Understanding the Need for an On-Premises Data Gateway
Many businesses rely on valuable data stored within their on-premises databases – systems like SQL Server, Oracle, and others. However, leveraging this crucial data for insightful Power BI reporting presents a challenge. Cloud-only Power BI solutions lack the direct access needed to these on-premises data sources. This limitation significantly restricts the ability to create comprehensive and up-to-date reports, hindering effective data-driven decision-making. An on-premises Power BI gateway acts as the critical bridge, securely connecting your local data to the cloud-based Power BI service. This allows for the creation of powerful and dynamic reports based on a complete data picture, significantly improving data access and leading to better business outcomes. The implementation of an on-premise power BI gateway unlocks the full potential of your data, transforming it into actionable intelligence. This enables organizations to make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge by utilizing all available data, not just a fraction of it. The on-premise power BI gateway thus represents a powerful tool for any organization seeking to improve its data analysis and reporting capabilities.
Without a solution like the on-premises Power BI gateway, organizations face significant limitations. Real-time data integration becomes impossible, leading to outdated reports and potentially flawed analyses. Decision-makers are left with incomplete information, hindering their ability to respond effectively to market changes and operational challenges. The inability to easily access and analyze on-premises data results in missed opportunities for optimization and innovation. Implementing an on-premise power BI gateway eliminates these limitations, providing a secure and efficient method for connecting to diverse on-premises data sources, including those with complex security protocols. The benefits extend to improved collaboration, as teams can access a single source of truth for reporting and analysis, regardless of location. The increased efficiency and enhanced data accessibility contribute to a significant return on investment by empowering data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
The value proposition of using an on-premise power BI gateway is clear: it democratizes access to critical business data. By bridging the gap between on-premises databases and the Power BI cloud service, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data assets. This translates to more informed decisions, improved operational efficiency, and the ability to create compelling and insightful reports. The on-premise power BI gateway empowers businesses to move beyond limited, cloud-only solutions and embrace a comprehensive approach to data analysis and reporting, ultimately driving business growth and success. This secure and reliable solution simplifies complex data integration, offering significant benefits in terms of improved data accessibility, enhanced decision-making, and the creation of richer, more informative reports.
Introducing the Power BI Data Gateway – A Deep Dive
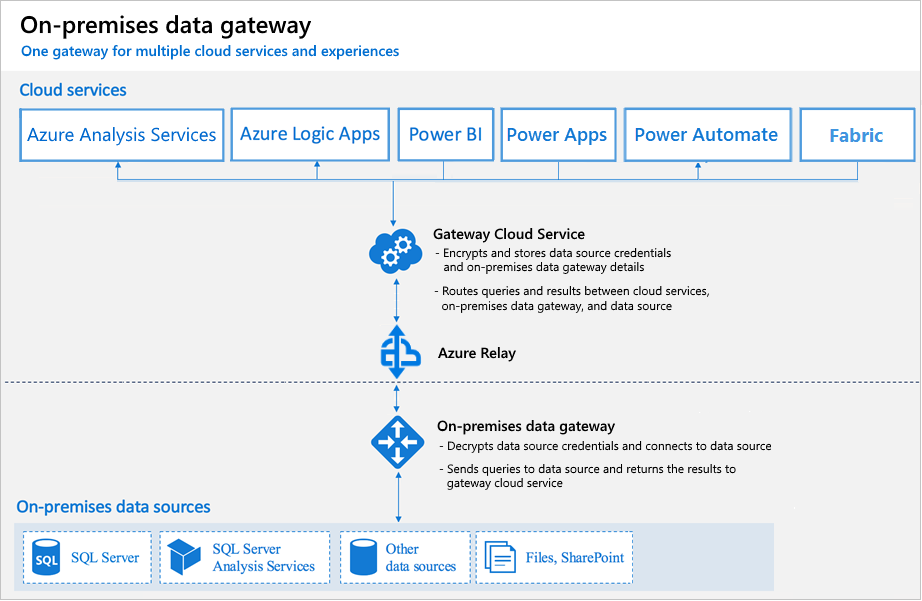
The Microsoft Power BI Data Gateway acts as a bridge, enabling seamless connectivity between your on-premises data sources and the cloud-based Power BI service. This on-premise Power BI gateway facilitates data access for Power BI reports and dashboards, even when the data resides behind your organization’s firewall. Its core functionality revolves around securely transferring data from on-premises databases to the cloud, empowering users to create comprehensive and insightful reports based on a complete view of their data. The Power BI on-premise gateway supports a wide array of data sources, including but not limited to SQL Server, Oracle, SAP HANA, MySQL, and many more. This versatility makes it adaptable to various business environments and data architectures. Understanding the on premise power bi gateway’s role is critical for leveraging the full potential of Power BI.
