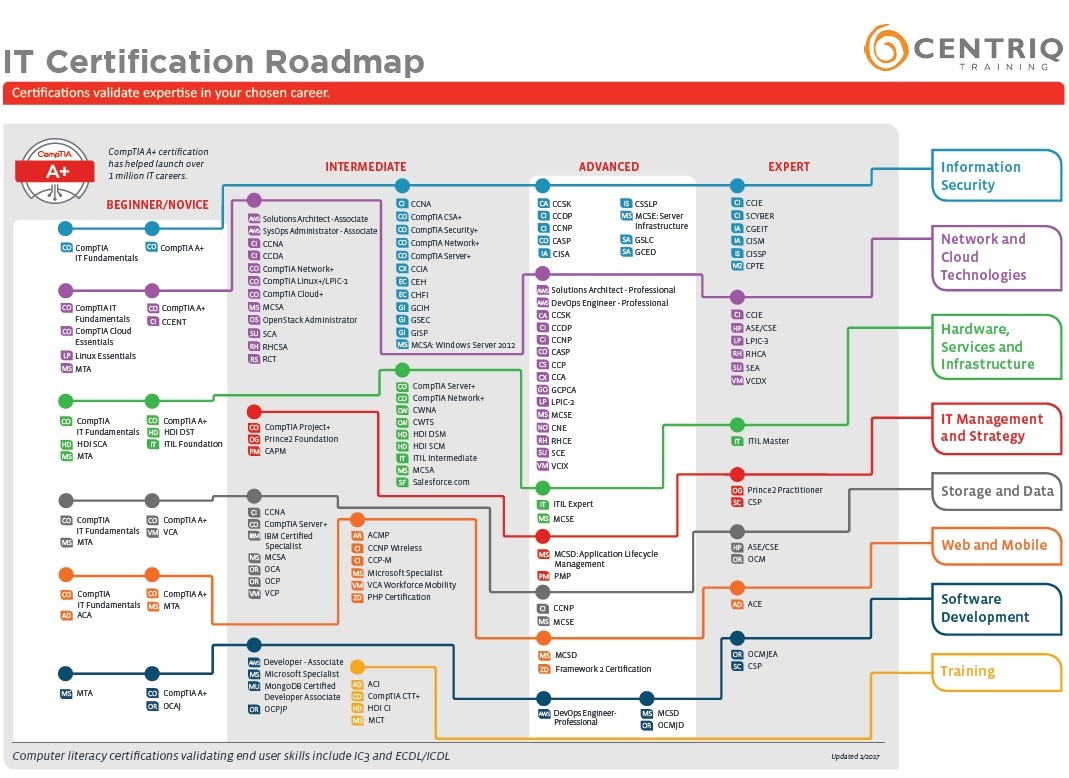
Understanding the Landscape of Information Security Credentials
The realm of cybersecurity certifications is vast and varied. It encompasses a wide array of credentials designed to validate an individual’s skills and knowledge in information security. These certifications can be broadly categorized. Foundational certifications introduce basic security concepts. Intermediate certifications delve into specialized areas. Advanced certifications demonstrate expertise and strategic thinking. Vendor-specific certifications focus on particular technologies. Each category plays a crucial role in a professional’s security certification progression chart. This landscape requires understanding to navigate career advancement effectively.
Several popular certifications illustrate this diversity. CompTIA Security+ serves as a common starting point. It validates fundamental security skills. The Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) stands as an advanced credential. It is targeted toward experienced security professionals. The Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) focuses on the managerial aspect of security. It is valuable for leaders. The Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) delves into offensive security tactics. These are just a few examples of many available options. Each certification has a specific purpose. They are all part of the broader security certification progression chart. The goal is to understand these categories. This sets the stage for career growth.
Navigating this complex landscape requires careful consideration. Individuals should assess their career aspirations. They should understand their current skill levels. This understanding is key to charting a successful path. The right certifications can unlock new opportunities. They can also significantly impact earning potential. A strategic approach to certification selection is essential. It allows professionals to build a coherent and progressive career. The selection must be aligned with career goals. The appropriate security certification progression chart serves as a roadmap.
