What are Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models?
Hybrid cloud deployment models refer to a computing environment that combines private and public cloud services, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both infrastructures. By integrating on-premises resources with cloud-based services, hybrid cloud deployment models offer increased flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. Organizations can seamlessly move workloads between private and public clouds, ensuring optimal resource utilization and reducing capital expenditures.
Private clouds are dedicated computing resources that an organization manages and maintains in-house. These resources offer enhanced security, control, and customization, making them ideal for sensitive workloads and data. On the other hand, public clouds are managed by third-party service providers and offer on-demand access to computing resources via the internet. Public clouds are highly scalable, cost-effective, and require minimal maintenance, making them suitable for non-sensitive workloads and applications.
Hybrid cloud deployment models enable organizations to strike a balance between the security and control of private clouds and the flexibility and cost savings of public clouds. By strategically deploying workloads across both environments, organizations can achieve their business objectives while minimizing risks and maximizing returns on their IT investments.
Key Components of Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
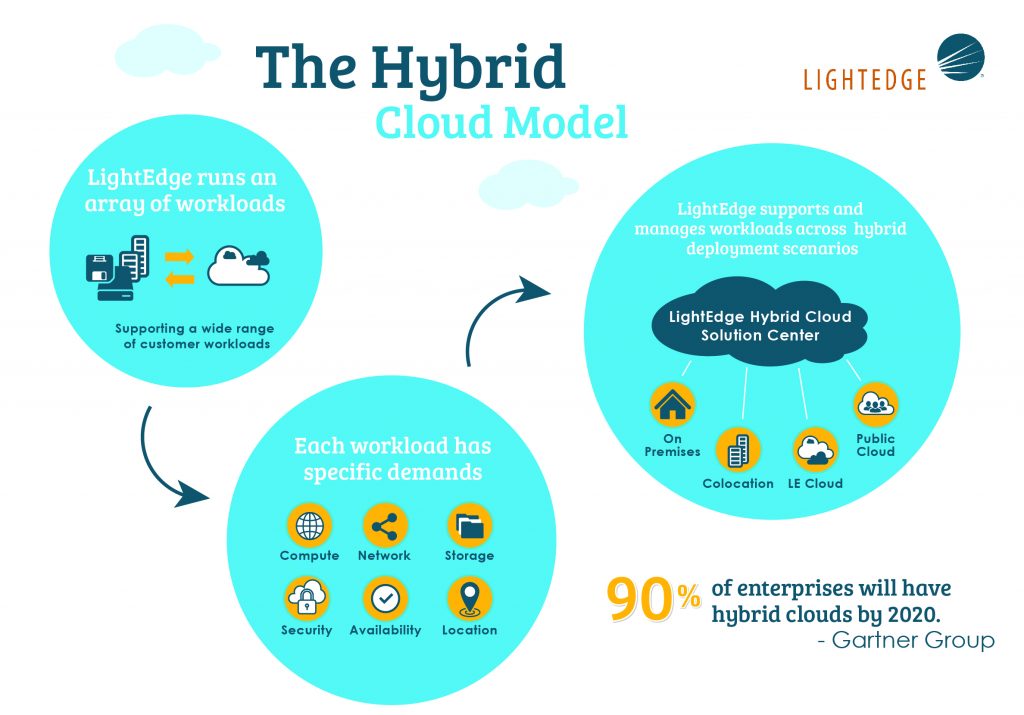
Hybrid cloud deployment models comprise several essential components that enable organizations to leverage the strengths of both private and public clouds. These components include:
- Cloud bursting: Cloud bursting is a hybrid cloud deployment model that allows organizations to seamlessly move workloads between private and public clouds. During periods of high demand, organizations can “burst” their workloads into the public cloud, providing additional computing resources and ensuring optimal performance. Cloud bursting offers cost savings by minimizing the need for on-premises infrastructure upgrades and allowing organizations to pay only for the public cloud resources they use.
