Understanding Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery for DevOps on Cloud
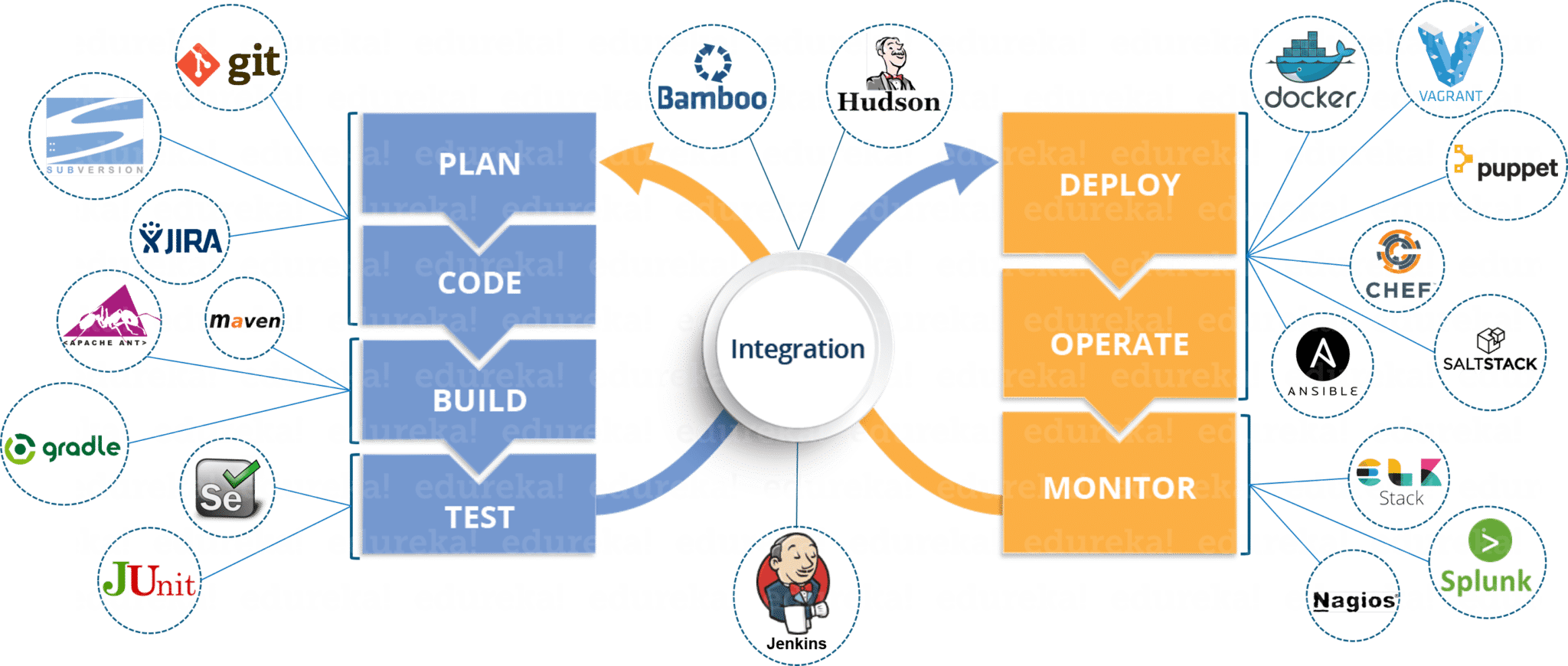
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) form the backbone of modern software development. CI is a practice where developers frequently merge code changes into a central repository. Automated builds and tests validate these changes. This process ensures that the codebase remains stable. CD then takes the validated code and automatically deploys it to various environments. This ranges from staging to production. The significance of CI/CD is greatly amplified in cloud-based environments. It enables faster release cycles. There is also reduced risk with frequent smaller deployments. The collaboration between development and operations teams improves dramatically. This is because of the automated nature of CI/CD pipelines. This shift contributes to faster innovation and more responsive software delivery. Cloud platforms provide the perfect infrastructure to implement these practices effectively. The benefits of CI/CD in such a context are numerous.
