Understanding Cloud Storage: A Digital Revolution
Cloud storage represents a transformative approach to data management in the modern digital age. At its core, cloud storage is a model for storing and accessing data over the internet, without relying on local storage devices or physical infrastructure. This paradigm shift offers numerous benefits, making cloud storage an increasingly popular choice for both individuals and organizations.
In essence, the “cloud” serves as a virtual data center, providing users with the ability to store, retrieve, and share information from any location with an internet connection. The “description of cloud storage” encapsulates this concept, highlighting the convenience, flexibility, and accessibility that cloud storage provides. By embracing cloud storage, users can enjoy a seamless data management experience, empowered by the power of the internet.
How Cloud Storage Works: A Breakdown of the Technology
At the heart of cloud storage are vast data centers housing thousands of servers, which facilitate data storage, retrieval, and protection. These data centers are connected via the internet, allowing users to access their data from anywhere in the world. The “description of cloud storage” must include an explanation of how this technology operates.
When data is uploaded to the cloud, it is typically broken down into smaller chunks and distributed across multiple servers, a process known as data redundancy. This ensures that data remains accessible and secure, even in the event of hardware failures or other disruptions. By relying on redundancy, cloud storage providers can maintain high levels of reliability and availability, benefiting users and their data management needs.
Data retrieval from the cloud involves sending a request over the internet to the appropriate data center. The server then collects the necessary data chunks, reassembles them, and transmits the complete data set back to the user. This process occurs seamlessly, providing users with a smooth and efficient data access experience. By understanding the underlying technology, users can better appreciate the capabilities and advantages of cloud storage solutions.
Key Benefits of Cloud Storage: Unlocking the Potential
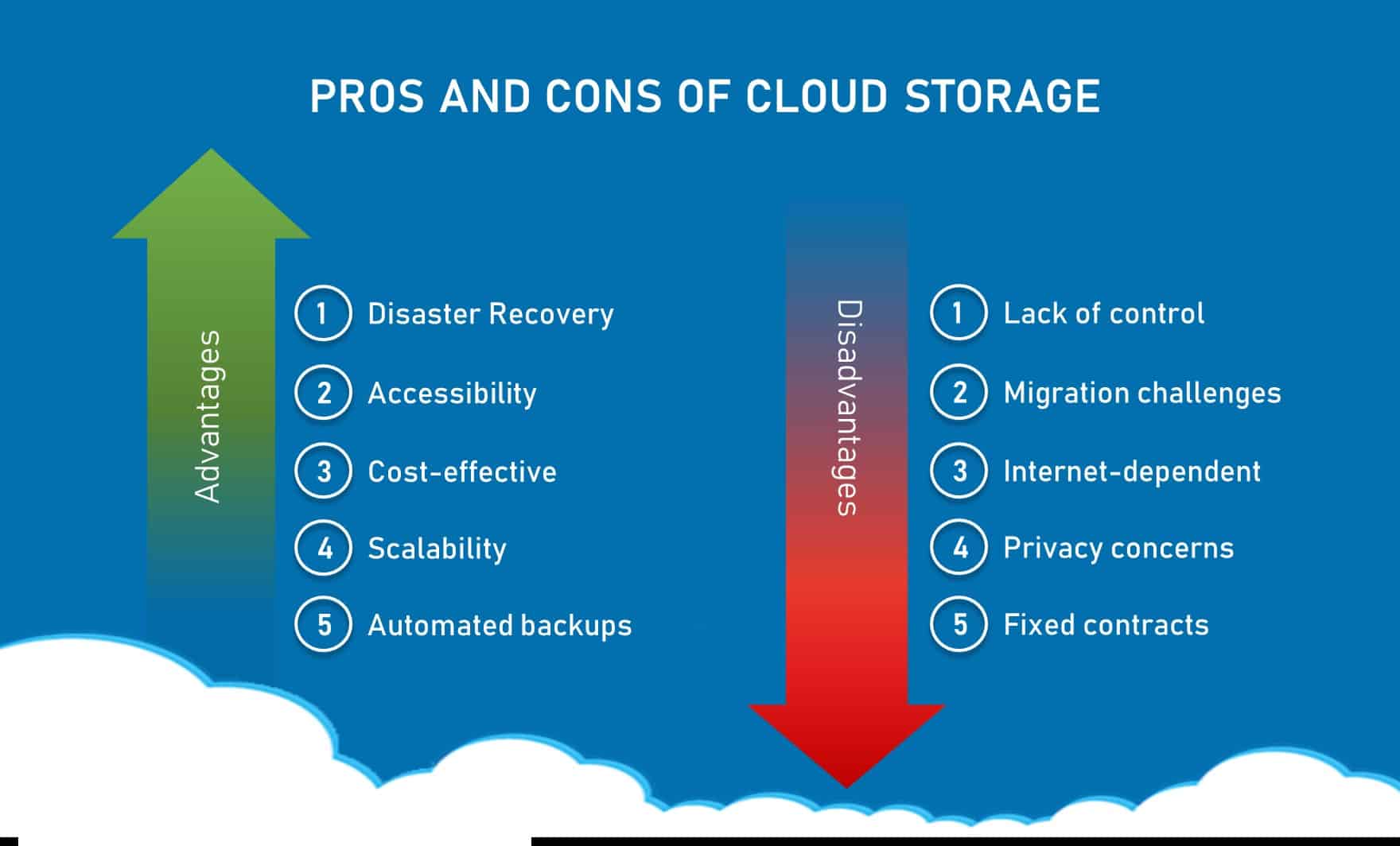
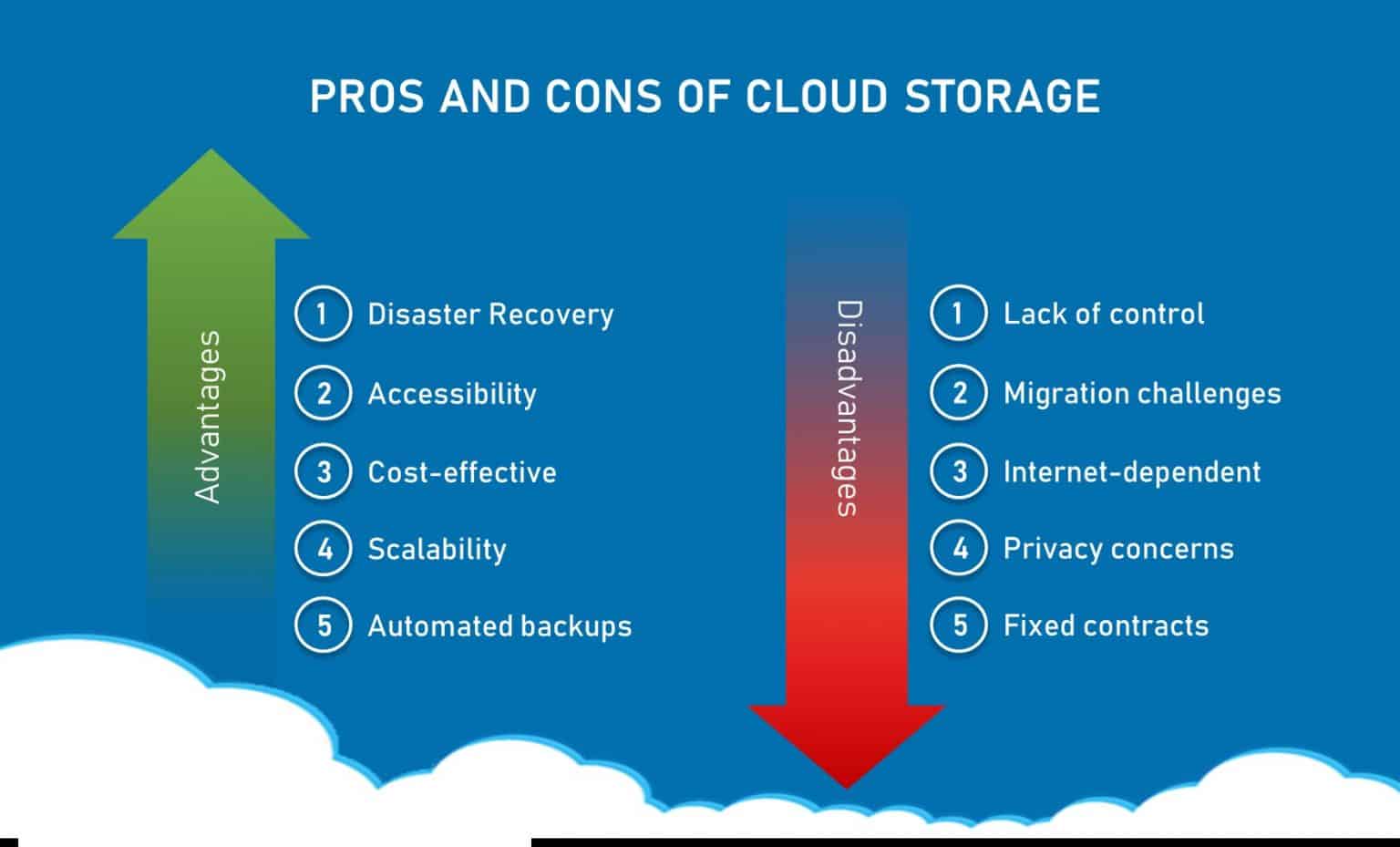
Cloud storage offers numerous advantages that contribute to its growing popularity. By understanding these benefits, users can make informed decisions about incorporating cloud storage into their data management strategies.
