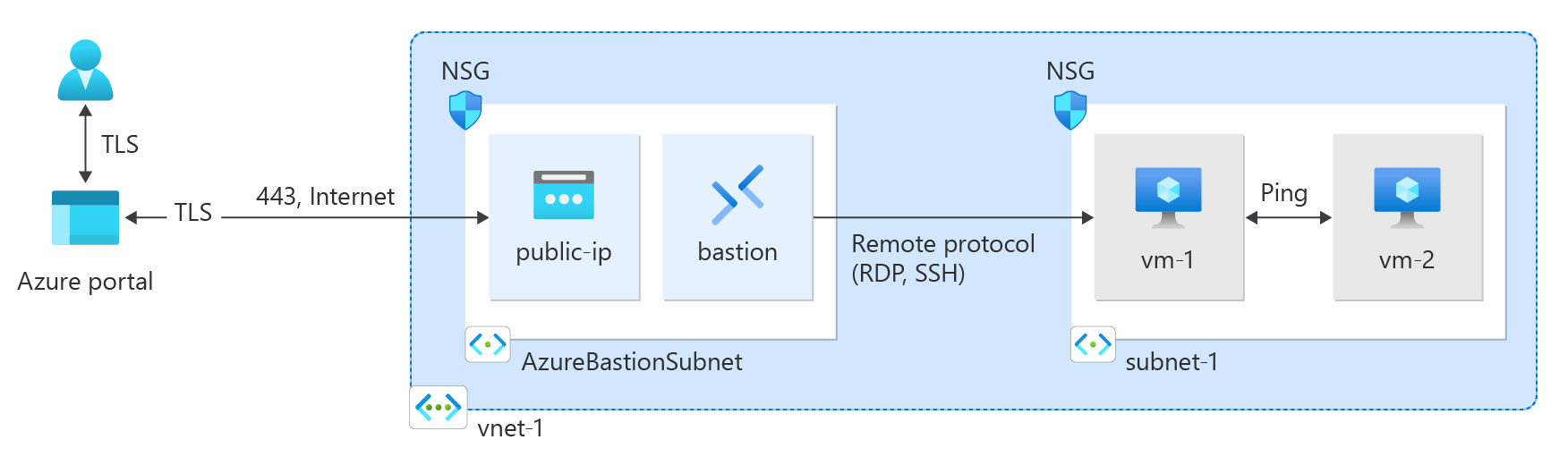
Why Consider Building Your Own Private Network?
The desire to create virtual private networks stems from a growing awareness of online security and privacy. Individuals are increasingly seeking ways to protect their sensitive data from prying eyes, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks in cafes, airports, or hotels. These networks, while convenient, often lack robust security measures, making them vulnerable to hacking and data interception. Creating a virtual private network provides a secure and encrypted connection, shielding your online activities from potential eavesdroppers and safeguarding your personal information.
Beyond security, creating virtual private networks offers enhanced privacy. A VPN masks your actual IP address, replacing it with one from the VPN server’s location. This makes it more difficult for websites and online trackers to monitor your browsing habits and collect data about your location and activities. For those concerned about online surveillance and data collection, a VPN provides a valuable layer of protection. Furthermore, many individuals choose to create virtual private networks to access geographically restricted content. Streaming services, news websites, and other online resources often impose regional limitations, preventing users in certain countries from accessing their content. A VPN allows you to bypass these restrictions by connecting to a server in a different location, effectively “spoofing” your location and unlocking access to the desired content.
In some regions, creating virtual private networks is motivated by the need to bypass censorship and access information freely. Governments or organizations may block access to certain websites, social media platforms, or news sources. A VPN can circumvent these blocks, allowing users to access information and express themselves without fear of censorship. The ability to create virtual private networks empowers individuals to maintain their online freedom and access a wider range of perspectives. Ultimately, the decision to create virtual private networks is driven by a desire for greater security, privacy, and freedom in an increasingly interconnected world. The ability to control your online experience and protect your digital footprint is becoming increasingly important, and a VPN offers a powerful tool to achieve these goals. The ability to create virtual private networks gives a user back their control.
