What is Oracle IAM? An Overview of Identity and Access Management
Oracle Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a comprehensive solution for managing user identities and controlling access to resources within an organization. IAM plays a critical role in ensuring security and compliance by providing a centralized platform for managing user access to various systems and applications. With Oracle IAM, organizations can streamline identity management tasks, such as user provisioning, de-provisioning, and access certification, while ensuring that access is granted according to the principle of least privilege.
Oracle IAM is a crucial component of any organization’s security strategy, as it helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems. By implementing a robust IAM solution, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and improve operational efficiency. Moreover, Oracle IAM provides a seamless user experience, enabling users to access the resources they need quickly and easily, while ensuring that access is granted according to the organization’s policies and procedures.
In summary, Oracle IAM is a comprehensive solution for managing user identities and controlling access to resources within an organization. By implementing Oracle IAM, organizations can ensure security and compliance, streamline identity management tasks, and provide a seamless user experience. In the following sections, we will explore the key components of Oracle IAM, its real-world applications and benefits, and how to implement it successfully.
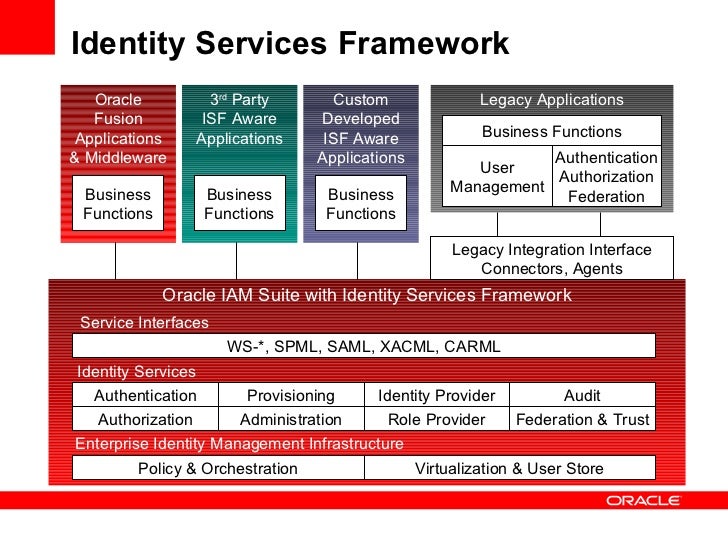
Key Components of Oracle IAM
Oracle IAM is a comprehensive solution that includes several key components, each of which plays a critical role in managing user identities and controlling access to resources. The main components of Oracle IAM are Identity Management, Access Management, and Security.
Identity Management
Identity Management is the process of managing user identities, including creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts. Oracle Identity Management provides a centralized platform for managing user identities across multiple systems and applications. With Oracle Identity Management, organizations can automate identity management tasks, such as user provisioning and de-provisioning, and ensure that user access is granted according to the principle of least privilege.
Access Management
Access Management is the process of controlling access to resources, including applications, data, and services. Oracle Access Management provides a centralized platform for managing access policies and enforcing access controls. With Oracle Access Management, organizations can ensure that users have the right level of access to the right resources at the right time, while preventing unauthorized access.
Security
Security is the process of protecting resources from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Oracle Security provides a range of security features, including authentication, authorization, and auditing, to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of resources. With Oracle Security, organizations can protect sensitive data and systems from internal and external threats, while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
These components work together to provide a robust IAM solution that enables organizations to manage user identities, control access to resources, and ensure security and compliance. By implementing Oracle IAM, organizations can streamline identity management tasks, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Oracle IAM: Real-World Applications and Benefits
Organizations use Oracle IAM to manage user identities, control access to resources, and ensure compliance. By implementing Oracle IAM, organizations can improve security, reduce IT costs, and increase productivity. In this section, we will discuss some of the real-world applications and benefits of using Oracle IAM.
Improved Security
Oracle IAM provides a range of security features, including authentication, authorization, and auditing, to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of resources. With Oracle IAM, organizations can protect sensitive data and systems from internal and external threats, while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. By implementing strong access controls and monitoring user activity, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Reduced IT Costs
Oracle IAM can help organizations reduce IT costs by automating identity management tasks, such as user provisioning and de-provisioning. By automating these tasks, organizations can reduce the workload on IT staff, minimize errors, and ensure that user access is granted according to the principle of least privilege. Moreover, Oracle IAM provides a centralized platform for managing user identities and access policies, reducing the need for multiple point solutions and simplifying IT management.
