Exploring Google’s Diverse Data Landscape
Google’s data management infrastructure is incredibly complex. Understanding what DBMS does Google use requires recognizing its scale. The company handles an unparalleled volume of data, encompassing search queries, user data from various Google services, maps data, YouTube videos, and much more. This isn’t managed by a single database management system (DBMS). Instead, Google employs a sophisticated ecosystem of diverse database technologies, each tailored to specific needs and data characteristics. The question “what DBMS does Google use?” doesn’t have a simple answer; it’s a multifaceted approach designed for optimal performance and scalability across its vast range of services. This intricate system reflects the unique challenges of managing data at Google’s scale, necessitating a multi-faceted, highly adaptable architecture.
To fully appreciate the complexity, consider the variety of data types Google processes. Structured data, like user profiles, requires relational capabilities. Unstructured data, such as YouTube videos or text documents, demands different storage and processing techniques. Real-time data feeds from Google Maps require immediate availability and updates. The sheer volume necessitates solutions capable of horizontal scaling, distributing data across numerous machines to handle the load. The need for high availability and fault tolerance further complicates the infrastructure requirements. Google’s solution is a carefully orchestrated combination of various database technologies, each playing a crucial role in managing specific data types and operational demands. The question of what DBMS does Google use is answered not with a single name, but with a description of this sophisticated ecosystem.
This multi-database approach addresses limitations of single-system solutions. Traditional relational database management systems (RDBMS) often struggle with the sheer volume and velocity of data Google handles. Real-time processing and global distribution pose significant challenges for traditional systems. Google’s answer? A distributed database architecture. This distributes the data and processing workload across multiple servers and geographical locations. This improves scalability, performance, and redundancy. This complex and highly-optimized system allows Google to maintain its services reliably, efficiently handling its massive and ever-growing dataset. The choice of a distributed, multi-DBMS approach directly answers the question “what DBMS does Google use?” by highlighting the inherent limitations of simpler solutions in the face of such a vast operational landscape.
Understanding the Need for a Multi-Database Approach
Google’s immense data volume and real-time processing needs make a single Database Management System (DBMS) impractical. Traditional relational databases, while robust for structured data, struggle with the scale and velocity of Google’s operations. Their limitations become apparent when considering the sheer volume of search queries, user data, maps data, YouTube videos, and countless other data streams Google processes daily. What DBMS does Google use? The answer isn’t a single system but a sophisticated ecosystem. A single system would face significant challenges in providing the speed and scalability required. The question “what dbms does google use” highlights the complexity of their infrastructure.
The limitations of a monolithic approach necessitate a distributed database system. This architecture distributes data across multiple servers, improving scalability, fault tolerance, and performance. Distributed systems offer greater flexibility in handling diverse data types and query patterns. They also enable parallel processing, accelerating data analysis and providing the low latency crucial for real-time applications like search and advertising. Understanding why Google employs a multi-database approach helps answer “what DBMS does Google use” – it’s not about a single solution but an optimized ecosystem.
A distributed system addresses the inherent limitations of a single point of failure. If one server fails, the others continue to operate. This architecture also allows for easier scaling. Google can add more servers as needed, seamlessly accommodating growth. This scalability is critical for handling the ever-increasing data volumes and user traffic. The question of “what DBMS does Google use” is therefore less about specific products and more about a strategic approach to data management tailored to their unique demands. The choice reflects a commitment to adaptable, high-performance infrastructure able to meet future challenges.
Google Spanner: A Globally-Distributed Database Powerhouse
Google Spanner stands as a testament to Google’s innovative approach to data management. What DBMS does Google use for its globally distributed needs? Spanner, a globally-distributed, strongly consistent database, forms a cornerstone of Google’s infrastructure. It excels at handling massive datasets spread across numerous geographical locations, ensuring high availability and strong consistency—a crucial aspect for many Google services. This means data remains accurate and reliable, even with concurrent updates from various points around the globe. Spanner’s architecture employs a unique design, employing true Paxos for distributed consensus. This allows for a level of data consistency unmatched by many other distributed databases, making it ideal for applications requiring utmost reliability. The question, “what dbms does google use for critical applications?”, often points to Spanner. Its capacity to handle billions of rows of data with sub-second latency is a key reason for its widespread use within Google.