How to Map Your Career with a Security Certification Path
Advancing a cybersecurity career requires careful planning. Individuals should first identify their specific career goals. Do they aspire to roles in penetration testing? Perhaps incident response or security management are more appealing. These aspirations directly influence the most suitable certifications. There is no universal approach to this. A personalized roadmap is key. It ensures long-term professional success. A thoughtfully constructed security certification progression chart will guide career development. It is essential to understand that the ideal path depends entirely on individual objectives and interests. This means that each aspiring cybersecurity professional should be aware of their requirements. They should actively tailor their certification choices. For example, someone interested in penetration testing might focus on certifications like CEH early on. Whereas, someone aiming for management roles would pursue CISM or CISSP credentials. Each certification should align with the defined career track. This thoughtful approach avoids unnecessary detours and focuses efforts effectively. It ensures every step adds value to the journey. Therefore, a well-defined career roadmap is vital for achieving a fulfilling career in cybersecurity.
It is important to regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen security certification progression chart. It ensures alignment with evolving professional ambitions. For those new to the field, consider starting with certifications like CompTIA Security+. Then move to more specialized certifications that align with specific roles. For example, cloud security certifications if you wish to work with AWS or Azure platforms. Always choose certifications that enhance practical skills. This approach is more beneficial than pursuing credentials purely for their prestige. The value of a certification increases when it directly contributes to professional growth. Also it should be tailored to the job you wish to achieve. Consequently, each step must be strategic, supporting both immediate and long-term career goals. Actively review and adapt your roadmap periodically. It ensures you remain aligned with the dynamic landscape of the field. Prioritizing relevant and targeted credentials accelerates professional advancement. It will make the cybersecurity career journey more meaningful.
Starting Your Journey: Foundational Security Certifications
For individuals venturing into the cybersecurity field, foundational security certifications are essential. These certifications provide the necessary groundwork for a successful career. A security certification progression chart often begins with certifications like CompTIA Security+ and Network+. CompTIA Security+ is a globally recognized certification that validates the baseline skills necessary to perform core security functions. It covers areas such as network security, compliance and operational security, threats and vulnerabilities, application, data and host security, access control, and cryptography. This certification is a great starting point. It provides a broad overview of the cybersecurity landscape. It also helps individuals understand fundamental security concepts. CompTIA Network+ focuses on networking concepts, including network infrastructure, network operations, network security, and network troubleshooting. Understanding network fundamentals is crucial for any security professional. It allows them to grasp how networks are built, secured, and how potential threats can move through them. These certifications are vital stepping stones. They help prepare candidates for various entry-level job roles. Examples include security analyst, help desk technician with security responsibilities, and network administrator. These roles help establish a solid base of understanding within the security field. The concepts learned within these certifications will be built upon in higher-level certifications. Gaining a solid foundation is paramount for any professional aiming for advanced roles.
These foundational certifications serve as essential building blocks in a security certification progression chart. They ensure candidates have the required preliminary knowledge and abilities. Starting with certifications like Security+ and Network+ offers a comprehensive overview of cybersecurity and networking principles. It allows a professional to comprehend how networks operate, how security is implemented, and where vulnerabilities may exist. Understanding these core concepts will better equip an individual for future specialization and advancement. These certifications establish a strong platform upon which more complex knowledge can be layered, such as in penetration testing or incident response. The foundational certifications are ideal for those seeking to enter cybersecurity. They are also excellent for those already in IT looking to transition to a security-focused role. Achieving these certifications is often the first step. They are a tangible demonstration of dedication to the field and provide a competitive advantage in the job market. Employers frequently look for these certificates when hiring entry-level security professionals. They signify a commitment to security practices and a basic understanding of the risks.
Building Expertise: Intermediate Level Security Qualifications
Transitioning from foundational knowledge, the next step in a security certification progression chart involves acquiring intermediate-level qualifications. These certifications are crucial for developing specialized skills and knowledge in focused areas. Examples include the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), which emphasizes penetration testing techniques. Another path is the Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), which is geared toward information security governance and risk management. Additionally, cloud security certifications such as AWS Certified Security – Specialty and Azure Security Engineer Associate are highly relevant. These credentials acknowledge the increasing importance of cloud platforms within modern security architectures. These intermediate certifications build on foundational understanding. They allow professionals to delve into specific security domains. They bridge the gap between basic concepts and advanced specialization. Choosing the right certification at this level depends on an individual’s career goals and interests.