Implementing a robust CI/CD pipeline on a cloud infrastructure means that software changes are integrated and delivered faster. With fewer errors and greater reliability. The cloud provides scalable resources. This allows CI/CD processes to handle increased workloads. This is particularly useful during peak development periods. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) further streamlines this process by defining resources. It is handled through code. This improves the consistency and repeatability of deployments. Modern software development depends on the synergy between CI/CD and devops on cloud. This approach allows organizations to release features more frequently. This improves responsiveness to market needs and customer feedback. The practices of CI and CD are central. They contribute to a more agile, robust, and efficient software development lifecycle. The cloud’s elasticity and scalability make these practices more accessible and effective.
The ability to automate testing and deployment in cloud enhances both speed and quality. Cloud-based CI/CD pipelines enable development teams to work more efficiently. This accelerates the entire development process. With cloud resources available on demand, teams can create and test environments quickly. This means they are ready to handle multiple integrations and deployments. It provides the ideal environment for development teams. The adoption of devops on cloud practices is thus becoming more critical. Cloud platforms also reduce operational overhead. This frees up resources to focus on other areas. This results in faster time to market. It also allows quicker implementation of new features and functionality. This makes it easy to address user needs. The combination of CI/CD and devops on cloud represents a move toward more agile, responsive, and dependable software delivery processes.
Selecting the Right Cloud Services for Your DevOps Pipeline
Understanding the various cloud services available is crucial for establishing an effective DevOps pipeline. These services encompass compute resources, storage solutions, databases, and managed service offerings. Different cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, offer distinct sets of tools and services that can support the entire DevOps workflow. Each platform provides a unique approach to handling the requirements of continuous integration and continuous delivery. For instance, AWS offers services such as CodePipeline that allows to automate the build, test, and deployment phases. Similarly, Azure DevOps is a suite of services designed for collaborative development and deployment. On the other hand, Google Cloud Build provides a serverless platform for building and testing software. The selection of specific services should be based on a thorough evaluation of project requirements, familiarity, and existing skill sets, ensuring they are suitable for each development team’s specific needs when implementing devops on cloud.
The choices made at this stage are foundational to a robust and streamlined pipeline. Compute services, for example, provide the necessary processing power, while storage solutions cater to various data needs. Databases, both relational and NoSQL, play a vital role in data management and accessibility. Additionally, managed services can simplify complex tasks, allowing teams to focus on core application development. Therefore, when implementing devops on cloud, it is crucial to choose cloud services that align with the specific needs of a software development project. This includes considering factors like scalability, cost-efficiency, and ease of integration with existing tools. A well-structured cloud-based infrastructure can greatly enhance the efficiency and reliability of the software delivery process.
Selecting the appropriate services is not merely a technical decision; it also involves strategic considerations related to business goals. It is critical to evaluate the specific features and functionalities offered by each service to see how they support the different stages of the DevOps lifecycle. A thoughtful selection process ensures a seamless integration of these services into the devops on cloud environment, thus maximizing the efficiency and minimizing the complexity of the software development process. The ability to quickly and reliably deploy applications depends greatly on a well-chosen set of cloud services that cater to the unique characteristics of each project.
Automating Infrastructure as Code with Cloud-Native Tools
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is vital for consistent and repeatable cloud environments. It involves managing and provisioning infrastructure through machine-readable definition files, instead of manual processes. IaC significantly enhances the efficiency of devops on cloud. Tools like Terraform, CloudFormation, and ARM templates are fundamental in this process. Terraform, a popular open-source tool, allows infrastructure management across multiple cloud providers. It uses HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) to describe infrastructure resources. CloudFormation, by Amazon Web Services, enables the creation and management of AWS resources using JSON or YAML templates. Similarly, Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates are used for defining and deploying resources in Microsoft Azure. These tools automate provisioning, minimizing human error and speeding up the entire process. The implementation of IaC ensures that infrastructure deployments are consistent and reproducible. Version control systems, like Git, track changes, providing a complete history and the ability to revert to previous configurations. This leads to better resource management and cost control in the long term. Effective IaC practices are crucial for achieving a robust devops on cloud strategy.
