What is Oracle Autonomous Database and Why Choose It?
Oracle Autonomous Database represents a groundbreaking advancement in database management, offering a fully managed, self-driving cloud database service. Unlike traditional databases requiring significant manual administration, oci autonomous database automates virtually all aspects of database operations, including patching, backups, tuning, and security. This automation significantly reduces the administrative overhead associated with managing complex database infrastructure, freeing up IT teams to focus on higher-value initiatives. The core value proposition of oci autonomous database lies in its ability to deliver exceptional performance, enhanced security, and improved availability with minimal human intervention. This translates to significant cost savings, reduced risk, and improved agility for organizations of all sizes. The inherent scalability and elasticity of the oci autonomous database further ensures optimal resource utilization, adapting seamlessly to changing workload demands.
One of the key advantages of adopting Oracle Autonomous Database is the significant improvement in performance. The self-tuning capabilities, driven by advanced machine learning algorithms, constantly optimize the database’s configuration and resource allocation to ensure optimal query execution and response times. This eliminates the need for manual performance tuning, a traditionally time-consuming and complex task. Moreover, oci autonomous database boasts robust security features, including automated security patching and encryption at rest and in transit, minimizing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. The platform’s proactive security monitoring and threat detection capabilities further enhance its security posture, providing an extra layer of protection against sophisticated cyber threats. These integrated security features, combined with the automated management capabilities, make oci autonomous database an ideal choice for organizations with stringent security requirements.
Choosing Oracle Autonomous Database empowers businesses to focus on their core competencies rather than database administration. The pay-per-use pricing model offers flexibility and cost-effectiveness, eliminating the need for upfront capital investments and aligning costs directly with actual usage. By leveraging the power of automation and machine learning, oci autonomous database not only simplifies database management but also enhances operational efficiency, improves performance, and strengthens security, ultimately enabling organizations to achieve greater agility and innovation. The platform’s intuitive interface and comprehensive documentation further simplify the adoption and management process, making it accessible to both experienced database administrators and novice users alike. Oracle’s commitment to continuous innovation ensures that oci autonomous database remains at the forefront of database technology, constantly evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of the modern enterprise.
Provisioning Your First Oracle Autonomous Database Instance: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating your first oci autonomous database instance is straightforward. Begin by logging into the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) console. Navigate to the Database service and select “Create Autonomous Database.” You’ll then be presented with a form requiring key decisions. First, choose the appropriate workload type: Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) for OLTP applications or Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW) for analytical workloads. Carefully consider your application’s needs; ATP excels in handling frequent, short transactions, while ADW is optimized for large-scale data analysis and reporting. Selecting the correct workload type is crucial for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Next, specify the desired compute resources, including the CPU cores and storage capacity. These options are scalable, allowing adjustments based on projected growth and resource demands. Remember to select a suitable compartment for organizing your resources within OCI. This step is vital for managing access control and resource allocation efficiently.
The next stage involves configuring network access for your oci autonomous database. You’ll need to specify a virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnet, ensuring appropriate connectivity for your applications and users. OCI provides detailed instructions and guidance on network configuration. Proper network setup is paramount for ensuring secure and reliable access to your database. Once the network is configured, proceed to define the database credentials. This includes specifying a unique administrator username and password. Choose strong and secure credentials to protect your database against unauthorized access. OCI enforces strict password complexity requirements to enhance security. Remember that these credentials will grant you administrative access, so secure them appropriately. Consider using a password management tool to help maintain strong and unique credentials across all your cloud resources. Finally, review your configuration settings carefully before clicking “Create.” OCI will then provision your autonomous database instance. The provisioning process may take some time depending on the selected resources. Upon completion, you will receive a notification indicating the instance is ready for use.
After successful provisioning of your oci autonomous database, you can connect to your instance using the provided connection details. Oracle provides various tools and clients for database connectivity. Familiarize yourself with the Oracle documentation and choose the client best suited to your application’s needs and your technical skills. Remember to always adhere to security best practices when connecting to your database instance, including using secure connection protocols and regularly updating your connection tools and clients. Monitoring the database instance’s performance is crucial for maintaining optimal efficiency. OCI offers various built-in performance monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into database activity. Regularly reviewing this data allows you to proactively identify and resolve potential performance bottlenecks, ensuring continuous and optimized operation of your oci autonomous database instance. Proactive monitoring is key to the long-term success of your cloud database strategy.