Spanner’s capabilities are integral to the smooth operation of several critical Google services. For instance, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) itself heavily relies on Spanner to maintain data consistency and availability across its global network of data centers. Spanner’s ability to guarantee strong consistency even during large-scale updates ensures that users experience seamless service across the world, regardless of location. The system’s design inherently accounts for network latency and geographical distance, offering a solution to the scalability challenges typically associated with global data management. The consistent response times and high availability that Spanner provides directly impact user experience in various Google products. Understanding the core functionalities of what dbms does Google use allows for a greater appreciation of the technological feats behind the services we use daily.
The design of Spanner addresses the limitations of traditional relational databases in managing globally distributed data. Unlike traditional systems that struggle with maintaining strong consistency at scale, Spanner leverages its unique architecture and sophisticated algorithms to achieve this goal efficiently. This allows for high concurrency while maintaining data integrity. Google’s choice to develop and deploy Spanner underscores the challenges inherent in managing massive datasets with global reach and high availability demands. By creating Spanner, Google not only solved its own internal data management issues but also set a new standard for globally distributed database systems. What DBMS does Google use for its most demanding applications? The answer is increasingly, Spanner, a true testament to Google’s engineering prowess.
Bigtable: Google’s NoSQL Wide-Column Store
Bigtable, a cornerstone of Google’s data infrastructure, serves as a powerful NoSQL wide-column store. It excels at handling massive datasets, offering high throughput and low latency. Understanding what DBMS does Google use requires recognizing Bigtable’s crucial role. This distributed database system efficiently stores and retrieves data, making it ideal for applications demanding rapid access to large amounts of information. Bigtable’s architecture is designed for scalability, allowing it to seamlessly handle ever-increasing data volumes without performance degradation. The system’s ability to distribute data across multiple servers ensures high availability and fault tolerance. This is vital for Google services that rely on continuous operation.
Google leverages Bigtable’s capabilities across various services. For example, Google Analytics, a platform processing enormous volumes of user data, relies on Bigtable to store and analyze user behavior patterns. The system’s flexibility allows for efficient querying and aggregation of data, enabling the generation of insightful reports. Another example of Bigtable’s use lies within Google Cloud Storage, where it plays a critical role in metadata management. Its capacity to handle both structured and unstructured data makes it an extremely versatile solution for Google’s diverse needs. Bigtable’s efficiency stems from its unique design, allowing for rapid data retrieval even with petabytes of data. This efficiency is crucial in answering what DBMS does Google use and why Bigtable is a key component.
Bigtable’s architecture, based on Google File System (GFS), provides inherent scalability and availability. Data is distributed across many machines, minimizing single points of failure. Its wide-column store model allows flexible schema design, accommodating evolving data structures and requirements. What DBMS does Google use for handling massive datasets? Bigtable’s role is significant. This adaptability makes it a versatile solution for applications with diverse data models. The system’s design prioritizes performance, enabling real-time processing and rapid response times. This is essential for Google’s high-volume, low-latency applications, showcasing its importance within Google’s diverse database ecosystem. Bigtable’s success highlights the strategic value of choosing the right database system for specific needs.
Cloud Spanner and Cloud Bigtable: Empowering Developers with Google’s Cutting-Edge Database Technology
Google’s internal database prowess extends beyond its own walls. Cloud Spanner and Cloud Bigtable, the commercially available versions of these powerful systems, offer developers and businesses access to the same technology that powers Google’s massive infrastructure. Understanding what DBMS does Google use internally provides valuable insight into the capabilities offered through GCP. These managed services handle the complexities of scaling, maintenance, and security, allowing developers to focus on building applications rather than managing infrastructure. The question “what DBMS does Google use?” frequently arises, and Cloud Spanner and Cloud Bigtable offer a glimpse into Google’s sophisticated approach.