Increased Productivity
Oracle IAM provides a seamless user experience, enabling users to access the resources they need quickly and easily, while ensuring that access is granted according to the organization’s policies and procedures. By providing a single sign-on (SSO) solution, organizations can reduce the number of passwords users need to remember, minimize help desk calls, and improve user productivity. Moreover, Oracle IAM provides self-service features, enabling users to manage their own profiles and reset their own passwords, further reducing the workload on IT staff.
Compliance
Oracle IAM provides features for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, such as access certification, auditing, and reporting. With Oracle IAM, organizations can demonstrate compliance with regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX, by providing evidence of access controls, user activity, and other compliance-related data. By implementing Oracle IAM, organizations can reduce the risk of non-compliance and associated fines and penalties.
In summary, Oracle IAM provides a range of real-world applications and benefits, including improved security, reduced IT costs, increased productivity, and compliance. By implementing Oracle IAM, organizations can streamline identity management tasks, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
How to Implement Oracle IAM: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing Oracle IAM can be a complex process, but by following best practices and a step-by-step approach, organizations can ensure a successful implementation. In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide to implementing Oracle IAM.
Step 1: Planning
The first step in implementing Oracle IAM is planning. During the planning phase, organizations should define their IAM requirements, identify the components of Oracle IAM that they will implement, and create a project plan. The planning phase should also include a risk assessment and a review of the organization’s current security policies and procedures.
Step 2: Configuration
The second step in implementing Oracle IAM is configuration. During the configuration phase, organizations should configure the components of Oracle IAM that they have chosen to implement. Configuration activities may include setting up user directories, defining access policies, and configuring single sign-on (SSO) solutions.
Step 3: Testing
The third step in implementing Oracle IAM is testing. During the testing phase, organizations should test the configuration of Oracle IAM to ensure that it meets their requirements. Testing activities may include functional testing, performance testing, and security testing.
Step 4: Deployment
The fourth step in implementing Oracle IAM is deployment. During the deployment phase, organizations should deploy Oracle IAM in a production environment. Deployment activities may include migrating user data, configuring connectors to other systems and applications, and training users on the new system.
Step 5: Maintenance and Monitoring
The final step in implementing Oracle IAM is maintenance and monitoring. During the maintenance and monitoring phase, organizations should ensure that Oracle IAM is operating effectively and that any issues are addressed promptly. Maintenance and monitoring activities may include regular audits, user access reviews, and software updates.
In summary, implementing Oracle IAM requires careful planning, configuration, testing, deployment, and maintenance. By following best practices and a step-by-step approach, organizations can ensure a successful implementation and reap the benefits of a robust IAM solution.
Oracle IAM vs. Competitors: A Comparative Analysis
When it comes to Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions, organizations have a variety of options to choose from. In this section, we will compare Oracle IAM to other IAM solutions in the market, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. We will also discuss factors to consider when choosing an IAM solution, such as cost, scalability, and functionality.
Strengths of Oracle IAM
Oracle IAM is a robust and comprehensive IAM solution that offers a wide range of features and functionalities. Some of the strengths of Oracle IAM include:
- Integration: Oracle IAM integrates seamlessly with other systems and applications, such as HR systems, CRM, and cloud services. This enables organizations to streamline workflows, improve data accuracy, and enhance security.
- Scalability: Oracle IAM is highly scalable and can support large and complex organizations with thousands of users and resources.
- Functionality: Oracle IAM offers a wide range of features and functionalities, including Identity Management, Access Management, and Security. This enables organizations to manage user identities, control access to resources, and ensure compliance.
Weaknesses of Oracle IAM
While Oracle IAM is a robust and comprehensive IAM solution, it does have some weaknesses. These include:
- Complexity: Oracle IAM can be complex to implement and manage, requiring specialized skills and knowledge.
- Cost: Oracle IAM can be expensive, especially for large and complex organizations with thousands of users and resources.
- User Interface: Some users have reported that the user interface of Oracle IAM can be difficult to navigate and use.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an IAM Solution
When choosing an IAM solution, organizations should consider several factors, including:
- Cost: The total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, and maintenance costs.
- Scalability: The ability of the IAM solution to scale and support the organization’s growth.
- Functionality: The features and functionalities offered by the IAM solution, including Identity Management, Access Management, and Security.
