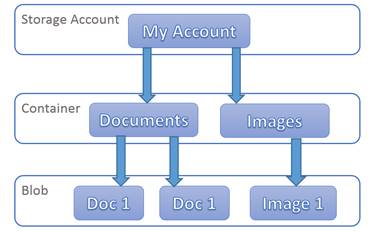
What is Blob Storage? A Key Term in Data Management
Blob storage, short for Binary Large Object, is a data storage solution that manages and stores unstructured data, such as text and binary files. It is a critical component in modern data management and storage, offering scalability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Blob storage is often associated with cloud computing, where it provides a flexible and efficient way to store and access large volumes of data.
Breaking Down the Blob Storage Acronym: Unraveling Its Components
Binary Large Object (BLOB) storage, often simply referred to as Blob storage, is a data storage solution designed for unstructured data. The term “Blob” is an acronym that highlights its purpose: storing Binary Large Objects, such as text and binary files. Blob storage is a key component in modern data management and storage, particularly in cloud computing environments, where it enables scalable, durable, and cost-effective storage for large volumes of unstructured data.
How to Implement Blob Storage in Your Data Management Strategy
Implementing Blob storage in your data management strategy involves several practical steps. First, assess your current data storage needs and determine whether Blob storage is the right solution for your organization. If so, consider the following best practices:
- Choose a suitable Blob storage provider: Select a cloud service provider that offers Blob storage services, such as Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, or Google Cloud Storage.
- Design a data organization structure: Create a logical and organized structure for your Blob storage, categorizing data based on access frequency, type, or other relevant factors.
- Configure access controls: Implement access controls to ensure data security and privacy, restricting access to authorized users and applications.
- Monitor and optimize performance: Regularly monitor Blob storage performance and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal data access and retrieval.
- Plan for scalability: Anticipate future data growth and design your Blob storage strategy to accommodate scaling and expansion.
Implementing Blob storage in your data management strategy offers several benefits, including cost savings, improved data accessibility, and enhanced security. However, it also presents potential challenges, such as data migration complexities, integration issues, and the need for ongoing management and maintenance.
Blob Storage vs. Other Storage Solutions: A Comparative Analysis
When comparing Blob storage to other storage solutions, it’s essential to consider the specific use case and data requirements. Blob storage offers several advantages over traditional file storage and block storage, including:
- Scalability: Blob storage easily scales to accommodate large volumes of unstructured data, providing a cost-effective solution for data storage growth.
- Accessibility: Blob storage enables data access from anywhere, at any time, and on any device, making it an ideal solution for remote and distributed teams.
- Durability: Blob storage offers built-in data redundancy and resiliency, ensuring data availability even in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
- Cost-effectiveness: Blob storage charges based on data storage and access, offering a more cost-effective solution for storing and accessing large volumes of unstructured data compared to traditional storage solutions.
However, Blob storage may not be the best solution for all use cases. For example, structured data or transactional data may be better suited for relational databases or other storage solutions. It’s essential to evaluate the specific data requirements and use cases when choosing a storage solution.
Real-World Applications of Blob Storage: Success Stories and Case Studies
Blob storage has been successfully implemented in various industries and use cases, demonstrating its versatility and effectiveness in managing unstructured data. Here are a few examples:
- Media and Entertainment: Blob storage enables media and entertainment companies to store, manage, and deliver large media files, such as videos, images, and audio, to users worldwide.
- Healthcare: Blob storage offers healthcare organizations a secure and scalable solution for storing medical images, patient records, and other unstructured data, ensuring data compliance and privacy.
- Manufacturing: Blob storage enables manufacturing companies to store and manage large product design files, enabling collaboration and efficient product development.
- Research and Development: Blob storage offers researchers and developers a scalable and cost-effective solution for storing and managing large datasets, enabling data analysis and insights.
These success stories demonstrate the impact of Blob storage on data management and storage, improving efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for various industries and use cases.
Best Practices for Implementing and Managing Blob Storage
Implementing and managing Blob storage effectively requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Monitor performance: Regularly monitor Blob storage performance to ensure it meets your data management needs. Use tools and analytics to identify trends, issues, and areas for improvement.
- Implement access controls: Implement access controls to ensure data security and privacy. Restrict access to authorized users and applications, and regularly review and update access controls as needed.
- Plan for scalability: Plan for future data growth and design your Blob storage strategy to accommodate scaling and expansion. Use tools and features to automate scaling and ensure efficient use of resources.
- Optimize performance: Optimize Blob storage performance by using features such as caching, tiering, and compression. Regularly review and update your Blob storage configuration to ensure optimal performance.
- Regularly backup data: Regularly backup Blob storage data to ensure data availability and recoverability. Use tools and features to automate backups and ensure efficient use of resources.
- Implement disaster recovery: Implement disaster recovery strategies to ensure data availability and recoverability in the event of a disaster. Use tools and features to automate disaster recovery and ensure efficient use of resources.
By following these best practices, you can ensure effective implementation and management of Blob storage, improving efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness for your data management strategy.
Future Trends and Developments in Blob Storage
Blob storage is continuously evolving, with new features, integrations, and innovations regularly emerging. Here are some future trends and developments to watch:
- Hybrid and multi-cloud solutions: As organizations adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, Blob storage solutions will need to integrate seamlessly across different cloud environments. Expect to see more hybrid and multi-cloud Blob storage solutions in the future.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being increasingly used in data management and storage. Blob storage solutions will need to integrate with AI and ML tools and platforms, enabling more efficient and automated data management and analysis.
- Data analytics and insights: Blob storage solutions will need to provide more advanced data analytics and insights, enabling organizations to extract more value from their data. Expect to see more Blob storage solutions with built-in data analytics and visualization tools.
- Security and compliance: Security and compliance will continue to be critical factors in data management and storage. Blob storage solutions will need to provide advanced security features, such as encryption, access controls, and auditing, to meet the evolving security and compliance requirements.
- Integration with edge computing: As edge computing becomes more prevalent, Blob storage solutions will need to integrate with edge computing devices and platforms, enabling more efficient and effective data management at the edge.
By staying up-to-date with these future trends and developments, organizations can ensure they are leveraging the full potential of Blob storage in their data management strategies.
Conclusion: The Role of Blob Storage in Modern Data Management
Blob storage has become an essential component of modern data management and storage strategies. Its ability to store and manage large volumes of unstructured data cost-effectively and efficiently has made it a popular choice for organizations of all sizes and industries.
By implementing Blob storage in your data management strategy, you can take advantage of its many benefits, including scalability, durability, and accessibility. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the practical steps required for implementation, including selecting the right Blob storage solution, designing a data organization structure, configuring access controls, and monitoring and optimizing performance.
When comparing Blob storage to other storage solutions, it’s essential to consider the specific use case and data requirements. Blob storage may not be the best solution for all scenarios, but its advantages in storing and managing unstructured data make it a valuable addition to any data management strategy.
As Blob storage continues to evolve, organizations can expect to see new features, integrations, and innovations that will further enhance its capabilities and value. By staying up-to-date with these trends and developments, organizations can ensure they are leveraging the full potential of Blob storage in their data management strategies.
In conclusion, Blob storage plays a critical role in modern data management, providing a cost-effective and efficient solution for storing and managing large volumes of unstructured data. By implementing best practices for implementation and management, organizations can take full advantage of its many benefits and ensure their data is secure, accessible, and scalable for the future.