Understanding Cloud Migration Strategies
Cloud migration strategies for enterprises are essential in today’s digital landscape. As businesses aim to modernize their IT infrastructure, adopting cloud technologies offers numerous benefits. These advantages include cost savings, increased scalability, and improved disaster recovery capabilities. By transitioning to the cloud, enterprises can reduce capital expenditures, minimize the need for on-premises hardware maintenance, and benefit from the flexibility of cloud resources.
Cloud migration strategies for enterprises involve carefully planned approaches to move workloads, applications, and data from on-premises or legacy systems to the cloud. These strategies cater to various business needs and technical requirements, ensuring a smooth transition with minimal disruption. By understanding the different cloud migration strategies available, enterprises can make informed decisions and successfully embark on their cloud journey.

Assessing Your Current IT Infrastructure
Before selecting a cloud migration strategy, it is crucial to evaluate the existing IT infrastructure. A comprehensive assessment of current systems, applications, and data helps determine migration readiness and identify potential challenges. This evaluation process includes several key steps:
- Inventory analysis: Identify all hardware, software, and applications within the organization. Document their configurations, interdependencies, and usage patterns. This information will help determine which components are suitable for migration and which may require upgrades or replacements.
- Performance assessment: Evaluate the performance of existing applications and systems to establish baseline metrics. This data will help determine the capacity and resource requirements for the target cloud environment.
- Security evaluation: Examine the existing security measures, policies, and procedures. Identify vulnerabilities and potential risks associated with migrating to the cloud. This assessment will inform the development of a robust security strategy during and after migration.
- Compliance review: Ensure that the current IT infrastructure complies with relevant industry regulations and standards. Understand how migration to the cloud may impact compliance and plan accordingly.
By thoroughly assessing the current IT infrastructure, enterprises can make informed decisions about the most appropriate cloud migration strategies and ensure a smooth transition to the cloud.
Selecting the Right Cloud Migration Strategy
When choosing a cloud migration strategy, enterprises should consider various factors, such as the complexity of the existing IT infrastructure, business objectives, and resource availability. Four common cloud migration strategies are:
- Rehosting (lift-and-shift): This approach involves moving applications and data from on-premises environments to the cloud without significant modifications. Rehosting is ideal for organizations seeking quick migration with minimal changes to existing systems. However, it may not fully leverage cloud-native features and may result in higher long-term costs due to inefficient resource utilization.
- Replatforming: Replatforming involves making minor updates to applications and data before migrating them to the cloud. This approach aims to optimize applications for the cloud environment while minimizing changes to the core architecture. Replatforming allows enterprises to take advantage of cloud-native features and improve scalability, but it may require additional time and resources compared to rehosting.
- Refactoring: Refactoring involves re-architecting applications to fully leverage cloud-native services and features. This approach requires significant changes to the application code and design but can lead to substantial improvements in performance, scalability, and cost efficiency. Refactoring is suitable for organizations with the resources and expertise to redesign applications and willing to accept the risks associated with major changes.
- Rearchitecting: Rearchitecting involves rebuilding applications from scratch using cloud-native services and tools. This approach is ideal for organizations looking to adopt new technologies, modernize their IT infrastructure, and achieve significant improvements in scalability, performance, and cost efficiency. However, rearchitecting is the most resource-intensive and time-consuming migration strategy, requiring specialized skills and a significant investment.
Each cloud migration strategy offers unique advantages and disadvantages. By carefully evaluating their existing IT infrastructure, business objectives, and resource availability, enterprises can select the most appropriate strategy for their needs and successfully transition to the cloud.