Key Features of Oracle Autonomous Database That Set it Apart
Oracle Autonomous Database distinguishes itself through a suite of innovative features designed to simplify database management and enhance performance. Automated patching and upgrades are a cornerstone, eliminating the need for manual intervention and minimizing downtime. This automated process ensures the oci autonomous database is always running on the latest version, benefiting from the latest security patches and performance enhancements. Furthermore, built-in security capabilities provide robust protection against threats. These capabilities encompass data encryption at rest and in transit, network security controls, and granular access management using database users and roles. The proactive security monitoring features continuously analyze the database for suspicious activity, providing an extra layer of defense against potential breaches. The platform’s self-scaling resources automatically adjust compute resources based on workload demands, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention. This dynamic resource allocation eliminates the need for capacity planning and reduces operational overhead. This scalability is a key advantage for organizations experiencing fluctuating workloads, allowing for efficient resource utilization and cost optimization.
Machine learning plays a crucial role in the performance tuning capabilities of Oracle Autonomous Database. The platform leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze database activity and automatically adjust configuration parameters for optimal performance. This intelligent tuning eliminates the need for manual performance optimization, freeing up database administrators to focus on higher-level tasks. The oci autonomous database’s self-driving nature extends to its self-healing capabilities, automatically detecting and resolving issues without human intervention. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and ensures continuous availability, a significant benefit for mission-critical applications. The cost-effective pay-per-use model further enhances the value proposition. Users only pay for the resources they consume, eliminating the need for upfront investments in hardware and reducing the total cost of ownership. This flexible pricing model makes Oracle Autonomous Database an attractive option for organizations of all sizes, from small startups to large enterprises.
Another key differentiator is the seamless integration with other Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) services. This integration allows for efficient data management and streamlined workflows across various cloud-based applications. The ease of use and intuitive interface makes oci autonomous database accessible to both experienced database administrators and less experienced users. The comprehensive documentation and readily available support resources further enhance usability, reducing the learning curve and accelerating deployment. The platform’s ability to handle various workloads, from transaction processing to data warehousing, further underscores its flexibility and adaptability to diverse business requirements. By automating routine tasks, enhancing security, and optimizing performance, Oracle Autonomous Database empowers organizations to focus on their core business objectives, rather than on managing complex database infrastructure. The innovative features provided by Oracle Autonomous Database position it as a leader in the self-driving database landscape, delivering both efficiency and resilience for modern data management needs.
Autonomous Data Warehouse vs Autonomous Transaction Processing: Which to Select?
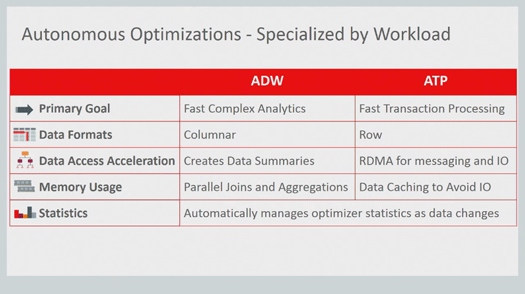
Understanding the nuances between Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW) and Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) is crucial for leveraging the full potential of Oracle’s autonomous database offerings. ADW is specifically designed for analytical workloads, focusing on large-scale data analysis and reporting. It excels in scenarios involving complex queries, data warehousing, and business intelligence applications. Its columnar storage and optimized query processing engine allow for efficient analysis of vast datasets, providing valuable insights from aggregated data. In contrast, ATP is tailored for transactional applications that require high concurrency and real-time data processing. It shines in environments where numerous transactions are processed simultaneously, with a focus on quick response times and data consistency. This makes ATP ideal for applications such as online banking, e-commerce platforms, and other systems demanding instant transactional updates. When choosing between these two, the primary consideration revolves around the intended use case: if the goal is deep analytical insight from large historical datasets, ADW is the superior choice. However, if the system needs to manage a high volume of transactions with rapid and reliable data access, then ATP is the preferred option. The oci autonomous database service offers both choices tailored for specific user needs.
Further differentiating ADW and ATP involves examining their technical underpinnings and performance characteristics. Autonomous Data Warehouse leverages features like column-oriented storage, which is optimized for analytical queries that typically read a small subset of columns across many rows. This contrasts with ATP’s row-oriented storage, which is more efficient for applications that need to access all columns of a few rows simultaneously in transactional workflows. The oci autonomous database is designed to manage these complexities, users can focus on using the selected technology. ADW typically uses query execution methods that are designed to leverage parallel processing and data aggregation, crucial for handling complex analysis and creating reports from large datasets. ATP, on the other hand, is equipped with features that guarantee transactional integrity and low-latency processing, essential for environments where transactions need to occur rapidly and reliably. The platform’s self-tuning capabilities ensure each environment is optimized for its specific purpose. For instance, the query optimizer in ADW is geared towards analyzing large datasets, while in ATP it’s designed to minimize transaction response times. Selecting the right autonomous database is really a matter of aligning the service’s capabilities with the application’s fundamental requirements.
