What is a Remote Desktop and Why Use One?
A remote desktop allows users to access and control a computer from a different location as if they were sitting directly in front of it. This technology bridges the physical gap, enabling interaction with applications, files, and the entire operating system of a distant machine. The core concept involves transmitting the display output of the remote computer to the user’s device while simultaneously relaying their input commands back to the remote machine. This functionality is particularly useful for various scenarios. For instance, professionals can access their work computers and files from the comfort of their homes or while traveling, ensuring continuity and flexibility in their workflows. Furthermore, a remote desktop environment is an excellent solution for running resource-intensive applications, such as video editing software or complex simulations, on less powerful personal devices by leveraging the processing power of a more capable remote machine. This eliminates the need for users to purchase expensive hardware, which provides cost savings and operational convenience. Cloud-based remote desktops take this convenience a step further, offering scalable and readily available computing resources without the need to manage physical servers. This accessibility, coupled with the ability to securely connect to systems from anywhere, makes remote desktops a valuable tool for individuals and organizations alike. For example, an ‘amazon rdp’ setup gives the user access to a remote machine running on the Amazon cloud.
The flexibility afforded by remote desktop technology extends beyond just accessing work files; it’s about creating seamless and versatile working environments. Imagine a scenario where a graphic designer can continue working on a high-resolution project from a basic laptop by tapping into the power of a remote workstation with a powerful graphics card. This ability to extend capabilities from any location, enhances productivity and ensures projects are finished on time without the limitations of the user’s hardware. Moreover, with the rise of cloud services, cloud-based remote desktops have emerged as a critical solution. They offer the same functionalities of traditional remote desktops but with the added benefits of scalability, availability, and simplified management. Cloud-based solutions, such as an ‘amazon rdp’, also ensure secure access to data by centralizing resources, enhancing compliance and reducing the risk of losing data stored on less secure devices. Additionally, these systems provide options for regular backups, meaning data can easily be restored in case of any issues. Cloud-based remote desktops are therefore not just tools but are foundations for how work can be approached in the modern era, empowering users with flexibility and enhanced capabilities.
In essence, the primary purpose of remote desktops, especially cloud-based ones like an ‘amazon rdp’ instance, is to create a productive environment where users are not constrained by their physical location or the capabilities of their local devices. It provides a bridge for anyone to get into their virtual office or home workstation from anywhere using any device. The evolution of technology has brought forth this new reality where distance is no longer a barrier for productivity or work continuity. This adaptability and efficiency are the core reasons why remote desktops have become indispensable, transforming how individuals and businesses function across the globe. Remote access and control are made possible by the underlying remote desktop protocol, which facilitates the flow of information and enables seamless user experience. This is crucial for maintaining consistency and performance as well as improving overall workflow regardless of the physical location of the user.
Navigating the Landscape of Cloud Remote Desktop Services
The realm of remote desktop access has evolved significantly, with cloud-based solutions offering unprecedented flexibility and scalability. Instead of relying on traditional methods, users now have a variety of cloud platforms to choose from, each providing a unique approach to remote computing. This section will explore the options available, setting the stage for a deeper look into specific technologies. While many providers offer cloud-based remote access, the focus here is to guide users to a general understanding of what is available. Services from major providers such as Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) present robust solutions for remote desktop needs. These services allow users to access virtual machines from any location with an internet connection, providing a seamless experience akin to working directly on a local computer. These platforms offer varying features, pricing models, and levels of customization, catering to a wide range of requirements, from individual users to large enterprises, however, this section will not deep dive into specific comparisons at this moment. It is crucial for users to understand that these solutions go beyond simple remote access; they are full-fledged computing environments hosted in the cloud. The diversity in offerings means that there’s likely a cloud-based remote desktop service that aligns with almost any need and budget.