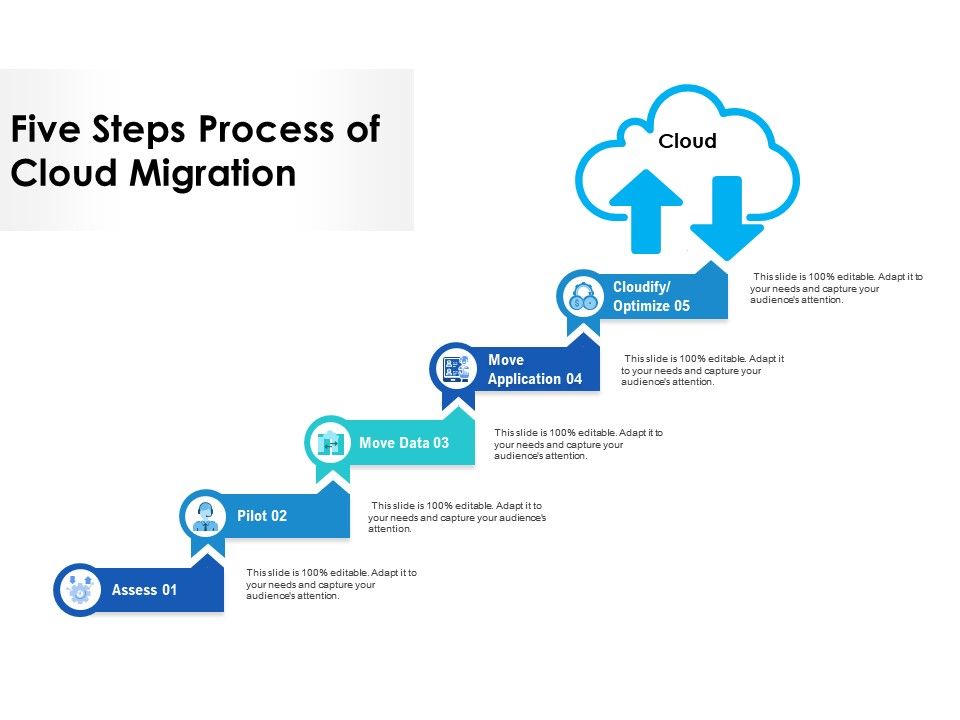
Implementing a Phased Migration Approach
A phased migration approach allows enterprises to gradually move workloads to the cloud, minimizing disruption and reducing risk. By prioritizing applications and data for migration based on business needs and technical requirements, organizations can ensure a smooth transition to the cloud.
- Identify critical applications and data: Begin by assessing the importance of various applications and data sets to the organization’s operations. Critical applications and data should be prioritized for migration to ensure minimal disruption to business processes.
- Evaluate technical requirements: Consider the technical dependencies and requirements of each application and data set. Some applications may require significant updates or modifications before migration, while others may be easily moved to the cloud. Prioritize applications with fewer dependencies and lower migration complexity.
- Plan the migration sequence: Develop a detailed plan for migrating applications and data to the cloud. This plan should outline the sequence of migration, including any necessary updates or modifications to applications and data before migration. A well-planned migration sequence can help minimize downtime and reduce the risk of data loss or corruption.
- Monitor and optimize: Continuously monitor the performance and resource utilization of applications and data in the cloud. Optimize resource allocation and configuration as needed to ensure optimal performance and cost efficiency.
By implementing a phased migration approach, enterprises can gradually transition to the cloud, minimizing risk and ensuring a smooth migration process. Real-world examples and case studies demonstrate the benefits of this approach, including improved scalability, cost savings, and enhanced disaster recovery capabilities.
Ensuring Security and Compliance During Migration
Maintaining security and compliance is crucial during the cloud migration process. By following best practices for securing data, applications, and infrastructure, enterprises can ensure a smooth and secure transition to the cloud.
- Secure data: Implement encryption for data at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information. Use secure cloud storage services that comply with industry standards and regulations, and establish strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
- Secure applications: Ensure that applications are secured and hardened against potential threats. Use web application firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and other security measures to protect applications in the cloud.
- Secure infrastructure: Implement security measures such as virtual private clouds (VPCs), security groups, and network access control lists (NACLs) to secure the underlying infrastructure. Use automation tools to enforce security policies and ensure consistent configuration across the cloud environment.