The on premise power bi gateway isn’t just about initial data import; it’s also crucial for maintaining data freshness. Through scheduled data refreshes, the gateway ensures that Power BI reports reflect the latest information from your on-premises systems. This real-time or near real-time capability is vital for timely decision-making and accurate reporting. The gateway handles the complex process of data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) transparently, shielding users from the technical complexities involved. Different deployment modes, such as personal gateways for individual users and organizational gateways for enterprise-wide access, cater to diverse needs and security requirements within an organization. The on premise power bi gateway provides granular control over data access, allowing administrators to define specific permissions and ensure data security. This robust functionality empowers data-driven decision making without sacrificing data integrity or security.
Beyond its core functionality, the on premise power bi gateway offers features designed for optimal performance and scalability. It incorporates efficient data transfer mechanisms to minimize refresh times and reduce the strain on network bandwidth. Furthermore, the gateway’s architecture is designed to handle large datasets and high-frequency refreshes without compromising performance. Administrative tools allow for comprehensive monitoring and management, giving administrators insights into data refresh status, resource usage, and any potential errors. These capabilities, combined with the gateway’s broad data source compatibility, make the on-premise Power BI gateway a powerful tool for organizations seeking to unlock the full potential of their on-premises data within the Power BI ecosystem. Properly configuring the on premise power bi gateway is essential for maximizing its benefits.
How to Set Up and Configure Your On-Premises Power BI Data Gateway
Setting up an on premise power bi gateway is a straightforward process, yet careful configuration is key for seamless data connectivity. The initial step involves downloading the gateway installer from the Power BI service website. During installation, you’ll be prompted to choose between a personal mode or an on-premises data gateway in standard mode. The personal mode is suited for individual use and allows connection to a single Power BI user account, ideal for testing and development. However, for organizational deployments, the standard mode is recommended. This mode enables multiple users to connect through the same gateway, and allows centralized management. When selecting the standard mode, ensure you have the appropriate administrative privileges on the machine. The installation wizard guides you through the necessary configurations, including selecting a service account under which the gateway will operate. It’s best practice to utilize a dedicated service account to provide greater security. Once installed, the on premise power bi gateway requires configuration through the Power BI service web interface, where it must be registered to your Power BI tenant.
After installing the on premise power bi gateway, the next crucial phase is configuring it within the Power BI service. Navigating to the “Manage gateways” section within Power BI service allows you to view your installed gateways and modify its settings. During the registration process, you will be asked to provide a name for your gateway for identification within Power BI, and create a recovery key to maintain gateway control. The registration process links the gateway to your Power BI tenant. Then, ensure the gateway service has the required network access and firewall exceptions to communicate with your on-premises data sources and the Power BI cloud. Furthermore, it’s important to establish connectivity to your data source, which requires providing the relevant server details and data access credentials. The on premise power bi gateway will then manage the secured connection between the data source and your Power BI reports. The gateway’s status, which should be “online,” can be monitored within the Power BI admin portal to ensure optimal functionality. Regular updates are crucial to maintain security and compatibility with the latest Power BI features, and these updates can be managed directly through the gateway configuration screen.