- Disaster recovery: Hybrid cloud deployment models can also support disaster recovery initiatives. By replicating critical workloads and data in the public cloud, organizations can ensure business continuity in the event of an on-premises disaster. Hybrid cloud disaster recovery solutions offer cost savings by minimizing the need for redundant on-premises infrastructure and enabling organizations to leverage the public cloud’s scalability and geographic distribution.
- Data migration: Hybrid cloud deployment models enable organizations to migrate data between private and public clouds seamlessly. Data migration can be performed for various reasons, including infrastructure upgrades, application modernization, or cost savings. Hybrid cloud data migration solutions offer flexibility by allowing organizations to choose the most appropriate cloud environment for their data and applications.
By incorporating these components into their hybrid cloud deployment models, organizations can achieve specific business objectives, such as improving application performance, reducing costs, and enhancing disaster recovery capabilities. However, it’s essential to carefully evaluate each component’s potential benefits and risks and develop a comprehensive strategy for integrating private and public clouds.
Popular Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
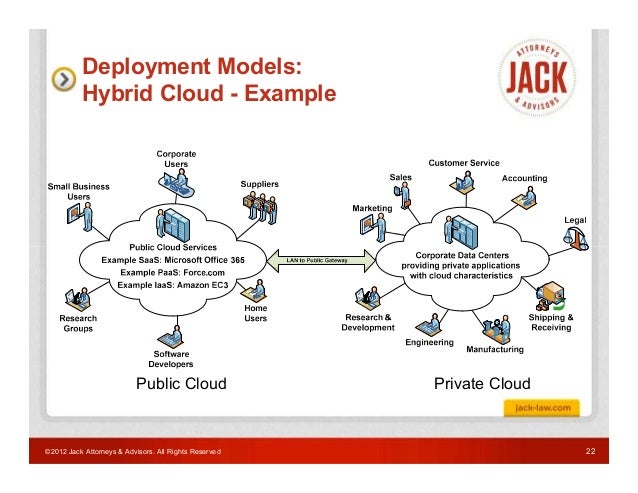
Hybrid cloud deployment models offer organizations a flexible and scalable approach to cloud computing by combining private and public cloud environments. There are several popular hybrid cloud deployment models, including:
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): IaaS hybrid cloud deployment models involve using public cloud infrastructure to augment on-premises infrastructure. Organizations can leverage public cloud resources to handle peak workloads, run development and testing environments, or support disaster recovery initiatives. IaaS hybrid cloud deployment models offer cost savings by minimizing the need for on-premises infrastructure upgrades and enabling organizations to pay only for the public cloud resources they use.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): PaaS hybrid cloud deployment models involve using a public cloud platform to develop, test, and deploy applications. Organizations can leverage public cloud resources to support application development and testing while maintaining control over their data and infrastructure. PaaS hybrid cloud deployment models offer cost savings by minimizing the need for on-premises infrastructure upgrades and enabling organizations to leverage the public cloud’s scalability and geographic distribution.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): SaaS hybrid cloud deployment models involve using a public cloud software application to support business processes. Organizations can leverage public cloud software applications to support functions such as customer relationship management (CRM), human resources management (HRM), or enterprise resource planning (ERP). SaaS hybrid cloud deployment models offer cost savings by minimizing the need for on-premises software upgrades and enabling organizations to leverage the public cloud’s scalability and geographic distribution.
Real-world use cases for hybrid cloud deployment models include:
- A retail organization using an IaaS hybrid cloud deployment model to handle peak holiday season workloads.
- A software development firm using a PaaS hybrid cloud deployment model to support application development and testing.
- A manufacturing company using a SaaS hybrid cloud deployment model to support CRM and HRM functions.
While hybrid cloud deployment models offer several advantages, they also have potential disadvantages. For example, IaaS hybrid cloud deployment models may require significant integration efforts, while PaaS and SaaS hybrid cloud deployment models may limit organizational control over data and infrastructure. Therefore, it’s essential to carefully evaluate each hybrid cloud deployment model’s potential benefits and risks and develop a comprehensive strategy for integrating private and public clouds.