- Maintain compliance: Ensure that the cloud environment complies with relevant industry regulations and standards. Use cloud compliance management tools to monitor compliance and automate compliance checks and reporting.
By following these best practices, enterprises can maintain security and compliance during the cloud migration process. Real-world examples and case studies demonstrate the importance of these measures, including the potential financial and reputational costs of data breaches and compliance violations.
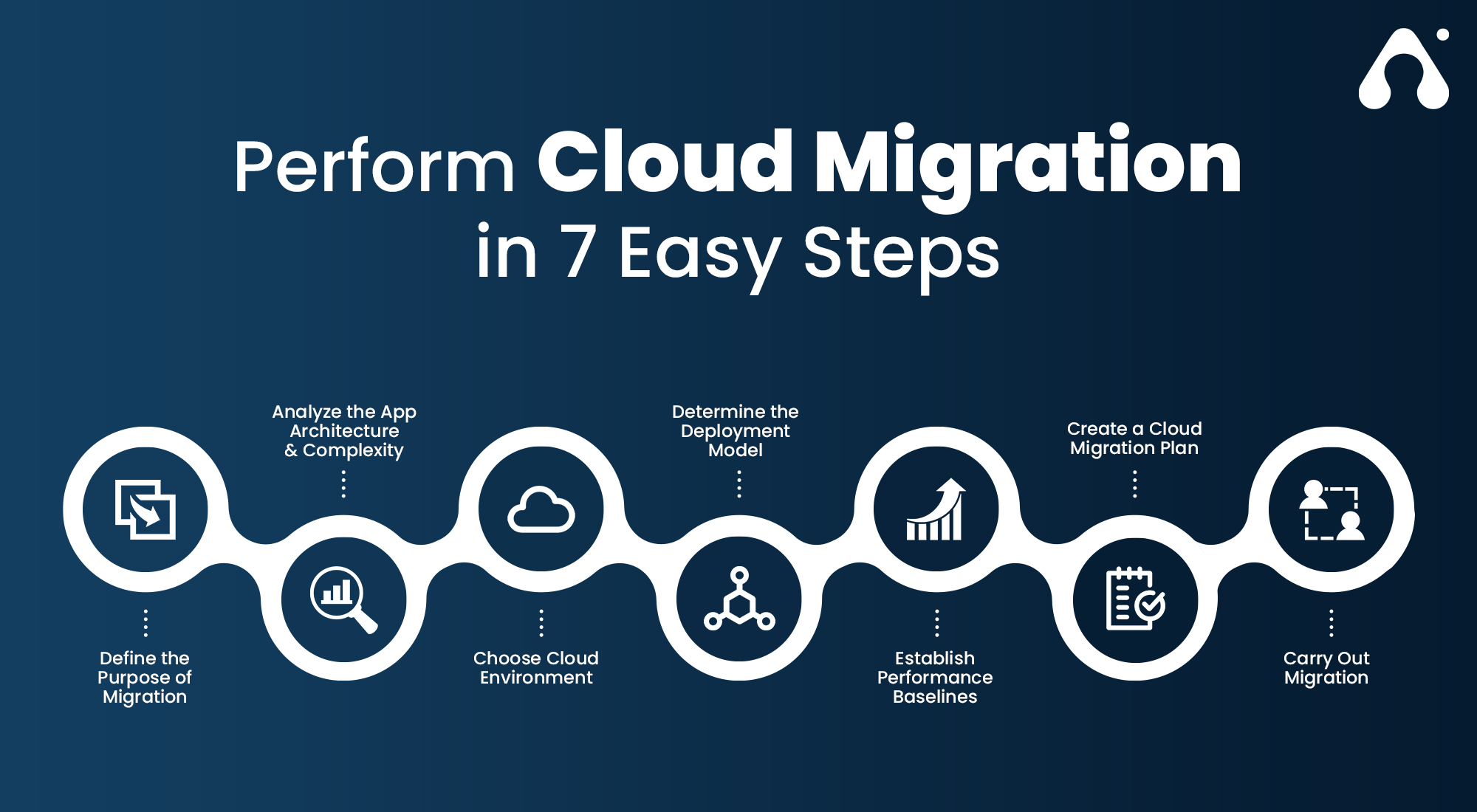
How to Successfully Execute a Cloud Migration
Executing a successful cloud migration requires careful planning, preparation, and execution. By following a step-by-step guide, enterprises can ensure a smooth and successful transition to the cloud.