The CEH certification, for instance, focuses on the offensive side of security. It teaches candidates to think like hackers to better defend against threats. CISM takes a more managerial approach. It focuses on establishing and overseeing security programs. Cloud-based certifications are essential for professionals who need to secure these environments. They validate a person’s understanding of specific cloud security services and implementations. Pursuing these intermediate credentials allows individuals to become experts. This level of security certification progression chart helps security professionals become highly skilled within specific domains. It creates a solid base for future advanced studies. The path at this point is about defining specialization and expertise. This progression is not just about gaining more certifications, but about developing relevant skills.
By attaining these intermediate certifications, individuals demonstrate their practical abilities. They can apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. These credentials can often lead to roles with more specific responsibilities. They might include positions such as security analyst, ethical hacker, cloud security engineer, or information security consultant. This step in the security certification progression chart is crucial for professional development. It allows professionals to gain a deeper expertise in their chosen field. It also prepares them for more advanced and strategic security roles. This progression is often not linear and should be guided by each professional’s specific career goals. It builds a strong middle ground from which to reach the apex of the security career path.
Achieving Mastery: Advanced Security Certification Pathways
Advanced certifications represent the pinnacle of security expertise. These credentials, such as the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) and the Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), demand a substantial level of experience. They also require profound knowledge in the field. Professionals pursuing these certifications often have several years of practical experience. Achieving these certifications signals a dedication to strategic and managerial aspects of cybersecurity. The CISSP is globally recognized and validates skills in security management practices. It is ideal for roles like Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). This security certification progression chart shows that CISSP is the next step after the intermediate level certifications. Meanwhile, CISA validates expertise in auditing, control, and security of information systems. It’s a strategic role in ensuring organizational compliance and risk management. These certifications signify the culmination of many security career journeys. They prepare individuals for leadership roles and complex security challenges.
These advanced certifications focus on broader security strategy and governance. They go beyond technical skills, encompassing areas like risk management, security architecture, and policy development. CISSP, for example, covers eight domains of security. These include security and risk management, asset security, security architecture and engineering, communication and network security, identity and access management, security assessment and testing, security operations, and software development security. CISA, on the other hand, places emphasis on information systems auditing. This includes governance, management of IT, information systems acquisition, and development implementation, and security. Both certifications require successful completion of a rigorous exam and adherence to a professional code of ethics. The pathway towards these certifications requires strategic planning and professional development. Security certification progression chart shows that these certifications are often the final goal for many security professionals. They represent a commitment to continuous learning and leadership.
Roles that these certifications lead to include senior security manager, security architect, and CISO. They indicate a capacity for strategic thinking and effective management of security programs. They demonstrate a depth of knowledge and experience in the field. These certifications are not for those new to the security field. They are designed for seasoned professionals ready to lead and make high-level decisions. They signify a commitment to excellence and a significant advancement within a security certification progression chart. The value of advanced certifications lies in their ability to open doors to the highest echelons of security leadership and strategic influence. Choosing one of these certifications needs careful consideration. Individuals should assess their career goals, current experience, and required effort.
Vendor-Specific Certifications: Deepening Specialized Skills
Vendor-specific certifications play a critical role in the broader landscape of security certification progression chart, catering to professionals who aim to specialize in particular technologies or platforms. These credentials focus on demonstrating proficiency with the products of specific vendors, such as Cisco, Microsoft, Amazon, and others. For instance, the Cisco Certified Network Professional Security (CCNP Security) validates expertise in implementing and managing Cisco security solutions, while the Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate certifies skills in securing Azure cloud environments. Similarly, other major vendors offer certifications designed to ensure users are highly competent in their respective security ecosystems. This level of specialization is not just about knowing the vendor’s technology, but also understanding how to implement it securely within the context of overall security strategies.
The strategic integration of vendor-specific certifications within a broader security certification progression chart can significantly enhance career opportunities. Individuals aiming to work with specific technologies often find these certifications essential. For example, someone aspiring to be a cloud security engineer would likely benefit from cloud-vendor certifications like the AWS Certified Security – Specialty, alongside broader foundational certifications. These certifications equip professionals with the detailed, hands-on knowledge necessary to configure, maintain, and troubleshoot vendor-specific security tools and systems. The timing and selection of these certifications should align with an individual’s chosen career path. These vendor-specific credentials are not usually a starting point but a targeted move after developing a solid security foundation, and when a specific area of expertise is desired. Vendor certifications complement general security qualifications by offering targeted skills.