In practical real-world scenarios, a retail company might utilize Autonomous Data Warehouse to analyze sales data, inventory levels, and customer demographics to identify purchasing patterns and optimize product placement, resulting in actionable business insights. They would leverage the power of the oci autonomous database’s analytics capabilities to make informed decisions. Conversely, the same company could use Autonomous Transaction Processing to handle online customer orders and real-time inventory updates. In this case, ATP would ensure each transaction is handled swiftly, maintaining a seamless and consistent experience for online shoppers. Similarly, a financial institution might employ ADW for compliance reporting, risk analysis, and detecting fraudulent activities, where large volumes of historical data are analyzed. At the same time, they would use ATP to manage the day-to-day processing of customer transactions and fund transfers. Understanding these key differences ensures each workload is deployed on the optimal platform, maximizing performance and minimizing costs. The proper selection of the oci autonomous database service is key for business goals.
Optimizing Performance of your Autonomous Cloud Database
Achieving optimal performance with an oci autonomous database involves a multi-faceted approach, leveraging both its inherent automated capabilities and user-directed optimization strategies. While the platform excels at self-tuning, understanding best practices for query optimization remains crucial. Begin by analyzing query execution plans to identify potential bottlenecks, such as full table scans or inefficient join conditions. Employ appropriate indexing techniques to accelerate data retrieval; creating indexes on frequently queried columns can significantly reduce query times. Consider composite indexes for queries involving multiple columns, and regularly review index usage to remove any unused indexes that might unnecessarily add overhead. Connection pooling is another key area where you can improve performance. By maintaining a pool of database connections rather than establishing new ones for each request, you dramatically reduce connection setup overhead and improve application response times. The oci autonomous database provides built-in connection pooling mechanisms that are often adequate, but adjustments may be needed based on application usage patterns. Also, utilize the platform’s built-in performance monitoring tools to gain insights into query performance and resource consumption, this data-driven approach allows you to make informed decisions about optimization techniques.
Further optimizing your oci autonomous database requires leveraging the autonomous tuning capabilities of the platform. The system continuously monitors performance and makes adjustments in the background to maintain efficiency. However, there are areas where user intervention might be necessary. For instance, when handling complex analytical queries, consider using materialized views to pre-compute results. This can greatly improve performance by avoiding redundant computation. Partitioning large tables can also improve performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be scanned for specific queries. Be mindful of data types used, and choose the most efficient type possible for columns. In addition, the database has sophisticated query rewrites and optimization techniques that are automatically applied, so familiarize yourself with these. Regularly review slow-running queries and consider query rewrite techniques to utilize indexes effectively. By combining an understanding of fundamental database optimization principles with the automated capabilities of the oci autonomous database, you can create a high-performing database environment that is efficient and cost-effective.
Securing your Data in Oracle Autonomous Cloud Database
Data security is paramount when leveraging cloud database services, and the oci autonomous database provides a comprehensive suite of features to protect your valuable information. One of the foundational security measures is data encryption, which is implemented both at rest and in transit. Data stored within the oci autonomous database is encrypted using strong algorithms, ensuring that it is unreadable to unauthorized parties. Additionally, data transmitted to and from the database is encrypted using secure protocols, safeguarding it during transit. Network security is another critical component, with the autonomous database residing within virtual cloud networks (VCNs), allowing for fine-grained control over network access. Customers can define security lists and network security groups to restrict traffic to only authorized sources. Access control within the oci autonomous database is managed through database users and roles. By implementing the principle of least privilege, administrators can grant users only the necessary permissions required to perform their tasks, limiting the potential impact of compromised accounts. The platform also provides proactive security monitoring features, which continuously scan for potential threats and vulnerabilities, triggering alerts and enabling rapid incident response.
Furthermore, the oci autonomous database adheres to rigorous compliance standards, reflecting Oracle’s commitment to maintaining data privacy and security. The service supports compliance with various industry-specific and global regulations, helping organizations meet their legal and contractual obligations. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are conducted to ensure the platform remains robust against emerging threats. In the realm of authentication, the autonomous database supports multiple authentication methods, including password-based authentication, Oracle Wallet-based authentication, and integration with identity providers for single sign-on capabilities. These authentication mechanisms add layers of protection against unauthorized access, making it exceedingly difficult for malicious actors to gain entry. The self-patching feature of the oci autonomous database further bolsters its security posture, automatically applying security patches and updates, reducing the administrative burden of ensuring the platform remains secure. This automation significantly decreases the attack surface and minimizes potential vulnerabilities resulting from unpatched systems. The integrated security features make the oci autonomous database a trusted choice for organizations with stringent security requirements.