The benefits of adopting Infrastructure as Code are numerous and impactful. Reduced manual errors are a direct result of automating infrastructure provisioning. Human intervention is minimized, decreasing the chances of misconfigurations and inconsistencies. This not only ensures greater reliability but also increases the overall speed of operations. The ability to rapidly provision and manage resources enables faster deployment cycles. This is critical in modern software development environments that require rapid iterations. IaC promotes a culture of consistency, ensuring that all development, testing, and production environments are identical, reducing the chance of unexpected behavior. Additionally, version control becomes a powerful asset, enabling tracking and rollbacks when needed. This promotes better collaboration among teams working on cloud infrastructure. These automated workflows streamline operations in devops on cloud implementations. The agility and reliability that result lead to substantial operational improvements. Ultimately, IaC is a cornerstone for devops success and overall efficiency in cloud environments.
Containerization and Orchestration for Scalable Applications
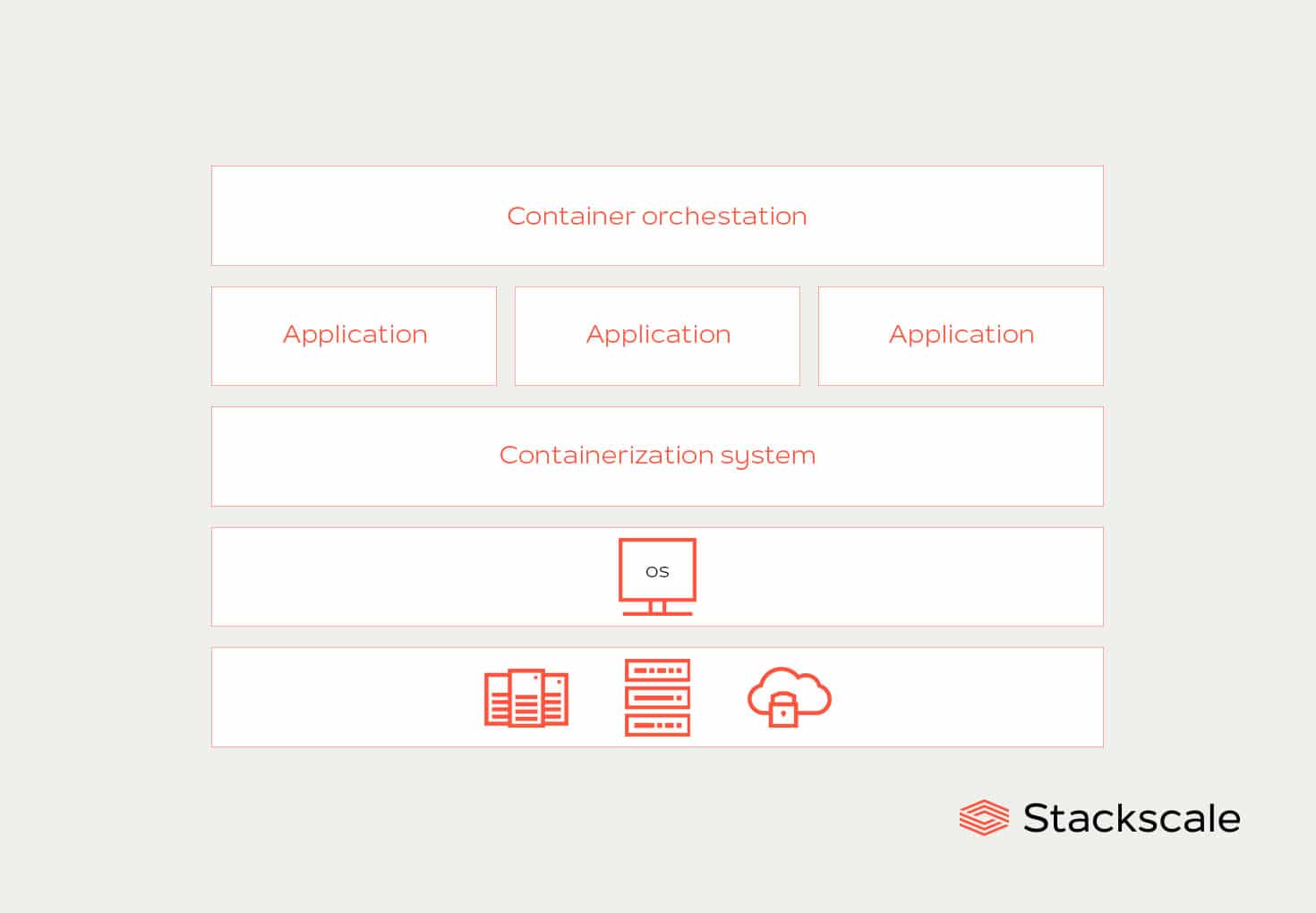
Containerization, using Docker, offers significant advantages for packaging applications. It ensures consistency across different environments. This approach simplifies the deployment process. Docker packages applications with all their dependencies into containers. These containers are lightweight and portable. They run consistently across various platforms. This consistency is vital for devops on cloud environments. Containerization improves application portability and simplifies management. It allows developers to package and ship applications more effectively. This makes it easier to handle different versions and configurations. Furthermore, it allows for faster and more reliable deployments. The use of containers also contributes to improved resource utilization. It ensures applications use only the necessary resources. This results in more efficient operation.