First and foremost, cloud storage is highly scalable. Users can easily increase or decrease their storage capacity as needed, without the limitations imposed by physical infrastructure. This flexibility makes cloud storage an ideal solution for businesses and individuals facing fluctuating data storage requirements.
Additionally, cloud storage is cost-effective. Users typically pay only for the storage they use, eliminating the need for upfront investments in hardware and maintenance. This subscription-based model allows for more predictable budgeting and can result in significant savings over time.
Accessibility is another key advantage of cloud storage. By storing data in the cloud, users can access it from any location with an internet connection, using a variety of devices. This level of accessibility promotes productivity, collaboration, and convenience, making cloud storage an attractive option for both personal and professional use.
Lastly, cloud storage facilitates collaboration by enabling multiple users to access, edit, and share data simultaneously. This real-time collaboration streamlines workflows, fosters teamwork, and enhances overall efficiency. By harnessing the power of cloud storage, users can unlock their potential and transform the way they manage and interact with data.
Popular Cloud Storage Providers: A Comparative Analysis
Choosing the right cloud storage provider is crucial for ensuring a seamless and secure data management experience. With numerous options available, it can be challenging to determine which provider best suits your needs. This comparative analysis highlights some of the leading cloud storage providers, focusing on their features, pricing, and user experience.
Google Drive
Google Drive offers users 15 GB of free storage, with additional storage available for a monthly fee. Integration with Google’s suite of productivity tools, such as Google Docs and Google Sheets, makes Google Drive an attractive option for users seeking a comprehensive cloud-based solution. Additionally, Google Drive’s search functionality allows users to quickly locate specific files, enhancing the overall user experience.
Dropbox
Dropbox provides users with 2 GB of free storage, expandable through referrals and promotions. Known for its sleek design and user-friendly interface, Dropbox is a popular choice for individuals and businesses alike. Dropbox also offers advanced features, such as team collaboration tools and version history, making it an ideal solution for users requiring robust data management capabilities.
Microsoft OneDrive
Microsoft OneDrive offers users 5 GB of free storage, with additional storage available for a monthly or annual fee. Integration with Microsoft Office Online allows users to create, edit, and share documents directly within the cloud environment. Microsoft OneDrive’s automatic file syncing and backup capabilities make it a convenient choice for users prioritizing ease of use and data protection.
When selecting a cloud storage provider, consider factors such as storage capacity, pricing, and user experience. By carefully evaluating these aspects, users can make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of cloud storage solutions.
Security Measures in Cloud Storage: Protecting Your Data
One common concern surrounding cloud storage is the security and privacy of users’ data. However, cloud storage providers employ various protective measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of users’ information. Understanding these security measures can help alleviate concerns and foster trust in cloud storage solutions.
Encryption
Encryption is a critical security measure used to protect data during transmission and storage. By converting plaintext data into a coded format, encryption prevents unauthorized access and safeguards sensitive information. Many cloud storage providers offer encryption as a standard feature, providing peace of mind for users concerned about data security.
Access Controls
Access controls are another essential security measure in cloud storage. These controls determine who can access specific data and under what conditions. By implementing robust access controls, cloud storage providers can minimize the risk of unauthorized data access and maintain the privacy of users’ information.
Redundancy and Data Backup
Redundancy and data backup are integral components of cloud storage security. By storing multiple copies of data across various servers and locations, cloud storage providers can ensure data availability in the event of hardware failures, natural disasters, or other unforeseen circumstances. This level of redundancy helps maintain business continuity and protect users’ data from loss or corruption.