Cloud Spanner provides a globally-distributed, strongly consistent database service. This means applications can rely on consistent data across multiple regions, crucial for applications requiring high availability and global reach. Businesses benefit from simplified global data management, eliminating the need to build and maintain their own complex distributed systems. Cloud Bigtable, on the other hand, offers a scalable NoSQL wide-column store, ideal for handling massive datasets with high throughput and low latency. Applications such as analytics platforms, recommendation engines, and IoT data processing can leverage Bigtable’s capabilities to efficiently store and query large volumes of data. When considering what DBMS does Google use for specific tasks, Cloud Bigtable’s capabilities become particularly relevant.
The accessibility of Cloud Spanner and Cloud Bigtable through GCP democratizes access to advanced database technology. Developers can leverage these powerful tools to build robust, scalable applications without the significant investment typically associated with developing and managing similar systems in-house. The managed nature of these services reduces operational overhead, allowing businesses to concentrate on their core competencies. The ease of integration with other GCP services further enhances their appeal, streamlining the development process and facilitating seamless data management within a larger cloud ecosystem. This highlights the practical application of understanding what DBMS does Google use and how this translates into powerful tools for external developers.
Other Database Technologies Employed by Google
While Spanner and Bigtable form the core of Google’s massive data infrastructure, understanding what DBMS does Google use requires acknowledging a diverse ecosystem. Google leverages a variety of other database technologies tailored to specific needs. For instance, relational databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL might serve specific applications requiring the structure and ACID properties of traditional systems. These are often used for applications needing strong data integrity and well-defined schemas. The question, “what DBMS does Google use?”, doesn’t have a single answer; it’s a multifaceted approach.
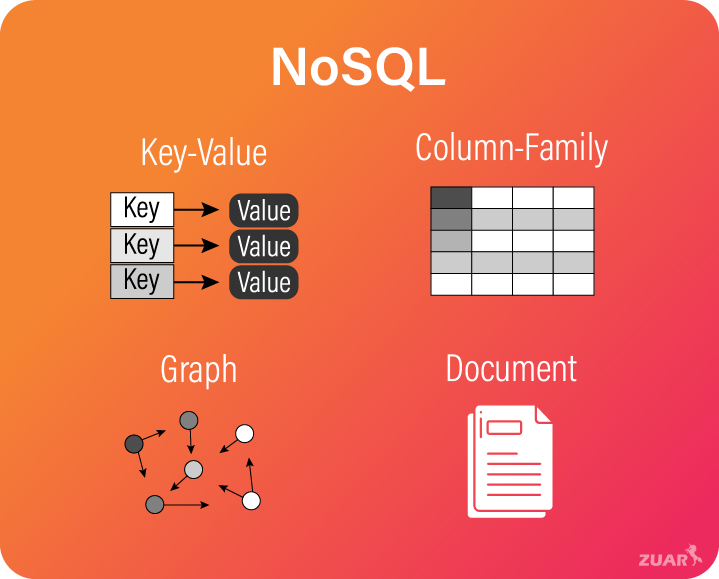
Furthermore, graph databases play a crucial role in handling data with complex relationships. These specialized systems are exceptionally efficient in modeling connections and dependencies between data points. Google likely uses such databases for applications like knowledge graphs, recommendation systems, and social network analysis. The choice of database is highly dependent on the type of data and the queries needed to be performed on the data. Google, in managing its data, cleverly selects database technology based on requirements. This is a key part of answering what DBMS does Google use.