Container orchestration tools such as Kubernetes are essential for managing containerized applications. Kubernetes, available as managed services like EKS, AKS, and GKE, automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containers. These services handle complex tasks. This includes load balancing, auto-scaling, and health checks. Kubernetes simplifies the management of containerized applications. It enables easier and faster scaling based on demand. It manages resources effectively. This ensures high availability and resilience. The integration of container orchestration into a devops on cloud pipeline is key. It allows for efficient management of containerized workloads. This orchestration provides a robust foundation. It enhances the scalability and reliability of cloud-based applications. It simplifies deployment and management processes.
The combination of containerization and orchestration significantly enhances application portability. This means applications are not tied to specific operating systems or infrastructure. This flexibility is a key advantage for modern devops on cloud practices. It improves resource efficiency. It makes better use of underlying infrastructure. This leads to cost savings. Also, applications can be deployed more frequently and with less risk. This enhances the overall agility of the development process. This combination provides a powerful approach to managing modern, scalable applications. It ensures efficient resource utilization. It supports rapid and consistent application deployment. This combination is a major step forward in devops on cloud strategies.
Monitoring and Logging in a Cloud DevOps Environment
Effective monitoring and logging are critical for maintaining robust cloud-based applications and infrastructure. These processes are essential for a successful implementation of devops on cloud. Monitoring involves the real-time observation of system performance, availability, and resource utilization. Cloud providers offer a range of powerful tools designed to simplify these tasks. For example, Amazon Web Services provides CloudWatch, which offers metrics, logs, and alarms for monitoring AWS resources. Azure Monitor provides similar functionalities for Azure environments, with robust capabilities for log analysis and application insights. Google Cloud Monitoring provides observability for Google Cloud Platform, offering comprehensive monitoring and alerting features. Beyond these provider-specific options, there are open-source alternatives like Prometheus and Grafana, which are also widely adopted for their flexibility and advanced visualization capabilities. These tools help track key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly impact user experience, allowing devops teams to proactively identify bottlenecks, troubleshoot issues, and maintain optimal application performance. Implementing a well-defined monitoring and logging strategy ensures that potential problems are detected quickly before they escalate into major disruptions.
A comprehensive approach to monitoring and logging includes establishing robust alerts and dashboards. These tools provide real-time visibility into system health. Alerting ensures that devops teams are notified immediately when critical thresholds are breached. This allows for quick action and incident response. Dashboards visualize critical performance metrics, enabling teams to gain insights into system behavior over time. This proactive approach helps to identify patterns and trends that might indicate underlying problems. Log management, on the other hand, focuses on the collection, analysis, and storage of system logs, which are invaluable for troubleshooting complex issues. Effective log analysis helps teams understand the causes of errors or performance degradation. This also assists in identifying security breaches. Together, these monitoring and logging capabilities form the backbone of a proactive devops on cloud strategy. This strategy ensures the stability, performance, and security of cloud-based applications. It also supports ongoing improvements and ensures that systems are consistently meeting business needs. The data gathered through monitoring and logging also provides key insights for cost optimization and resource management in the cloud.