Among the various cloud-based remote desktop options, ‘Amazon RDP’ stands out as a popular and powerful solution, it is important to recognize that while the general term RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) is widely used, specific implementations can differ, and we will focus on Amazon’s implementation. When discussing cloud-based remote desktops, various terms like ‘Virtual Desktop’ and ‘Cloud Desktop’ often emerge. While these terms are frequently used interchangeably, they generally refer to the same concept: accessing a desktop environment that resides on a remote server. However, ‘Amazon RDP’ is more specific in that it is an established term, which signifies a remote desktop solution hosted on Amazon Web Services utilizing the RDP protocol. This article will use ‘Amazon RDP’ to specifically refer to this implementation. It’s important to note that while Amazon offers more specialized services like Amazon WorkSpaces, which provide a fully managed desktop solution, this section primarily focuses on understanding the landscape and not on a single service and how a manual RDP can be created on Amazon’s Cloud. So, as you navigate the landscape of cloud remote desktop services, keep in mind that different terminology can refer to similar concepts, but a clear understanding of the differences is paramount. Understanding ‘Amazon RDP’ as part of a broader remote desktop context will enable you to navigate the many options and choose the best for your needs.
How to Set Up Your Remote Desktop with Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Creating an Amazon RDP environment involves several key steps, starting with launching an Amazon EC2 instance. Begin by accessing the AWS Management Console and navigating to the EC2 service. Select “Launch Instance” and choose an appropriate Amazon Machine Image (AMI). For a Windows-based remote desktop, opt for a Windows Server AMI; for a Linux-based RDP, select a suitable Linux distribution. The selection of the instance type is vital; choose a type based on your anticipated workload, with considerations for memory, CPU, and storage. For general use, instance types like t3.medium or t3.large may suffice. Next, configure the instance details, including network settings, VPC, and subnet selection. Security Groups play a critical role; configure them to allow RDP access (typically port 3389 for Windows or port 22 for Linux using SSH) from your IP address or a specific range. Carefully review all configurations before launching the instance to avoid any errors or issues in the future. Once the instance is running, remember to create a strong user password for the administrator account for security. This process is foundational for establishing a stable Amazon RDP setup.
Once the EC2 instance is active, connecting remotely involves different steps depending on the operating system. For Windows, download the RDP file provided by AWS and use the built-in Remote Desktop Connection tool. In Linux environments, use an SSH client to connect initially. Once connected, install the necessary desktop environment (if not pre-installed) and install an RDP server like xrdp. Further configuration may include setting up static IPs, adjusting display settings, and configuring firewall rules within the operating system. Enabling remote access is a crucial step, ensuring the firewall allows incoming traffic on the RDP port. For Windows environments the remote desktop feature needs to be enabled on the system control panel. For increased access control, carefully manage the users that can connect to the Amazon RDP. Additional configuration like setting up security certificates can increase security of the RDP connection. All these steps contribute to the successful setup of your Amazon RDP, which will let you to remotely work on the system.
Optimizing Your Amazon Cloud Remote Desktop Experience
Enhancing the performance of your Amazon RDP setup involves several key considerations, primarily focused on network optimization and fine-tuning the remote desktop environment. To start, analyze your network connection; a stable, high-bandwidth internet connection is crucial for a smooth, responsive remote desktop experience. Network latency can dramatically impact the interactivity of the session. Therefore, using a wired connection rather than Wi-Fi when possible can minimize latency. Additionally, within your Amazon EC2 instance, adjusting display settings can often yield improvements; try reducing the screen resolution, color depth, or visual effects settings to lessen the amount of data being transmitted over the network. Optimizing these settings is particularly relevant if you’re using amazon rdp on a connection with limited bandwidth.
Storage and backup strategies also play a pivotal role in optimizing your amazon rdp experience. Leveraging AWS services like EBS (Elastic Block Storage) for your virtual machine’s storage is recommended. Choose a storage type (like SSD) and size that matches your performance and capacity needs. Regular backups are essential for protecting your data, so consider using AWS Backup, which offers automated and managed backup services. Another important aspect is how you handle user access. Employing AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial for securely controlling who can access your remote desktop environment. Ensure all users have the correct permissions, and rotate credentials frequently. For managing multiple users, consider creating specific IAM user profiles for better control. Also investigate the possibility of using AWS Session Manager to gain access to the EC2 instance, providing secure, audited access without requiring open RDP ports. This can significantly enhance your security posture for your amazon rdp setup.