Beyond these, Google undoubtedly employs numerous specialized databases for particular services. These might include time-series databases for analyzing sensor data, document databases for handling unstructured information, or even custom-built solutions optimized for unique Google services. The sheer scale and diversity of Google’s operations necessitate a highly adaptable and specialized database landscape. Therefore, the question “what DBMS does Google use?” is best answered with: a diverse array of technologies strategically deployed to meet unique needs. The company’s approach highlights the importance of selecting the right tool for the job in managing massive datasets.
How to Choose the Right Database for Your Needs: Lessons from Google’s Approach
Selecting the optimal database management system (DBMS) is crucial for any organization, and understanding the factors influencing this choice is paramount. Google’s diverse approach, as explored in the preceding sections—what DBMS does Google use? The answer is multifaceted—demonstrates the complexities involved. Data volume is a primary consideration. Smaller datasets might be efficiently managed by a relational database like MySQL or PostgreSQL. However, for massive datasets typical of a Google-scale operation, distributed systems like Spanner become necessary. The structure of your data also plays a critical role. Relational databases excel with structured data, while NoSQL options like Bigtable are better suited for semi-structured or unstructured data. This is a key factor that Google carefully considers when choosing what DBMS to use.
Query patterns significantly impact database selection. If your application requires frequent complex joins and transactions, a relational database might be more suitable. Conversely, if your application involves high-volume reads and writes with less emphasis on complex queries, a NoSQL database like Bigtable could provide better performance. Google’s utilization of both relational and NoSQL databases underscores the importance of aligning database technology with specific query patterns. Scalability is another essential factor. Businesses must consider how their data volume and processing requirements are expected to change over time. A scalable solution is crucial for future growth and adaptability. Considering Google’s reliance on scalable solutions like Spanner and Bigtable, this factor is essential for long-term success.
Ultimately, the best database system depends on a careful assessment of your specific needs. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Analyzing data volume, structure, query patterns, and scalability requirements allows for an informed decision. By understanding the trade-offs between different types of databases, organizations can choose the system that best supports their applications. Google’s diverse database ecosystem serves as a powerful example of how a strategic selection process can create a highly efficient and robust data management infrastructure. The question, what DBMS does Google use, highlights the importance of a tailored approach, rather than a single solution.
The Future of Google’s Database Infrastructure
Predicting the precise evolution of Google’s database infrastructure is challenging. However, several key trends suggest the direction of future development. Serverless database technology, offering scalability and cost efficiency, will likely play a more prominent role. Google’s expertise in artificial intelligence (AI) will undoubtedly be integrated further. AI-powered database management systems can optimize performance, automate tasks, and improve data insights. This integration will be crucial as the volume and complexity of data continue to grow exponentially. What DBMS does Google use? The answer is multifaceted, reflecting its complex data landscape. The ongoing evolution will likely see an increased reliance on specialized databases tailored to specific needs, alongside advancements in distributed systems like Spanner.
Google’s commitment to innovation is evident in its ongoing research and development efforts. Expect advancements in areas such as distributed consensus algorithms, improved fault tolerance, and enhanced query optimization techniques. The search for even greater scalability and performance will drive these advancements. New approaches to data modeling and management, influenced by emerging technologies like quantum computing, might also find their way into Google’s infrastructure. The integration of advanced analytics and machine learning directly into the database layer itself will improve data processing and decision-making capabilities. Understanding what DBMS does Google use requires recognizing its commitment to adapting its systems to handle constantly evolving needs.
The question, “What DBMS does Google use?”, highlights the sophisticated nature of Google’s approach. Instead of relying on a single solution, Google leverages a diverse ecosystem of database technologies. This layered approach provides flexibility and allows them to optimize for specific use cases. Future development will likely center around further refining this ecosystem, enhancing interoperability between different database systems, and seamlessly integrating emerging technologies. The challenge will be to maintain consistency and manage the complexity of this increasingly diverse and powerful infrastructure. The ongoing evolution emphasizes the need for constant adaptation and innovation in the field of database management. What DBMS does Google use? The answer continues to evolve.