Troubleshooting common installation issues for an on premise power bi gateway usually involves verifying network connectivity and proper service account permissions. Check if the server where the gateway is installed can communicate with the Power BI service. You might need to configure proxy settings if your organization uses a proxy server. Often, installation failures stem from conflicts with existing software or insufficient permissions during installation. Consult Microsoft’s extensive documentation for troubleshooting specific installation error codes. Addressing these issues quickly ensures the gateway operates as expected, enabling consistent access to your on-premises data, allowing seamless and timely data refreshes in your Power BI reports. Remember, successful implementation is fundamental for empowering data-driven insights in your organization.
Connecting Your On-Premises Data Sources to Power BI
Establishing a connection between your on-premises data and Power BI involves several key steps, primarily leveraging the installed on premise power bi gateway. After successfully installing and configuring your on premise power bi gateway, the next phase entails connecting it to your specific data sources. This process begins within the Power BI Desktop environment, where you’ll initiate the connection to your on-premises database, such as SQL Server, Oracle, or other supported platforms. Within Power BI Desktop, you’ll select the “Get Data” option, choose your specific data source, and then you will be prompted to provide connection details. Crucially, when configuring the connection, you must select the option to connect via the on premise power bi gateway, which directs the request through your configured gateway rather than attempting a direct cloud connection. When you pick this option, Power BI will display a list of all the gateways available, and you will pick the one that is linked to your data source. After picking your gateway and inserting the required connection credentials, Power BI Desktop will allow you to access and load data from your on-premises source. Screenshots at each step offer visual guidance for the connection process within the Power BI Desktop interface and the gateway settings pages. These screenshots will help verify your connection is correctly established, highlighting the importance of having an active gateway connection for data access. Proper configuration ensures that Power BI can smoothly communicate with your on-premises infrastructure and retrieve the required data.
To configure data refresh schedules for your on premise power bi gateway, you will do so within the Power BI Service, the cloud based version of Power BI. After publishing your report created in Power BI Desktop, you can navigate to the dataset settings within the Power BI Service. Here, you can set the frequency of data refreshes, specifying how often Power BI should connect through your on premise power bi gateway to retrieve updated data. Options range from hourly, daily, or weekly depending on your need and data volume. It is critical to configure your data credentials securely through the Power BI Service and within the gateway itself. This step ensures that all connection information is securely stored and properly authenticated every time the data refresh happens. These credentials need to match the authentication requirements of the on-premises database you are using, so you have to consider the authentication type that your database requires, such as Windows authentication or database user credentials. You may need to add your data source to the on premise power bi gateway’s configuration to enable it for refresh. After all these configurations, it will be possible to keep your Power BI reports up-to-date using your on-premise data without any manual intervention. The on premise power bi gateway thus serves as a secure and efficient bridge, ensuring that your cloud-based Power BI dashboards reflect the most recent changes in your on-premises systems.
Optimizing Data Refresh and Performance with the Gateway
Efficient data refresh and optimal performance are crucial for effective Power BI reporting, particularly when dealing with on-premises data. The on premise power bi gateway plays a pivotal role in this process. Several strategies can significantly enhance your experience. Firstly, data modeling is key. Creating optimized data models in Power BI Desktop, which includes only the necessary tables and columns, can greatly reduce the data being transferred. This minimizes the load on both the gateway and the on-premises data source. Avoid importing excessive data and implement data transformations in Power Query to streamline the data retrieval process. Query optimization at the source database level is another essential practice. Ensure that your queries are written efficiently, making use of indexes and other database-specific techniques to minimize data retrieval times. It is recommended to regularly review and adjust SQL queries being sent by Power BI for the on premise power bi gateway. The configuration of the on premise power bi gateway itself also affects performance; allocating sufficient memory and CPU resources to the gateway server can improve data processing and transfer speeds. Consider the impact of network bandwidth and latency; a reliable and high-bandwidth connection between the gateway and the data source is vital for efficient data transfers. Scheduling data refresh strategically is also important. Rather than setting overly frequent refreshes, determine the optimal refresh schedule that balances data freshness with system resource utilization, ensuring that the on premise power bi gateway isn’t overloaded during peak business hours.
