Power BI Desktop and Power BI Service: An Overview
Power BI comprises distinct tools, each designed for specific purposes within the data analysis workflow. Power BI Desktop is a local application primarily used for report development. The Power BI service is a cloud-based platform for sharing and collaborating on those reports. Understanding the difference between Power BI Desktop vs Power BI service is crucial for effective utilization of the Power BI ecosystem.
Power BI Desktop serves as a comprehensive development environment. Here, users connect to various data sources, model data, design interactive visualizations, and construct reports. These reports are not meant to stay confined to the desktop. Instead, they are published to the Power BI service. This cloud platform is where collaboration and sharing take center stage.
The Power BI service enables users to share insights with colleagues, embed reports into websites, and access them via mobile devices. Workspaces within the Power BI service facilitate organized sharing and controlled permission management. Therefore, while Power BI Desktop is the tool for creation, the Power BI service is the hub for distribution and collaboration, highlighting the power bi desktop vs power bi dynamic. Choosing the right tool depends greatly on the task and project requirements. One develops; the other shares.
Crafting Reports: A Deep Dive into Power BI Desktop
Power BI Desktop serves as a robust development environment for building impactful data visualizations and reports. It is a free desktop application where users connect to various data sources, model data, and design interactive dashboards. Understanding its functionalities is crucial in the power bi desktop vs power bi debate. Power BI Desktop empowers analysts and developers to transform raw data into actionable insights.
The core strength of Power BI Desktop lies in its extensive data connectivity. It supports connections to a wide array of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, cloud services, and more. This allows users to consolidate data from disparate systems into a single, unified data model. Once connected, users can leverage the Power Query Editor to clean, transform, and shape the data to meet their specific analytical needs. This is a key differentiator when considering power bi desktop vs power bi.
Furthermore, Power BI Desktop provides a rich set of features for designing compelling reports. The report designer offers a drag-and-drop interface for creating visualizations, adding interactive elements, and formatting the overall report layout. DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) calculations enable users to perform complex calculations and derive new metrics from the data. These calculations extend the analytical capabilities of Power BI, empowering users to uncover deeper insights. This makes Power BI desktop a powerful tool. When discussing power bi desktop vs power bi, it’s important to remember that the Desktop version is where the magic happens, allowing for extensive customization and complex data manipulation. Power BI Desktop is an indispensable tool for any organization seeking to unlock the full potential of its data. Power BI desktop is often the starting point for any Power BI project.
Sharing Insights: How to Publish Power BI Reports
The Power BI service acts as a collaborative environment, extending the reach of reports crafted in Power BI Desktop. Once a report is finalized in Power BI Desktop, it can be published to the Power BI service. This crucial step transforms a locally developed report into a shareable asset. Publishing to the Power BI service allows distribution to colleagues, embedding into websites or applications, and accessibility through mobile devices via Power BI Mobile apps. Therefore, understanding how Power BI desktop vs power bi service work together is very useful.
Workspaces are a cornerstone of collaboration within the Power BI service. These act as containers for reports, dashboards, and datasets. They allow for the organization of content and the management of user permissions. Access to a workspace, and the content within it, can be granted to individuals or groups, controlling who can view, edit, or share the reports. Different roles, such as Admin, Member, Contributor, and Viewer, define the level of access each user has. This robust permission management ensures data security and controlled collaboration. The Power BI service enhances accessibility, enabling users to interact with reports from various devices and locations.
Beyond simple sharing, the Power BI service offers features that enhance report consumption and interaction. Reports published to the service can be scheduled for automatic data refresh, ensuring that the information displayed is always up-to-date. Users can also create dashboards, which are collections of visualizations from one or more reports, providing a high-level overview of key metrics. These dashboards can be customized and shared, offering a personalized view of the data. The Power BI service also supports interactive features, such as commenting and subscribing to reports, further fostering collaboration and data-driven decision-making. This functionality exemplifies the collaborative power of the cloud-based platform, a key differentiator when comparing power bi desktop vs power bi. The ability to publish and share insights broadly is a major advantage of leveraging the Power BI service alongside Power BI Desktop. The collaboration and data sharing in the Power BI service make all the difference when working in teams, where the reports can be accessed by various members with specific permission management.