The proactive approach to security is a defining characteristic of the oci autonomous database, with advanced capabilities that monitor not just for external threats but also for internal vulnerabilities. Automated vulnerability scanning, along with real-time anomaly detection, allows for proactive identification and mitigation of issues before they escalate. Security information and event management (SIEM) integration allows for centralized monitoring and incident management, further enhancing the overall security posture. By continuously reviewing and improving the security architecture, the oci autonomous database maintains a high level of protection, allowing users to focus on innovation and growth without the constant worry of security threats. Overall, the security features built into the autonomous database allow for a truly secure environment, mitigating many of the risks typically associated with database management.
Real-World Use Cases for Oracle’s Self-Driving Database
Oracle Autonomous Database has proven its value across diverse sectors, streamlining operations and delivering significant benefits. In the finance industry, a large multinational bank leveraged oci autonomous database to enhance its fraud detection system. By migrating its transactional database to this platform, the bank achieved a substantial reduction in operational costs associated with database administration, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives. The self-driving nature of the oci autonomous database also ensured high availability and performance, minimizing downtime and improving the overall efficiency of its fraud detection processes. The automated security features of the platform further strengthened the bank’s security posture, mitigating risks associated with data breaches.
Within the retail sector, a major online retailer implemented oci autonomous database to handle its rapidly growing e-commerce operations. The scalability and elasticity of the oci autonomous database allowed the retailer to seamlessly manage peak demand during promotional periods and holiday seasons, ensuring a consistently smooth customer experience. The automated performance tuning features of the platform optimized query performance, leading to faster transaction processing speeds and improved website responsiveness. This resulted in increased customer satisfaction and higher conversion rates. The retailer also benefited from the simplified data management processes, reducing the need for extensive IT resources and lowering overall operational costs. This successful deployment underscores the advantages of oci autonomous database in handling large-scale transactional workloads in a dynamic retail environment.
The healthcare industry also benefits from the capabilities of oci autonomous database. A large healthcare provider utilized the platform to consolidate its disparate data sources into a centralized data warehouse. This allowed for improved data analysis and reporting, enabling more effective population health management and more informed clinical decision-making. The automated security features of the oci autonomous database ensured compliance with stringent healthcare data privacy regulations, protecting sensitive patient information. The platform’s scalability facilitated the seamless integration of data from various sources, offering a unified view of patient information for improved care coordination. The reduced administrative overhead allowed the healthcare provider to focus on enhancing patient care rather than managing database infrastructure, showcasing the value proposition of oci autonomous database in the demanding healthcare landscape. The improved data accessibility also facilitated research and development initiatives, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.
Making the Move: Migrating to Oracle Autonomous Database
Migrating existing databases to Oracle Autonomous Database presents a significant opportunity to modernize infrastructure and streamline operations. Several strategies facilitate a smooth transition, minimizing downtime and ensuring data integrity. Oracle provides robust tools and services to support diverse migration scenarios, from simple schema conversions to complex, large-scale database migrations. Understanding the source database environment and meticulously planning the migration is paramount. This includes a thorough assessment of data volume, schema complexity, and application dependencies. A phased approach, migrating data in segments, can effectively manage risks and complexities associated with large datasets. For those already leveraging Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), the process is further streamlined, taking advantage of OCI’s integrated services and robust network capabilities. OCI autonomous database offers several tools to simplify and accelerate the data migration process, ensuring efficiency and minimal disruption. Consider utilizing Oracle’s Data Migration tools, such as GoldenGate, for high-speed, low-impact data transfer, especially beneficial for large and complex databases. Proper planning and utilization of these tools are critical to a successful migration to oci autonomous database.
Regardless of the chosen migration path, meticulous pre-migration steps are crucial for success. This includes thorough data validation and cleansing to ensure data quality and consistency within the new oci autonomous database environment. Creating detailed test plans and conducting thorough testing on a non-production instance is essential to identify and resolve potential issues before impacting live systems. Testing should encompass various aspects, including data integrity, performance, and application compatibility. A well-defined rollback plan is equally critical, outlining procedures for reverting to the original database system should unforeseen issues arise during the migration. This proactive approach ensures resilience and mitigates the risk of prolonged downtime. Comprehensive documentation throughout the migration process is also vital, providing a valuable record for future reference and troubleshooting. The migration to oci autonomous database should not be viewed as a single event, but rather as an ongoing process of optimization and refinement. Regularly reviewing performance and adjusting configurations as needed will maximize the benefits of the new platform.
Successfully migrating to oci autonomous database requires a strategic approach that combines careful planning, leveraging Oracle’s powerful migration tools, and a commitment to thorough testing. By adhering to best practices and anticipating potential challenges, organizations can realize the full potential of this self-driving database platform, experiencing enhanced performance, improved security, and reduced administrative overhead. The resulting gains in efficiency and cost savings contribute significantly to the overall business value derived from the migration. The transition to oci autonomous database is not merely a technological upgrade, but a strategic move toward a more agile and resilient IT infrastructure.