Finally, consider the applications being used within your amazon rdp environment. Running multiple heavy processes on the remote machine simultaneously can impact performance. Monitor resource usage within the EC2 instance to understand which applications are consuming the most CPU, memory, or disk I/O. Based on this data, you may need to adjust the EC2 instance type, add additional memory, or even create multiple remote desktops for different tasks. Efficiently managing resources ensures that your amazon rdp experience remains productive and efficient. To further improve the user experience consider leveraging AWS tools like Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring resource utilization and setting alarms to proactively address performance issues. Regular monitoring will help you fine-tune the setup to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction with your remote desktop setup.
Understanding Cost Implications of Amazon RDP Services
The financial aspects of utilizing Amazon RDP services are multifaceted and warrant careful consideration. The primary cost driver is the Amazon EC2 instance itself, which is billed based on the chosen instance type, size, and operating system, as well as the duration of usage. Costs will also accrue from data transfer, where both inbound and outbound network traffic are charged, and these costs can vary based on the amount of data moved. Storage costs also need to be factored in, covering the storage volume attached to the Amazon RDP instance, in addition to any backups or snapshots taken. Furthermore, software licenses, if needed, can add to the overall expenditure, especially for Windows Server instances that require their own licensing fees. Understanding these different elements is crucial for effective budget management. Careful planning can lead to cost optimization of your Amazon RDP environment.
Several strategies are available to minimize costs while maintaining the necessary performance and availability of your Amazon RDP setup. Utilizing Reserved Instances, for example, can provide substantial discounts on EC2 usage compared to on-demand pricing if you can commit to a consistent level of usage. Selecting the appropriate instance type and size according to the actual workload is also vital; over-provisioning leads to unnecessary expenses while under-provisioning can cause performance issues. Regularly reviewing and optimizing data usage can help control transfer fees. It’s also wise to explore options for storage and backups that are cost-effective, balancing data protection needs with budgetary limitations. By adopting these practices, users can ensure they are only spending on what is absolutely necessary for their Amazon RDP needs and avoiding budget overruns. Choosing the right tools and setting up cost alerts in AWS can also prevent unexpected bills. A well-planned amazon rdp solution will always be more cost effective.
Beyond the base EC2 costs, be mindful of associated expenses such as the storage for your AMIs, if you create and save your machine images, as well as any additional network costs for using load balancers or other services associated with your Amazon RDP deployment. Considering all components within your AWS environment will help with accurate budget management. Finally, if your instances are not being used 24/7, look into options to start and stop your amazon rdp instances. Doing so will save a considerable amount of money if the instances are only used during working hours, for example.