Feature Comparison: Desktop Application vs. Cloud Platform
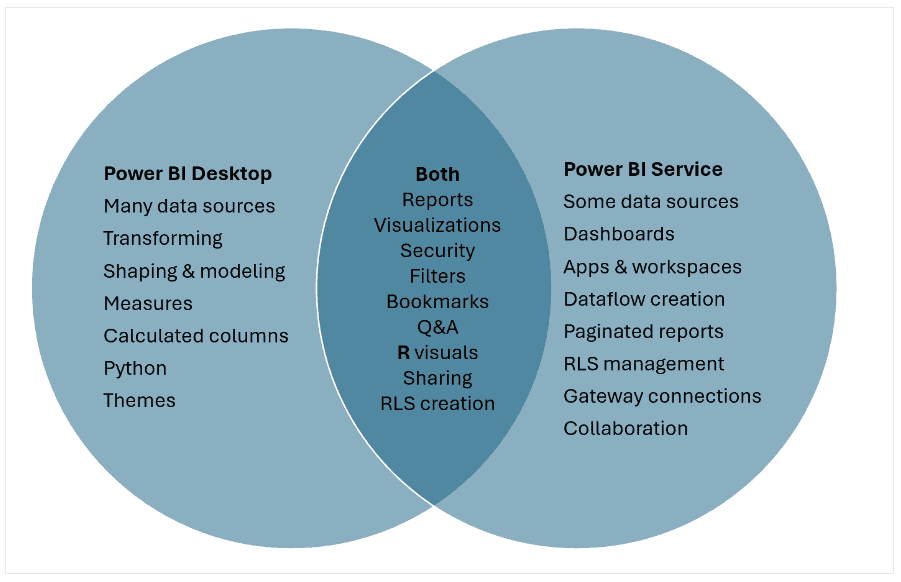
A detailed comparison of features is essential when evaluating Power BI Desktop versus Power BI service. While some functionalities overlap, key differences dictate which tool is best suited for a particular task. Power BI Desktop excels in data modeling and report design, offering a robust environment for connecting to various data sources, performing complex DAX calculations, and creating visually appealing reports. The Power BI service, on the other hand, prioritizes collaboration, sharing, and accessibility.
Consider data transformation capabilities. Power BI Desktop provides Power Query Editor for advanced data cleaning, shaping, and transformation. The Power BI service offers limited data transformation options, primarily focusing on refreshing data and applying minor adjustments. Regarding report design, Power BI Desktop offers greater flexibility and control over visual elements. While the Power BI service allows for report customization, it is less extensive than the desktop application. This becomes critical in advanced power bi desktop vs power bi report creation.
Collaboration is a major differentiator. The Power BI service shines with features like workspaces, app publishing, and permission management, enabling seamless sharing and collaboration among team members. Power BI Desktop lacks these collaborative features, as it is primarily a single-user development environment. Scheduling data refreshes is another crucial aspect. The Power BI service allows for automated data refreshes, ensuring reports are always up-to-date. Power BI Desktop requires manual data refreshes unless connected to a data source that supports scheduled refreshes through the Power BI service. Therefore, when considering power bi desktop vs power bi, it’s about individual creation versus team collaboration and automation. Here’s a concise breakdown:
- Data Transformation: Power BI Desktop (Advanced Power Query Editor) vs. Power BI Service (Limited).
- Report Design: Power BI Desktop (Extensive customization) vs. Power BI Service (Moderate customization).
- Collaboration: Power BI Desktop (Limited) vs. Power BI Service (Workspaces, app publishing, permissions).
- Scheduling Refreshes: Power BI Desktop (Manual) vs. Power BI Service (Automated).
How to Choose: Selecting the Right Power BI Tool for Your Needs
Selecting between Power BI Desktop and Power BI service depends heavily on your specific needs. Often, the optimal approach involves using both tools in conjunction. Power BI Desktop serves as the primary tool for data modeling and report creation. The Power BI service is essential for sharing and collaboration.
Consider Power BI Desktop when the task involves connecting to various data sources, transforming data, and designing interactive reports. Data analysts and report developers will spend the majority of their time within Power BI Desktop. It allows granular control over data shaping and visualization design. For instance, a financial analyst building a monthly performance report would use Power BI Desktop to connect to accounting systems, clean the data, create DAX measures, and craft compelling visuals. This detailed work is best suited for the desktop environment. The discussion about power bi desktop vs power bi must include the ability to use offline Power BI desktop for development, and the online Power BI service to share the reports. The decision about power bi desktop vs power bi also affects the project cost because Power BI desktop is free but Power BI service requires a paid subscription.
The Power BI service is the preferred choice when the focus shifts to sharing reports and dashboards with a wider audience. It facilitates collaboration among team members. Features like workspaces and app publishing make it easy to distribute insights. Consider using the Power BI service when needing to embed reports in a website or access them on mobile devices. A sales manager, for example, might use the Power BI service to share a sales dashboard with their team. They can set permissions to control access, ensuring that sensitive data remains secure. Another scenario is to schedule automated data refreshes to ensure that the reports in the Power BI service are based on the most recent data. Therefore, the best approach involves understanding the differences between power bi desktop vs power bi to implement it based on a project’s specific needs. In reality, for most Power BI users, there is no decision on power bi desktop vs power bi because they will use both for their Power BI solutions.