How to Choose the Right Hybrid Cloud Deployment Model
Hybrid cloud deployment models offer organizations a flexible and scalable approach to cloud computing by combining private and public cloud environments. However, selecting the right hybrid cloud deployment model can be challenging, given the various options available and the unique needs of each organization. Here are some factors organizations should consider when selecting a hybrid cloud deployment model:
- Security requirements: Organizations should evaluate the security features of each hybrid cloud deployment model and ensure that they meet their specific security requirements. For example, organizations in regulated industries may require hybrid cloud deployment models that offer advanced security features such as data encryption, access controls, and compliance reporting.
- Performance needs: Organizations should evaluate the performance requirements of their applications and workloads and select a hybrid cloud deployment model that can meet those needs. For example, organizations that require low latency and high throughput may prefer hybrid cloud deployment models that offer dedicated connections between private and public clouds.
- Budget constraints: Organizations should evaluate the cost of each hybrid cloud deployment model and ensure that it fits within their budget constraints. For example, organizations that have limited budgets may prefer hybrid cloud deployment models that offer cost-effective public cloud resources.
Here is a step-by-step guide for evaluating different hybrid cloud deployment model options and selecting the best fit for a given business scenario:
- Identify the organization’s specific needs and requirements for cloud computing.
- Research the available hybrid cloud deployment model options and evaluate their features, benefits, and drawbacks.
- Assess the security, performance, and budget constraints of each hybrid cloud deployment model option.
- Select the hybrid cloud deployment model option that best meets the organization’s needs and requirements.
- Develop a comprehensive strategy for integrating private and public clouds, managing data and applications, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
While hybrid cloud deployment models offer several advantages, they also have potential disadvantages. For example, hybrid cloud deployment models may require significant integration efforts, while PaaS and SaaS hybrid cloud deployment models may limit organizational control over data and infrastructure. Therefore, it’s essential to carefully evaluate each hybrid cloud deployment model’s potential benefits and risks and develop a comprehensive strategy for integrating private and public clouds.

Implementing Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
Implementing hybrid cloud deployment models requires careful planning and consideration of both technical and organizational factors. Here are some best practices for integrating private and public clouds, managing data and applications, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements:
- Integrating private and public clouds: Organizations should establish a secure and reliable connection between their private and public cloud environments. This can be achieved through a virtual private network (VPN), a dedicated network connection, or a cloud exchange provider. Additionally, organizations should ensure that their data and applications are compatible with both private and public cloud environments and can be easily transferred between them.
- Managing data and applications: Organizations should develop a comprehensive strategy for managing data and applications across private and public cloud environments. This includes establishing data governance policies, defining application deployment and scaling strategies, and implementing monitoring and alerting mechanisms to ensure optimal performance and availability.
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements: Organizations should ensure that their hybrid cloud deployment models comply with relevant regulatory requirements, such as data privacy and security regulations. This includes implementing appropriate security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and compliance reporting, and regularly auditing their hybrid cloud environments for compliance.
Here are some best practices for implementing hybrid cloud deployment models:
- Define the organization’s specific requirements for hybrid cloud deployment models, including security, performance, and budget constraints.
- Select a hybrid cloud deployment model that meets the organization’s requirements and provides the necessary flexibility and scalability.
- Develop a comprehensive strategy for integrating private and public clouds, managing data and applications, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Implement the hybrid cloud deployment model in a phased approach, starting with a small-scale pilot project and gradually scaling up to the full deployment.
- Regularly monitor and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the hybrid cloud deployment model and make adjustments as necessary.
While hybrid cloud deployment models offer several advantages, they also have potential disadvantages. For example, hybrid cloud deployment models may require significant integration efforts, while PaaS and SaaS hybrid cloud deployment models may limit organizational control over data and infrastructure. Therefore, it’s essential to carefully evaluate each hybrid cloud deployment model’s potential benefits and risks and develop a comprehensive strategy for integrating private and public clouds.