Implementing Security Best Practices in a Cloud DevOps Workflow
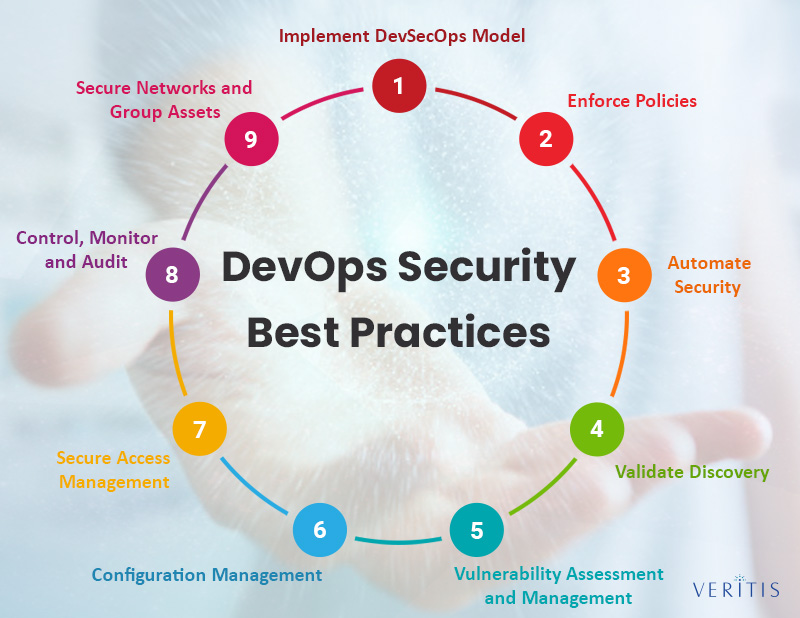
Securing a DevOps on cloud environment requires a multifaceted approach that integrates security into every stage of the software development lifecycle. Access management is fundamental; implementing the principle of least privilege ensures that users and services have only the permissions necessary to perform their tasks. This is often achieved by using Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles provided by cloud platforms, which allow fine-grained control over who can access what resources. Network security is equally crucial. Employing security groups or network access control lists to restrict traffic to essential ports and protocols will minimize the attack surface. This involves segmenting your network into different zones with varying levels of access based on security requirements. Vulnerability scanning tools should be integrated into the CI/CD pipeline to automatically detect and remediate security flaws before code is deployed. Regular scans identify potential weaknesses in dependencies and application code, allowing for proactive fixes. Furthermore, secret management is paramount to protect sensitive data. Storing credentials, API keys, and other confidential information securely using cloud-native services is essential. Avoid hardcoding these secrets within the code; instead, use dedicated secret management tools. These should encrypt secrets at rest and in transit, preventing unauthorized access. These practices of a robust devops on cloud environment ensure a strong security posture.
Integrating security into a DevOps on cloud workflow also means shifting left, meaning security considerations start early in the development phase. This involves training developers to be security-aware and embedding security checks into the development process. For example, static code analysis can catch security vulnerabilities early in the code lifecycle. Implementing infrastructure as code (IaC) adds another layer of security by ensuring consistency in the deployment of secure infrastructure. Security configurations are defined in code, which can be version controlled and reviewed, similar to application code. Employing techniques like encryption, both at rest and in transit, helps protect data from unauthorized access. Data encryption can be achieved using cloud-provided encryption services. These services encrypt data stored in databases and object storage and also encrypt communication between applications and services. Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential. These help to identify any blind spots in the security strategy, and they ensure that security controls are effective. By integrating security checks into every stage, organizations create a security-first culture in their DevOps on cloud practices. This continuous security approach is vital for mitigating risks and maintaining the integrity of cloud-based applications.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Cloud-Based DevOps
Managing cloud costs effectively is a crucial aspect of maintaining a sustainable devops on cloud environment. This requires careful planning and continuous monitoring. Organizations need to actively seek ways to reduce expenses without compromising performance. Several strategies can be implemented to optimize costs associated with cloud-based devops. One effective method involves right-sizing resources. This means choosing the appropriate instance sizes for applications. Avoid over-provisioning, which leads to unnecessary spending. Regularly assess resource utilization and adjust instance sizes as needed. Utilizing spot instances or preemptible virtual machines is another viable option. These are available at a significantly lower cost compared to on-demand instances. However, they can be interrupted, so they are best suited for fault-tolerant workloads. Leveraging reserved instances provides another cost-saving opportunity. By committing to a specific instance type for a longer duration, you can receive substantial discounts. This strategy is beneficial for predictable workloads. Implementing a robust cost tracking and reporting system is also essential for devops on cloud. This provides visibility into resource consumption and identifies areas where costs can be reduced. Tools are available to monitor cloud usage and generate reports to assess spending patterns. By continuously monitoring and making adjustments, organizations can avoid unexpected cloud expenses.