Furthermore, consider incremental refresh capabilities within Power BI, when appropriate. This feature retrieves only the data that has changed since the last refresh, reducing the time and resources required for data updates with your on premise power bi gateway. This works best with large datasets where changes are more predictable. Regularly monitor the on premise power bi gateway’s performance via the Gateway Performance Monitoring in the Power BI admin center. This allows for detecting bottlenecks and addressing them promptly. It provides crucial information on gateway performance, CPU and memory usage and general connectivity. Another critical aspect is to keep your on premise power bi gateway up to date with the latest version; each new release brings performance enhancements and bug fixes which are crucial for optimal operations. Implement a scheduled check up to upgrade and maintain a healthy version to avoid unexpected issues. By carefully combining data modeling, query optimization, proper gateway configuration and strategic refresh management, the efficiency of the on premise power bi gateway can be maximized to provide timely and accurate data for impactful Power BI reports. Regular performance checks and constant adjustments will be needed to guarantee optimal dataflow.
Troubleshooting Common On-Premises Gateway Issues
Navigating the intricacies of an on premise power bi gateway can sometimes present challenges. Connectivity issues often top the list, frequently arising from incorrect network configurations or firewall restrictions preventing communication between the gateway and the Power BI service or the data source. Ensure that the machine hosting the on premise power bi gateway has the necessary network access to both the Power BI service and the on-premises data sources. Double-check firewall rules and proxy settings to allow for seamless communication. Authentication errors can also be a hurdle, often stemming from incorrect credentials stored within the gateway or expired data source passwords. Verify that the credentials used by the gateway are valid and have the appropriate permissions to access the data source. Furthermore, ensure that the correct authentication type is selected when setting up the data source connection.
Another prevalent issue is slow data refresh times. Several factors can contribute to this, including the complexity of data queries, network latency, and insufficient resources allocated to the on premise power bi gateway server. Optimizing data models, streamlining queries, and ensuring the gateway server has ample CPU and memory resources is crucial. Analyzing the gateway logs can often pinpoint bottlenecks and provide valuable insights into the source of the problem. It’s important to explore resources available from Microsoft which provide detailed information on common errors and recommended solutions, helping users proactively address these issues. Additionally, issues may be caused by the gateway service itself, restarting the gateway service can also help solve some of the errors. Remember to also check the status of your on premise power bi gateway on the Power BI admin portal for more insight.
Security Best Practices for On-Premises Data Gateways
Securing the on premise power bi gateway is paramount for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of your business intelligence infrastructure. A robust security strategy must encompass multiple layers, starting with network security. The gateway should ideally reside within a protected network zone, shielded from direct exposure to the public internet. Employing firewalls and intrusion detection systems further reinforces this perimeter. Access controls are equally critical; restrict access to the gateway configuration to only authorized personnel. User authentication plays a vital role here, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized users can manage the gateway or access connected data sources. Implement strong passwords or multi-factor authentication for an additional layer of protection. Beyond access control, consider the data itself: when moving data between on-premise systems and Power BI, data encryption is essential. Confirm that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Leverage TLS (Transport Layer Security) for data transfer, and where possible use encryption features offered by your database systems. Regular monitoring of the on premise power bi gateway is essential for detecting any unusual activity or potential breaches, and proactive alerting configurations can help you respond promptly.