- Planning: Define the migration strategy and goals, including cost savings, scalability, and disaster recovery. Identify the applications and data to be migrated, and establish a timeline and budget for the migration.
- Preparation: Prepare the existing IT infrastructure for migration by cleaning up and optimizing applications and data. Ensure that the cloud environment is properly configured and secured, and establish a disaster recovery plan.
- Migration: Use automated tools to migrate applications and data to the cloud. Test the migration process thoroughly to ensure that data is not lost or corrupted, and that applications function as expected.
- Testing: Test the migrated applications and data thoroughly to ensure that they function as expected. Identify and address any issues or bugs before moving to the next phase of the migration.
- Optimization: Continuously monitor and optimize cloud performance, including resource utilization, cost management, and performance optimization. Use automated tools to enforce security policies and ensure consistent configuration across the cloud environment.
Real-world examples and case studies demonstrate the importance of these steps, including the potential financial and reputational costs of a failed migration. By following best practices and using automated tools, enterprises can ensure a successful cloud migration and reap the benefits of the cloud.

Monitoring and Optimizing Cloud Performance
Monitoring and optimizing cloud performance is crucial for ensuring that cloud migration strategies for enterprises are successful. Continuous monitoring helps to identify and address any issues or bottlenecks, while optimization ensures that resources are being used efficiently and cost-effectively.
Tools and techniques for monitoring and optimizing cloud performance include:
- Resource utilization: Monitor resource utilization, such as CPU, memory, and storage, to ensure that they are being used efficiently. Identify any spikes or trends that may indicate the need for additional resources or optimization.
- Cost management: Monitor cloud costs and identify any areas where costs can be reduced. This may include optimizing resource usage, using reserved instances, or taking advantage of volume discounts.
- Performance optimization: Monitor application and infrastructure performance to ensure that they are meeting business needs and user expectations. Identify any bottlenecks or issues that may be impacting performance, and take steps to optimize performance, such as scaling up or out, or using caching and load balancing.
By continuously monitoring and optimizing cloud performance, enterprises can ensure that their cloud migration strategies are successful and that they are realizing the full benefits of the cloud, including cost savings, increased scalability, and improved disaster recovery.
Overcoming Common Cloud Migration Challenges
Cloud migration can be a complex and challenging process for enterprises. However, with careful planning and execution, many of the common challenges can be overcome. Here are some potential issues and solutions to consider:
- Data loss: Data loss is a major concern during cloud migration. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to have a robust data backup and disaster recovery plan in place. Regular backups should be taken, and data should be verified for accuracy and completeness. Additionally, data should be encrypted during migration to ensure its security.
- Downtime: Cloud migration can result in downtime, which can impact business operations and user experience. To minimize downtime, it is important to plan the migration carefully and schedule it during a time that will have the least impact on the business. Additionally, using tools and techniques such as load balancing, auto-scaling, and caching can help to ensure that applications and data are always available.
- Skill gaps: Cloud migration requires specialized skills and knowledge. If an enterprise lacks the necessary expertise in-house, it may need to hire external consultants or train existing staff. Providing training and development opportunities can help to bridge skill gaps and ensure that the enterprise has the necessary expertise to manage and maintain its cloud infrastructure.
By anticipating and addressing these common challenges, enterprises can ensure a successful cloud migration and realize the full benefits of the cloud, including cost savings, increased scalability, and improved disaster recovery.