By understanding these security measures, users can feel confident in the safety and reliability of cloud storage solutions. As the “description of cloud storage” continues to evolve, so too will the protective measures implemented by cloud storage providers, ensuring the long-term viability and security of these platforms.
Best Practices for Cloud Storage: Maximizing Efficiency and Safety
Adopting best practices for cloud storage can significantly enhance users’ experiences, ensuring efficiency, security, and ease of use. By following these guidelines, users can optimize their cloud storage usage and make the most of the available features.
Organizing Files
Maintaining an organized file structure is essential for efficient data management. Users should create logical folders and subfolders, utilizing naming conventions that make it easy to locate specific files. By keeping files organized, users can minimize search time and streamline their workflows.
Setting Up Backups
Regularly backing up data is crucial for protecting against data loss or corruption. Users should configure automatic backups to ensure their data is consistently updated and secure. Additionally, it’s essential to verify that backups are functioning correctly and that data can be successfully restored when needed.
Managing Sharing Permissions
Cloud storage platforms enable users to share files and folders with others easily. However, managing sharing permissions is crucial for maintaining data security. Users should grant access only to necessary individuals and regularly review sharing settings to ensure they are up-to-date and appropriate.
By incorporating these best practices into their cloud storage usage, users can ensure a seamless and secure experience. As the “description of cloud storage” continues to evolve, so too will the best practices for optimizing its use, making it essential for users to stay informed and adapt as needed.
Future Trends in Cloud Storage: Preparing for the Evolution
As technology continues to advance, the cloud storage landscape will evolve, offering users new possibilities and innovative features. By staying informed about emerging trends and innovations, users can ensure they are well-prepared to adapt and take full advantage of these developments.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize cloud storage by automating data management tasks and providing predictive analytics. AI-powered cloud storage solutions can analyze user behavior and data patterns, optimizing storage allocation, backup schedules, and access permissions. This level of automation can significantly enhance efficiency and security, making AI a promising trend in cloud storage.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology has the potential to address security concerns in cloud storage by offering decentralized, tamper-proof data storage. By distributing data across a network of computers, blockchain-based cloud storage solutions can minimize the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Additionally, blockchain’s transparent transaction history can provide users with greater visibility and control over their data, further enhancing security and trust.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing represents a significant leap in data processing power, with the potential to solve complex problems far beyond the capabilities of classical computers. As quantum computing technology matures, it may significantly impact cloud storage by enabling faster data analysis, encryption, and decryption. This enhanced processing power can lead to more secure, efficient, and innovative cloud storage solutions.
By staying informed about these future trends in cloud storage, users can prepare for the evolving landscape and make the most of new opportunities as they emerge. As the “description of cloud storage” continues to advance, users can look forward to increasingly sophisticated, secure, and user-friendly experiences.
Making the Switch to Cloud Storage: A Step-by-Step Guide
Transitioning from traditional storage methods to cloud storage can seem daunting, but with the right guidance, the process can be seamless and efficient. By following this step-by-step guide, users can confidently make the switch and begin enjoying the benefits of cloud storage.
Step 1: Selecting a Provider
Choosing the right cloud storage provider is crucial for a successful transition. Users should compare features, pricing, and user experience to find a provider that best suits their needs. Factors to consider include storage capacity, security measures, and compatibility with existing devices and applications.
Step 2: Setting Up an Account
Once a provider has been selected, users should create an account by providing basic information and selecting a payment plan. Many cloud storage providers offer free trials or limited-capacity free accounts, allowing users to test the service before committing to a paid plan.
Step 3: Transferring Data
After setting up an account, users can begin transferring data to the cloud. This process can be accomplished manually by uploading files and folders or automatically using cloud migration tools. Users should ensure that their internet connection is stable during the transfer to avoid data loss or corruption.
Step 4: Configuring Settings
Once data has been transferred, users should configure settings to optimize their cloud storage experience. This may include setting up backups, organizing files, managing sharing permissions, and enabling security features such as two-factor authentication and encryption.
By following these steps, users can make a smooth transition to cloud storage, unlocking the potential of this revolutionary technology. Understanding the “description of cloud storage” and its benefits can help users embrace this change and take full advantage of the opportunities it presents.