It’s important to view vendor-specific certifications as part of a cohesive strategy rather than isolated achievements. They are most effective when combined with broader security certifications and real-world experience. This blend enables a well-rounded understanding of both general security principles and the practical application of these principles within specific vendor ecosystems. A well-planned security certification progression chart will include a careful selection of vendor-specific certifications that enhance one’s professional skill set and makes a clear path towards career advancement. Choosing the correct vendor credentials is highly dependent on the technology stack the professional is working with or intends to work with. Therefore, professionals should always assess their career aims before deciding to pursue these specialist credentials.
Maintaining Your Credentials and Staying Current
Continuing education and periodic recertification are crucial for maintaining the value of any security certification. The cybersecurity field is dynamic, with new threats and technologies emerging constantly. Therefore, maintaining your credentials is more than just fulfilling requirements; it is a commitment to continuous learning. Many security certification providers require professionals to earn Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits or equivalent to keep their certifications active. This process ensures that professionals are consistently updated on the latest industry standards and best practices. This investment in ongoing education directly impacts a professional’s ability to stay relevant and effective. The process of recertification and consistent education serves as a quality assurance checkpoint. It confirms professionals maintain the knowledge and skills that certifications initially represent. It highlights a commitment to professional development, which is highly valued by employers in the cybersecurity sector. Individuals should actively seek out training opportunities, workshops, and conferences to meet these ongoing requirements.
The significance of continuous learning in cybersecurity should never be underestimated. The speed at which new threats emerge makes ongoing education essential for anyone in the field. The security certification progression chart is not a static path. It’s a dynamic, ever-evolving journey, therefore, professionals should continuously update their knowledge and skills. Staying current with emerging technologies and security practices not only enhances professional expertise but also creates a competitive advantage in the job market. Those who proactively engage in continuous learning are the ones who excel in the long run. They contribute meaningfully to their organizations’ overall security posture. This focus on continuous learning is a vital component of professional growth and long-term career success. The continuous learning approach ensures the security certification progression chart remains a valuable asset.
Choosing The Right Security Credentials For You
Selecting the optimal security certifications requires a thoughtful approach. The ideal security certification progression chart is not a universal template. It is a personalized pathway reflecting individual goals. Consider your interests within cybersecurity. Are you drawn to technical roles or management positions? Your passions should inform your choices. Align your certification strategy with your desired career trajectory. This ensures that your investment in professional development is strategic. The “best” path is subjective, tailored to each individual’s unique professional needs. It is a journey of continuous growth and adaptation. Therefore, reflect on your long-term objectives. Understand where you see yourself in the future. This reflection will guide you in creating a relevant security certification progression chart. Begin to chart your course, considering your passions, professional goals, and the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. Your personalized security certification progression chart is the foundation of a fulfilling and successful career in the security field.
Begin by assessing your current skills and knowledge. Identify areas where you want to grow. Research the job market for desired roles. This research will help identify required certifications. For instance, a network engineer might focus on Cisco certifications. An aspiring security manager might target CISM or CISSP. This clarity will assist you in making informed decisions. Remember, the security certification progression chart should evolve. As you gain experience, you might add more advanced qualifications. Stay informed about new technologies and methodologies in cybersecurity. This awareness will enable you to adapt your learning strategy accordingly. A strategic approach to certifications maximizes career advancement. It also ensures that your expertise remains relevant. Consider vendor-specific certifications to enhance specialized skills, while not losing sight of the larger picture. Blend these with generalist options to create a balanced skill set. Ultimately, a successful security career is a continuous journey of learning, adaptation, and growth.
Map out your desired security career path. Consider your current role and ambitions. Determine which specific areas you want to specialize in, creating your own security certification progression chart. Do you want to specialize in cloud security? Perhaps you want to focus on penetration testing? Or are you more inclined to the management side? Your choices should be intentional and focused. Consider the return on investment for each certification. Some certifications will have greater impact in specific fields. It’s also important to consider the time and cost of each. Select certifications that not only enhance your knowledge. Ensure they align with your professional progression. This individualized approach is the key. Your career growth should be aligned with a personally relevant security certification progression chart. Start mapping out your journey, taking the first steps toward realizing your professional aspirations in security. Ultimately, each step forward will help you to achieve your career goals.