Understanding the Basics of Network Tunneling
To understand how to create virtual private networks, it’s helpful to grasp the fundamental concept of a VPN. Imagine a VPN as a secure, private tunnel for your internet traffic. When you connect to the internet without a VPN, your data travels directly from your device to the websites and services you use, potentially exposing it to eavesdropping or interception. A VPN interposes itself, creating an encrypted connection between your device and a VPN server.
This “tunnel” effectively masks your IP address, replacing it with the IP address of the VPN server. This makes it significantly more difficult for websites, advertisers, or malicious actors to track your online activity back to your actual location. Furthermore, the data transmitted through the tunnel is encrypted, meaning it’s scrambled into an unreadable format. Even if someone were to intercept the data, they wouldn’t be able to decipher its contents without the decryption key. This is a crucial aspect of how a VPN works to protect your privacy and security.
Think of it like this: imagine you want to send a secret message to a friend across a crowded city. Sending it directly carries the risk of someone overhearing the message. A VPN is like using a secret, underground tunnel. The message is placed in a secure box (encrypted data), transported through the tunnel (the VPN connection), and delivered to your friend without anyone else knowing its contents or who sent it. This is a simplified analogy, but it illustrates the core function of a VPN: creating a secure and private pathway for your online data. Understanding this basic principle is the first step toward appreciating the value of a VPN and how you can create virtual private networks to enhance your online security and privacy.
How to Establish a Personal Network: A Step-by-Step Approach
Setting up a personal network to create virtual private networks involves several distinct methods, each offering a unique balance of convenience, control, and technical complexity. The optimal choice depends largely on an individual’s technical expertise, budget, and specific security requirements. This section serves as a roadmap, outlining the primary options available for users looking to create virtual private networks and enhancing their online privacy and security. Before diving into the technical specifics, understanding the available pathways is crucial for making an informed decision.
One of the simplest methods is to leverage pre-existing VPN services. These providers offer user-friendly applications and readily available support, making them an attractive option for those seeking immediate protection. However, considerations such as subscription costs, the provider’s logging policies (with a preference for “no-log” VPNs), the availability of server locations, and connection speeds must be carefully evaluated. The ease of use comes with a trade-off: reliance on a third party to maintain privacy and security. This contrasts sharply with more hands-on approaches that allow for greater control over the entire network infrastructure.
For users with some technical skills, configuring a VPN server directly on a compatible home router presents an appealing alternative to create virtual private networks. This approach offers the advantage of protecting all devices connected to the home network simultaneously, eliminating the need for individual VPN installations on each device. However, router compatibility is a significant factor, and the setup process can be complex, requiring a degree of technical proficiency. Another advanced approach involves building a dedicated VPN server using software like OpenVPN or WireGuard. This can be done on a physical server or a virtual machine hosted on a cloud platform such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. While this method provides maximum flexibility and control, it demands substantial technical expertise to set up and maintain. Each of these options will be explored in detail in the following sections, offering a comprehensive guide to creating and managing your own personal network to create virtual private networks. The next steps will enable users to make an informed choice that best aligns with their individual needs and technical capabilities.
Leveraging Existing VPN Services for Instant Protection
For those seeking immediate online protection, leveraging existing VPN providers offers a convenient solution. These services abstract away the complexities of setting up and managing a personal network, allowing users to quickly create virtual private networks and enjoy enhanced security and privacy. The primary benefit lies in their ease of use. Most providers offer user-friendly applications for various devices, simplifying the connection process with just a few clicks.
Established VPN providers typically boast readily available customer support, assisting users with troubleshooting and configuration. Performance is another key advantage, with many providers maintaining extensive server networks across numerous locations. This allows users to choose servers close to their actual location for optimal speed or select servers in different countries to access geographically restricted content. When selecting a VPN provider to create virtual private networks, several considerations are paramount. Cost is an obvious factor, with subscription fees varying significantly. More importantly, users should carefully review the provider’s logging policies. “No-log” VPNs, which claim not to retain any records of user activity, are generally preferred for maximizing privacy. The number and location of servers also influence performance and the ability to bypass geo-restrictions. Speed is crucial for streaming and downloading, so it’s wise to research speed test results for different providers.