Further cost optimization in devops on cloud can be achieved through strategic implementation. Automating resource scaling based on demand ensures efficient resource utilization. This means resources scale up during peak times and scale down during off-peak hours, which minimizes idle resource costs. Optimizing storage is also important. Implement lifecycle policies to automatically move or delete older data. Choose storage types based on the data’s access frequency. For example, archive data can be moved to lower cost storage options. Evaluate the usage of managed services. Managed services often have built-in cost-optimization capabilities, which save on operational overhead. They can be less expensive than managing infrastructure manually. Another important strategy is implementing a culture of cost awareness within the devops team. Educating team members about the importance of cost management can lead to more careful resource usage. Regularly reviewing and updating the cost optimization strategies should be part of the continuous devops on cloud process. By adopting these practices, teams can significantly reduce cloud costs while maintaining the quality and performance of their applications. Cost optimization is not a one-time task; it requires consistent effort and adaptation to maintain cost-effectiveness in devops on cloud.
Future Trends in Cloud and DevOps Adoption
The landscape of devops on cloud is continually evolving, with several exciting trends poised to shape the future of software delivery. Serverless computing represents a significant shift, enabling developers to focus solely on code without managing underlying infrastructure. This approach greatly simplifies deployment and scaling, reducing operational overhead. AI-powered devops tools are also gaining traction, utilizing machine learning to automate tasks, predict potential issues, and optimize performance. These intelligent tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, thereby improving the efficiency and reliability of software pipelines. Moreover, GitOps, a practice that leverages Git as the single source of truth for infrastructure and application configurations, is becoming increasingly popular. It promotes automation, version control, and enhanced collaboration between development and operations teams. These advancements promise more agile, resilient, and cost-effective devops on cloud workflows.
Further advancing the trajectory of devops on cloud is the integration of low-code or no-code platforms. This development allows a wider range of professionals to participate in devops processes. It simplifies application development, accelerates deployment cycles and also reduces dependency on specialized coding expertise. The rise of edge computing also adds another dimension. Edge computing pushes processing closer to the data source, enhancing response times and reducing latency. These shifts impact how applications are designed and deployed, creating new challenges and opportunities for devops strategies. The increased adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies signifies a desire for flexibility and resilience. Organizations are choosing the best-of-breed services across different providers. This involves a need for devops practices and tools that work seamlessly across disparate environments. The continuing evolution suggests that flexibility, automation, and security will become increasingly essential for effective devops on cloud implementation.
Looking ahead, it is likely that the industry will witness increased adoption of advanced automation. This includes fully automated pipelines, self-healing infrastructure, and predictive maintenance systems. Such automation will reduce manual intervention and minimize downtime, boosting the overall efficiency of software delivery. Furthermore, enhanced collaboration and communication across teams will become more critical. This is supported by new tools that facilitate seamless information sharing and knowledge transfer. Security, a paramount concern, will continue to be deeply integrated into all stages of the devops lifecycle, moving beyond a bolted-on approach. This proactive integration makes security an intrinsic part of the workflow. Therefore, continuous learning, adaptation and a keen understanding of emerging trends will be essential for leveraging the full potential of future devops on cloud methodologies. Embracing these new practices will be key to staying competitive and meeting the growing demands of the software landscape.