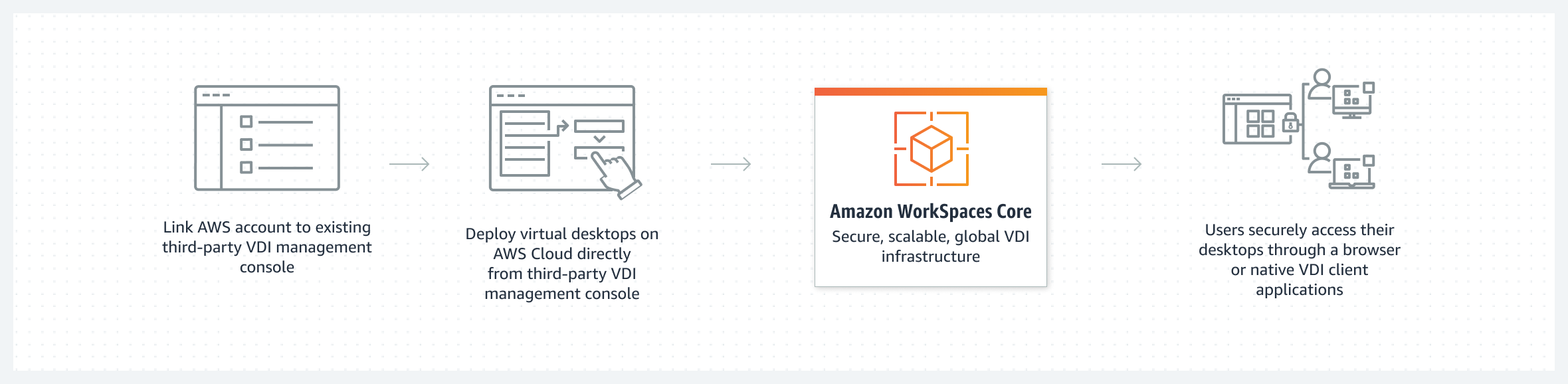
Alternatives to Traditional RDP: Exploring Amazon WorkSpaces
While setting up a manual Amazon RDP environment using EC2 instances offers considerable flexibility, it might not always be the most efficient or manageable solution, especially for larger organizations. This is where Amazon WorkSpaces presents itself as a compelling alternative. Amazon WorkSpaces is a fully managed desktop-as-a-service (DaaS) solution that provides users with access to cloud-based desktops, simplifying the complexities often associated with manual remote desktop configurations. Unlike the do-it-yourself approach with EC2, WorkSpaces handles the underlying infrastructure, provisioning, and maintenance, allowing administrators to focus on user needs rather than infrastructure upkeep. The deployment process is significantly streamlined, allowing quick scaling of virtual desktops for a growing workforce and the management of operating system upgrades, patching, and backups become less burdensome. This managed approach not only reduces the operational overhead but also accelerates the time to deploy and onboard new users, making it an attractive option for environments that prioritize agility and ease of use. Furthermore, using Amazon WorkSpaces allows for granular access controls and centralized management of all user environments, enhancing security across the organization without the overhead of creating and maintaining custom Amazon RDP solutions.
One of the key advantages of Amazon WorkSpaces over traditional Amazon RDP setups is its built-in support for various client devices and operating systems, offering a consistent user experience regardless of the device being used to connect. Additionally, WorkSpaces provides integrated security features, such as data encryption and single sign-on options, which make it an ideal solution for maintaining a secure environment. For organizations looking to offer their employees a simple, ready-to-use cloud-based desktop environment, WorkSpaces effectively eliminates the need for the manual configuration of remote access software and all the related complexities that may arise while trying to manage it. Moreover, unlike managing individual Amazon RDP instances, WorkSpaces is designed to facilitate user access management, permissions, and compliance with ease of use for administrators, especially when managing many users. Choosing WorkSpaces might lead to a more efficient overall operation, eliminating the complexities of manual setup and ongoing management of multiple Amazon RDP instances, particularly in situations where scalability, security, and simplified management are essential.
The cost structure of Amazon WorkSpaces, while different from EC2-based Amazon RDP, is designed to be predictable. Typically, pricing is either per user per month or hourly, allowing organizations to align expenses with usage patterns, thus optimizing cost-effectiveness. The value proposition of Amazon WorkSpaces lies in its blend of flexibility, security, and ease of management, making it an ideal solution for those who want to avoid the complexities associated with manual Amazon RDP configurations and want a more streamlined, secure, and efficiently managed cloud desktop environment. Although it might come at a different price point than a simple Amazon RDP, the total cost of ownership over time, including time spent in manual maintenance, can often be lower for managed services like WorkSpaces, specially considering the scalability and user access management it offers.