Certificate management is another significant aspect of on premise power bi gateway security. The gateway uses certificates for secure communication, so ensure you use valid and trusted certificates. Monitor certificate expiration dates and renew them before they lapse to prevent disruptions. Furthermore, data governance policies should extend to your on premise data gateway. Defining clear rules for data access, data usage, and data privacy is crucial in ensuring compliance and protecting your organization’s information assets. Establish clear responsibilities for managing the gateway, including user accounts and data source connections. Secure configuration settings will also reduce security risks, so avoid sharing sensitive information in configuration files. Best practices include ensuring the gateway server’s operating system is up-to-date with the latest security patches to mitigate vulnerabilities and using a dedicated server for the on premise power bi gateway to reduce the impact of potential security issues. Properly managing and regularly updating the on premise power bi gateway enhances security and promotes reliable data access for your Power BI reporting.
Migrating from Older Gateway Versions to the Latest Release
Upgrading to the latest on premise Power BI gateway version offers several significant advantages. Newer releases often include performance enhancements, improved security features, and support for the latest data sources and Power BI functionalities. A smoother, more efficient data refresh process is a key benefit, resulting in faster report loading times and a more responsive Power BI experience. Enhanced security protocols in newer gateway versions better protect sensitive on-premises data, mitigating potential vulnerabilities and ensuring data integrity. Furthermore, upgrading ensures compatibility with future Power BI updates and avoids potential issues arising from using outdated software. The migration process itself is generally straightforward, although the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the source and target versions. Microsoft provides comprehensive documentation and support resources to guide users through the upgrade procedure. The process typically involves uninstalling the old gateway, downloading the latest installer from the official Microsoft website, and then following the installation wizard. It’s crucial to back up the gateway configuration before starting the upgrade to ensure a seamless transition and facilitate rollback if necessary. Careful consideration should be given to downtime, as the gateway might need to be temporarily offline during the upgrade. Scheduling the upgrade during off-peak hours can minimize disruption to users. Before initiating the upgrade, carefully review the release notes and compatibility requirements to ensure a smooth and successful migration to the newest on premise Power BI gateway version.
Addressing potential compatibility issues during a gateway upgrade requires proactive planning and preparation. The first step involves reviewing the release notes for the new version to identify any potential breaking changes or known compatibility problems with existing data sources or Power BI configurations. Thorough testing in a non-production environment before deploying the upgrade to the production system is strongly recommended. This allows for the identification and resolution of any compatibility issues in a controlled setting, minimizing the risk of disruption to business operations. Furthermore, understanding the dependencies of your current on premise Power BI gateway configuration is crucial. This includes identifying any custom scripts or configurations that may need adjustments to maintain compatibility with the new version. Microsoft provides detailed documentation and troubleshooting resources to aid in resolving any unexpected compatibility problems. When faced with compatibility challenges, consulting Microsoft’s support channels or community forums can provide valuable insights and solutions from experienced users. Proactive problem-solving through careful planning, comprehensive testing, and utilization of readily available support resources can ensure a smooth and efficient upgrade of the on premise Power BI gateway.
Successfully migrating to the latest on premise Power BI gateway release hinges on a well-defined strategy and meticulous execution. This involves a thorough assessment of the current gateway setup, careful review of release notes and compatibility documentation, and a comprehensive testing phase in a non-production environment. By following a structured approach that includes backing up the existing configuration, scheduling downtime strategically, and utilizing Microsoft’s support resources, organizations can ensure a seamless transition to the latest gateway version. This upgrade not only enhances data connectivity and reporting capabilities but also reinforces security and optimizes performance. The advantages of improved speed, enhanced security, and compatibility with future Power BI enhancements outweigh any potential inconvenience associated with the upgrade. Addressing compatibility challenges through thorough preparation and testing enables a smooth transition to the latest on premise Power BI gateway version, maximizing the benefits of this crucial component of the Power BI ecosystem. The result is a more efficient, secure, and future-proof on premise Power BI gateway infrastructure, fully leveraging the benefits offered by the latest version.