- Integration: The ability of the IAM solution to integrate with other systems and applications, such as HR systems, CRM, and cloud services.
- User Experience: The ease of use and user experience of the IAM solution.
In summary, when comparing Oracle IAM to other IAM solutions in the market, organizations should consider factors such as cost, scalability, and functionality. While Oracle IAM is a robust and comprehensive IAM solution, it does have some weaknesses, such as complexity and cost. By considering these factors, organizations can choose the IAM solution that best meets their needs and ensures the long-term success of their IAM program.
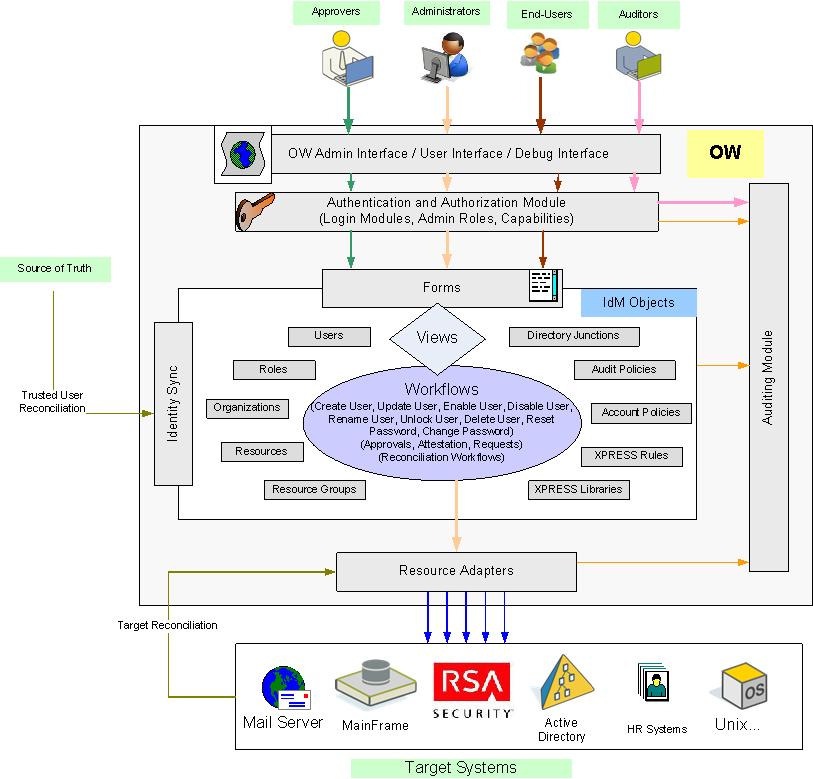
Oracle IAM Integration: Connecting with Other Systems and Applications
In today’s digital landscape, organizations use a variety of systems and applications to manage their operations. From human resources systems to customer relationship management (CRM) tools, these systems contain sensitive data that must be protected. This is where Oracle IAM integration comes in. By integrating Oracle IAM with other systems and applications, organizations can ensure secure access to resources while streamlining workflows and improving data accuracy.
Benefits of Oracle IAM Integration
Integrating Oracle IAM with other systems and applications offers several benefits, including:
- Streamlined Workflows: By integrating Oracle IAM with other systems, organizations can automate workflows and reduce manual processes. For example, user provisioning can be automated, reducing the time and effort required to grant access to resources.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Integration ensures that user data is accurate and up-to-date across all systems. This reduces the risk of errors and improves the overall quality of data.
- Enhanced Security: Integration enables organizations to enforce consistent security policies across all systems and applications. This ensures that access to sensitive data is granted only to authorized users, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
How Oracle IAM Integrates with Other Systems and Applications
Oracle IAM integrates with a variety of systems and applications, including:
- HR Systems: Oracle IAM can integrate with HR systems to automate user provisioning and deprovisioning. This ensures that access to resources is granted only to current employees and revoked when employees leave the organization.
- CRM Tools: Oracle IAM can integrate with CRM tools to ensure that sales and marketing teams have access to the resources they need to do their jobs. This can include customer data, marketing materials, and sales collateral.
- Cloud Services: Oracle IAM can integrate with cloud services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, to ensure secure access to cloud-based resources. This is especially important as more organizations move their operations to the cloud.