It’s essential to be aware of the trade-offs. While convenient, using a third-party VPN service requires trusting the provider with your data. Therefore, thorough research and selecting a reputable provider with a proven track record are vital to create virtual private networks with confidence. Some popular VPN providers include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, and CyberGhost, each offering different features and pricing plans. However, this is not an exhaustive list, and users should conduct their own due diligence before making a decision. Remember to carefully compare the features, pricing, and privacy policies of different providers before committing to a subscription. Ultimately, choosing the right VPN service depends on individual needs and priorities. By carefully evaluating the available options, users can select a provider that effectively protects their online privacy and security.
Setting Up a Secure Tunnel on Your Home Router
Configuring a VPN server directly on a compatible router presents a compelling option for users seeking to create virtual private networks and extend protection to all devices connected to their home network. This approach offers the advantage of securing every device that connects to the router, including smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT devices that may not natively support VPN software. By creating a virtual private network at the router level, users can ensure consistent and comprehensive protection without the need to install and manage VPN software on each individual device. It is a centralized solution to create virtual private networks.
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that this method necessitates a certain degree of technical expertise. Not all routers support VPN server functionality. Before attempting this setup, it’s essential to verify that the router is compatible with VPN protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard. Some routers come with built-in VPN server features, while others may require flashing custom firmware like DD-WRT or Tomato to unlock this capability. The configuration process can involve navigating the router’s settings, generating encryption keys, and configuring client devices to connect to the VPN server. While the initial setup may be complex, the ongoing management is relatively straightforward once the virtual private network is established.
The benefits of this method extend beyond comprehensive device protection. By setting up a VPN on the router, users can effectively mask their home network’s IP address, enhancing their online privacy and security. This can be particularly useful when accessing sensitive information or using public Wi-Fi networks, as all traffic originating from the home network will be encrypted and routed through the VPN server. Furthermore, this approach can facilitate secure remote access to the home network, allowing users to access files, printers, and other resources from anywhere in the world. While creating a virtual private network on a router may require more technical effort than using a pre-existing VPN service, it offers a powerful and versatile solution for protecting the entire home network and enhancing online privacy. Creating virtual private networks in this way gives flexibility but needs expertize.
Building Your Own Network Server: A Technical Deep Dive
For those seeking ultimate control and customization, setting up a VPN server offers unparalleled flexibility. This approach involves installing VPN server software, such as OpenVPN or WireGuard, on a dedicated server. This server can be a physical machine located at your home or office or, more commonly, a virtual server hosted on a cloud platform. Choosing to create virtual private networks this way demands a higher level of technical expertise, but the rewards include tailoring the VPN to your precise needs and maintaining complete ownership of your data.
The process typically begins with selecting a server operating system, such as Linux (Ubuntu, Debian, or CentOS are popular choices). Once the operating system is installed and secured, the VPN server software can be configured. Both OpenVPN and WireGuard are open-source solutions, offering robust security and performance. OpenVPN is a mature and widely supported option, while WireGuard is a newer protocol known for its speed and simplicity. Configuration involves generating encryption keys, setting up user accounts, and configuring firewall rules. Cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure provide virtual machines suitable for hosting VPN servers. These platforms offer scalability and reliability, allowing you to create virtual private networks that can handle varying levels of traffic. Creating your own VPN server ensures all your data passes through a server you control, enhancing privacy and security.