Security Best Practices for Your Cloud-Based Remote Desktop
Securing your cloud-based remote desktop environment, particularly when using Amazon RDP, is of paramount importance. A compromised remote desktop can expose sensitive data and provide a gateway for malicious activities. Therefore, implementing robust security measures is not just advisable—it’s a necessity. A fundamental step is the enforcement of strong, unique passwords for all user accounts. Avoid using easily guessed passwords or reusing passwords across multiple services. For an added layer of protection, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors, such as a password and a code from a mobile device, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised. Furthermore, restrict access based on IP addresses. This can be achieved through the configuration of security groups within your Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment, only allowing connections from known and trusted IP ranges, limiting potential entry points for malicious actors. Another critical aspect involves routinely updating all software on your Amazon RDP instance, including the operating system, RDP client, and any installed applications. Software vulnerabilities are constantly being discovered and exploited, so keeping your systems updated ensures you’re protected against the latest threats.
Network security is another cornerstone of a robust Amazon RDP setup. AWS Security Groups act as virtual firewalls, controlling inbound and outbound traffic to your Amazon EC2 instances. Configure these security groups to only permit traffic on necessary ports, specifically the RDP port (typically 3389). Avoid exposing unnecessary ports, as these can be exploited by attackers. Consider further enhancing your network security through network isolation techniques. This could involve placing your RDP instances within private subnets and routing traffic through secure gateways, adding layers of defense that hinder lateral movement within your network if an intrusion occurs. Always use the principle of least privilege by granting only necessary permissions to users, minimizing the potential impact of compromised credentials. Regularly audit access logs to detect any unusual activity and maintain your Amazon RDP system security. Remember that security is not a one-time task; it is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats. By implementing and maintaining these security best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your sensitive data when using Amazon RDP.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Amazon Remote Desktops
Encountering technical difficulties is a common part of the remote desktop experience, and understanding how to address these challenges is key to a seamless workflow. When working with an Amazon RDP setup, connection problems are among the most frequently reported issues. These can range from simple network connectivity glitches to more complex firewall configurations blocking access. A primary step is verifying that the security group rules for the Amazon EC2 instance are correctly configured to allow RDP traffic on port 3389. Furthermore, ensure that the remote computer’s operating system firewall is not preventing incoming connections. It’s also critical to double-check the network path between your local computer and the Amazon RDP instance, ensuring that there are no intermediary network devices blocking communication. Another common hurdle is related to login credentials; if you cannot log in to the Amazon RDP, be sure you have the correct username and password. For Windows instances, the initial password is generated by AWS and can be retrieved using the private key associated with your EC2 instance.
Performance issues, such as slow screen updates and lags in input response, are often reported with an Amazon RDP. Optimizing the connection for better performance can involve several techniques. Start by ensuring that your local internet connection is stable and has sufficient bandwidth. Network latency also plays a critical role; try to establish the amazon rdp connection from a location closer to the AWS server region. Display settings on both the local computer and the remote server can significantly impact performance; reducing the color depth and display resolution can alleviate bottlenecks, particularly when working over slower connections. The choice of the AWS EC2 instance can also heavily influence the overall experience; instances with limited CPU or memory will result in poor performance, so choosing an instance type with appropriate resources is essential. Additionally, it is necessary to check the resource usage on the Amazon RDP server. If the instance is maxed out, then the performance will be affected, which might require a larger instance size. If the issues persist, consider restarting the EC2 instance or applying updates to the operating system.
Software compatibility problems may occur when running certain applications within the amazon rdp environment. Not all programs are designed to work flawlessly over a remote connection. If you notice applications crashing, lagging, or not working correctly, examine the specific program requirements to verify if the Amazon RDP is the bottleneck. Some applications can be configured with different settings to work better with remote access. Verify that the latest video drivers are installed, particularly if the software relies heavily on graphics processing. Moreover, if an application needs a specific Windows version, it might also be the root of the problem. If all else fails, troubleshooting logs on both the amazon rdp server and the client computer should be consulted to identify clues. If you are still encountering issues with a specific piece of software, consider consulting support forums or the software developers for advice.