Challenges and Risks of Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
While hybrid cloud deployment models offer several benefits, they also come with potential challenges and risks. Here are some of the most common issues organizations may face when implementing hybrid cloud deployment models:
- Data security: Hybrid cloud deployment models involve transferring data between private and public cloud environments, which can increase the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks. Organizations should implement appropriate security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and compliance reporting, to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their data.
- Network latency: Hybrid cloud deployment models may introduce network latency, which can affect application performance and user experience. Organizations should ensure that their private and public cloud environments are connected through a reliable and high-speed network to minimize latency and ensure optimal performance.
- Vendor lock-in: Hybrid cloud deployment models may rely on specific cloud providers or technologies, which can make it difficult for organizations to switch vendors or technologies in the future. Organizations should ensure that their hybrid cloud deployment models are flexible and scalable and can accommodate future changes in technology and business requirements.
To mitigate these risks and ensure a successful hybrid cloud deployment, organizations should consider the following strategies:
- Implement a comprehensive security strategy that includes data encryption, access controls, and compliance reporting.
- Establish a reliable and high-speed network connection between private and public cloud environments.
- Ensure that the hybrid cloud deployment model is flexible and scalable and can accommodate future changes in technology and business requirements.
- Regularly monitor and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the hybrid cloud deployment model and make adjustments as necessary.
- Provide training and support to employees and stakeholders to ensure a smooth transition to the hybrid cloud deployment model.
By following these best practices, organizations can leverage the strengths of both private and public clouds and achieve their specific business objectives through hybrid cloud deployment models.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
Hybrid cloud deployment models are constantly evolving, and new trends and innovations are emerging that are shaping the future of hybrid cloud computing. Here are some of the most exciting developments to watch:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML are becoming increasingly important in hybrid cloud deployment models, enabling organizations to automate complex workflows, optimize resource utilization, and make data-driven decisions. By integrating AI and ML with hybrid cloud deployment models, organizations can unlock new insights and create new business models that were previously impossible.
- Containerization: Containerization is a lightweight virtualization technology that enables organizations to package and deploy applications in a consistent and portable way across different cloud environments. By using containerization with hybrid cloud deployment models, organizations can achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and agility, while reducing the risk of application compatibility issues.
- Edge computing: Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the edge of the network, near the source of the data. By integrating edge computing with hybrid cloud deployment models, organizations can reduce network latency, improve application performance, and enable new use cases, such as IoT and real-time analytics.
These trends and innovations are just the beginning of what’s possible with hybrid cloud deployment models. As organizations continue to explore the potential of hybrid cloud computing, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the future. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices, organizations can leverage the full potential of hybrid cloud deployment models and drive business innovation and growth.
Conclusion: The Power of Hybrid Cloud Deployment Models
Hybrid cloud deployment models offer a powerful and flexible approach to cloud computing, enabling organizations to leverage the strengths of both private and public clouds to achieve specific business objectives. By combining the security, control, and customization of private clouds with the scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use of public clouds, hybrid cloud deployment models provide a winning solution for businesses of all sizes and industries.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored the key components, popular models, and best practices for implementing hybrid cloud deployment models. From cloud bursting and disaster recovery to IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, we have examined the essential elements that enable organizations to achieve increased flexibility, scalability, and cost savings.
However, as with any technology solution, there are potential challenges and risks associated with hybrid cloud deployment models, such as data security, network latency, and vendor lock-in. To mitigate these risks and ensure a successful hybrid cloud deployment, organizations must carefully evaluate their security requirements, performance needs, and budget constraints, and develop a comprehensive strategy that aligns with their business goals and objectives.
As we look to the future, emerging trends and innovations, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and containerization, are shaping the landscape of hybrid cloud computing and enabling new use cases and business models. By staying up-to-date with the latest developments and best practices, organizations can leverage the full potential of hybrid cloud deployment models and drive business innovation and growth.
In conclusion, hybrid cloud deployment models offer a powerful and flexible approach to cloud computing, enabling organizations to achieve specific business objectives and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation. By embracing the flexibility and scalability of hybrid cloud computing, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and thrive in an ever-changing business landscape.