However, it’s crucial to understand the responsibilities involved. You are responsible for maintaining the server’s security, including applying security updates and monitoring for intrusions. You must also ensure the server has sufficient resources (CPU, memory, and bandwidth) to handle your VPN traffic. Furthermore, you must be comfortable with command-line interfaces and network configuration. Despite the technical challenges, the ability to create virtual private networks with complete control over the server environment is a compelling option for technically proficient users. Remember that successfully create virtual private networks through this method requires continuous learning and adaptation to new security threats and software updates, but offers a great advantage in customizing your own privacy and security solution.
Enhancing Your Privacy: Best Practices for Network Usage
To truly maximize the benefits when you create virtual private networks, it’s crucial to adopt a holistic approach to online security. A VPN is a powerful tool, but it’s most effective when combined with other privacy-enhancing measures. Start with the basics: use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts. A password manager can greatly simplify this process. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible, adding an extra layer of security beyond just a password. This makes it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access your accounts, even if they somehow obtain your password.
Regularly update your software, including your operating system, web browser, and all applications. Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Be mindful of your online behavior. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from untrusted sources. Phishing scams are a common way for attackers to steal your personal information. Always double-check the sender’s address and the link’s destination before clicking. Furthermore, review the privacy settings on your social media accounts and other online services. Limit the amount of personal information you share publicly. Consider using privacy-focused search engines and browsers that don’t track your browsing activity.
Understand the limitations of VPNs. While a VPN encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address, it doesn’t make you completely anonymous online. Your online activities can still be tracked through cookies, browser fingerprinting, and other techniques. A VPN also does not protect you from malware or viruses. It’s essential to use a reputable antivirus program and practice safe browsing habits. To further enhance your privacy, consider using a combination of tools, such as a VPN, Tor browser, and privacy-focused browser extensions. Regularly review your VPN’s settings and ensure that it is configured correctly. Choose a VPN provider with a clear and transparent privacy policy, particularly regarding logging practices. Opt for a “no-log” VPN that doesn’t store any information about your online activities. By implementing these best practices, you can significantly enhance your online privacy and security when you create virtual private networks.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Challenges
When you create virtual private networks, occasional hiccups are normal. Connection drops are a frequent frustration. Usually, these occur because of unstable internet connections. Begin by verifying your internet is working properly without the VPN. Resetting your modem and router might solve the issue. If the problem persists, investigate your VPN client’s settings. Perhaps a firewall or antivirus program is blocking the VPN connection. Add the VPN application to your firewall’s exception list. Another cause might be the VPN server you are connected to. Servers can sometimes become overloaded. Switch to a different server location within your VPN application. Experimenting with different protocols (like OpenVPN UDP or TCP, or WireGuard) in your VPN settings can also improve stability. You can create virtual private networks, but make sure you know how to keep it up and running.
Slow speeds are another common complaint when you create virtual private networks. VPNs inherently introduce some speed overhead due to encryption. However, significant slowdowns require investigation. The distance to the VPN server dramatically impacts speed. Choose a server closer to your actual location for optimal performance. Server load also plays a role; less congested servers offer better speeds. Your internet service provider (ISP) might be throttling VPN traffic. While this is less common, it is still possible. Try connecting to different VPN server locations. If speeds improve on a different server, throttling might be the cause. Check your VPN settings and ensure you’re using the most efficient protocol available. WireGuard is generally faster than OpenVPN. Some VPN providers offer split tunneling, allowing you to route only specific traffic through the VPN, improving speeds for other activities.
IP address leaks pose a significant security risk when you create virtual private networks. An IP leak means your real IP address is visible, defeating the purpose of the VPN. Most reputable VPNs have built-in leak protection. Verify that this feature is enabled in your VPN client. You can use online tools to check if your IP address is leaking. Search for “IP leak test” on your browser. If a leak is detected, immediately disconnect from the VPN and contact your VPN provider’s support. Ensure your web browser isn’t configured to use WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication), which can sometimes bypass the VPN. Disabling WebRTC in your browser settings or using a browser extension designed to prevent WebRTC leaks will enhance your privacy. Regularly monitor your VPN connection and conduct leak tests to maintain a secure online experience. It is possible to create virtual private networks and have a false sense of security when your IP is leaking.