Best Practices for Oracle IAM Integration
When integrating Oracle IAM with other systems and applications, organizations should follow best practices, such as:
- Defining Clear Integration Goals: Before integrating Oracle IAM with other systems, organizations should define clear integration goals. This can include streamlining workflows, improving data accuracy, and enhancing security.
- Conducting Thorough Testing: Organizations should conduct thorough testing to ensure that the integration is working as expected. This can include testing user provisioning, deprovisioning, and access to resources.
- Regularly Reviewing Integration: Organizations should regularly review the integration to ensure that it is meeting their needs and that any issues are addressed promptly.
In summary, integrating Oracle IAM with other systems and applications offers several benefits, including streamlined workflows, improved data accuracy, and enhanced security. By following best practices, organizations can ensure a successful integration and stay ahead of the curve in Identity and Access Management.
Oracle IAM Best Practices: Tips for Successful Implementation and Management
Implementing and managing an Oracle IAM solution can be a complex process, but following best practices can help ensure a successful implementation and long-term success. Here are some tips and best practices for implementing and managing Oracle IAM:
1. Conduct Regular Audits
Regularly auditing your Oracle IAM solution can help identify any potential issues or vulnerabilities and ensure that your solution is compliant with industry standards and regulations. Audits should include reviewing user access rights, password policies, and security settings.
2. Implement User Access Reviews
User access reviews can help ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and resources. Regularly reviewing user access rights and removing access for former employees or contractors can help reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
3. Provide Training
Providing training for employees and administrators can help ensure that they understand how to use the Oracle IAM solution effectively and securely. Training should include best practices for password management, access control, and security settings.
4. Implement Role-Based Access Control
Role-based access control (RBAC) can help simplify access management by assigning access rights based on job functions or roles within the organization. This can help reduce the risk of human error and ensure that users have the appropriate level of access to resources.
5. Monitor and Log Activity
Monitoring and logging activity within the Oracle IAM solution can help identify potential security threats and ensure that any issues are addressed promptly. Logs should include user activity, access requests, and security events.
6. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) can help ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and resources. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a fingerprint or a security token, to gain access.
7. Keep Up-to-Date with Patches and Updates
Keeping up-to-date with patches and updates for the Oracle IAM solution can help ensure that the solution is secure and compliant with industry standards and regulations. Patches and updates should be applied as soon as they are available to reduce the risk of vulnerabilities.
8. Work with a Trusted Partner
Working with a trusted partner, such as an Oracle partner or consultant, can help ensure a successful implementation and long-term management of the Oracle IAM solution. A trusted partner can provide expertise, best practices, and support throughout the implementation and management process.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure a successful implementation and long-term management of their Oracle IAM solution. Regular audits, user access reviews, training, role-based access control, monitoring and logging activity, multi-factor authentication, keeping up-to-date with patches and updates, and working with a trusted partner can all help reduce the risk of data breaches, ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, and improve overall security and productivity.
Oracle IAM Future Trends: Preparing for the Next Generation of Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is an ever-evolving field, with new trends and technologies emerging all the time. As we look to the future, it’s clear that artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and biometrics will play a significant role in the next generation of IAM. In this article, we’ll explore how Oracle IAM is preparing for these trends and how organizations can stay ahead of the curve in IAM.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are already being used in IAM to automate processes, improve security, and enhance the user experience. For example, AI and ML can be used to analyze user behavior and detect anomalies, which can help prevent fraud and unauthorized access. Oracle IAM is investing in AI and ML to provide more advanced IAM capabilities, such as intelligent identity analytics and automated access certifications.
Biometrics
Biometrics, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, are becoming increasingly popular in IAM as they offer a more secure and convenient way to authenticate users. Oracle IAM is preparing for the growing use of biometrics by providing biometric authentication options, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, in its IAM solutions. By using biometrics, organizations can reduce the risk of password-related breaches and improve the user experience.
Preparing for the Future of IAM
To prepare for the future of IAM, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Stay informed about the latest IAM trends and technologies, such as AI, ML, and biometrics.
- Regularly review and update their IAM policies and procedures to ensure they are aligned with the latest best practices and regulations.
- Invest in IAM solutions that are flexible, scalable, and able to adapt to changing business needs and technologies.
- Provide training and education for employees and users on IAM best practices and the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
- Work with trusted IAM partners and vendors to ensure they have access to the latest IAM technologies and expertise.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure they are well-prepared for the future of IAM and can take advantage of the latest trends and technologies to improve security, reduce costs, and enhance the user experience.