Data Visualization and Reporting: Capabilities in Each Tool
Power BI Desktop excels in offering a rich and interactive environment for data visualization. Its extensive library of built-in visuals, including bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and maps, allows users to create compelling reports. The drag-and-drop interface simplifies the process of designing visualizations, and the advanced formatting options enable customization to match specific branding guidelines. Power BI Desktop also supports custom visuals, expanding the possibilities for unique and tailored data representations. For those focused on creating intricate and highly customized reports, Power BI Desktop provides the necessary tools and flexibility. Data exploration and transformation are key strengths, making it ideal for analysts who need to manipulate and refine data before visualization.
The Power BI service offers robust data visualization and reporting capabilities, geared towards sharing and collaboration. While it provides access to many of the same visual types as Power BI Desktop, its focus is on interactive dashboards and reports consumed through a web browser or mobile app. Users can create dashboards by pinning visuals from reports, offering a high-level overview of key metrics. The Power BI service facilitates collaboration through features like sharing reports and dashboards with colleagues, embedding reports in websites or applications, and subscribing to email updates. While the Power BI service may not offer the same level of granular control over visual design as Power BI Desktop, it prioritizes accessibility and ease of use for a wider audience. The “power bi desktop vs power bi” decision often hinges on whether the priority is deep data manipulation and custom report design or widespread sharing and accessibility.
A key difference in “power bi desktop vs power bi” lies in the interactive elements each offers. Power BI Desktop allows for extensive interactivity within the report design itself, including drill-through, tooltips, and custom navigation. These features enhance the user experience and enable deeper data exploration. The Power BI service retains much of this interactivity when reports are published, allowing users to filter, sort, and drill down into the data. Furthermore, the Power BI service enables natural language queries through its Q&A feature, allowing users to ask questions about their data and receive instant visual answers. Considering the specific visualization needs and the target audience is critical when weighing the capabilities of “power bi desktop vs power bi”. Both tools offer a comprehensive suite of options for visualizing data and sharing insights, but their strengths lie in different areas of the reporting workflow.
Understanding Power BI’s Architecture: A Holistic View
To fully appreciate the relationship between Power BI Desktop and the Power BI service, it’s crucial to understand the broader Power BI ecosystem. Thinking of them as isolated tools would be a mistake; they are components of a cohesive suite designed for business intelligence. This section outlines how these elements interact, revealing the comprehensive architecture that Power BI offers.
Power BI Desktop is the initial development environment where data is modeled, visualizations are designed, and reports are created. These reports are then published to the Power BI service, a cloud-based platform. The Power BI service then acts as a central hub for sharing, collaboration, and distribution of these reports. Users can access these reports through web browsers, mobile devices via Power BI Mobile apps, or even embedded within other applications using Power BI Embedded. Therefore, the data flows seamlessly from data sources through Power BI Desktop for transformation and design, then to the Power BI service for broader consumption.
Power BI Mobile applications extend the reach of Power BI, allowing users to view and interact with reports on the go. Power BI Embedded empowers developers to integrate Power BI visualizations into their own applications, providing analytics to their users without requiring them to leave the application. This interconnectedness is what makes Power BI a powerful and versatile tool. Understanding this architecture is critical in selecting the appropriate tool for the task at hand. The choice isn’t necessarily “Power BI Desktop vs Power BI” but rather, “Power BI Desktop and then Power BI service” to leverage the full potential of the platform. The architecture highlights that it’s a suite of tools working together. This creates a business intelligence solution, and it empowers users to derive insights from their data, share those insights, and take action based on them.
Licensing and Costs: What You Need to Know About Power BI
Understanding the licensing and associated costs is crucial when implementing Power BI within an organization. Power BI Desktop is generally available as a free download. This allows users to develop reports and dashboards without incurring any initial expenses. It’s a cost-effective solution for individual users or small teams focused on report creation and data exploration. However, to share and collaborate on these reports, the Power BI service comes into play, introducing different subscription options.
The Power BI service offers various subscription tiers, each tailored to different organizational needs and feature requirements. Power BI Pro is a per-user license that unlocks collaboration features, enabling report sharing, workspace access, and ad-hoc analysis. Power BI Premium, on the other hand, provides dedicated capacity and enhanced performance, suitable for larger enterprises with demanding data workloads. Power BI Embedded allows developers to integrate Power BI visuals into their own applications. The choice between these options hinges on factors such as the number of users, data volume, performance expectations, and the extent of collaboration required. The core functionality to create reports in Power BI desktop vs power bi service is different when talking about sharing.
For the most current and detailed pricing information, it’s advisable to consult the official Power BI website. Microsoft regularly updates its pricing models and feature sets, so referring to the official source ensures you have the latest details. Keep in mind that the optimal choice depends on a careful assessment of your organization’s specific needs and usage patterns for power bi desktop vs power bi, weighing the benefits of each subscription level against its associated cost. While Power BI desktop vs power bi is a common comparison, many organizations find value in using both tools, and should understand the cost implications involved with Power BI service.