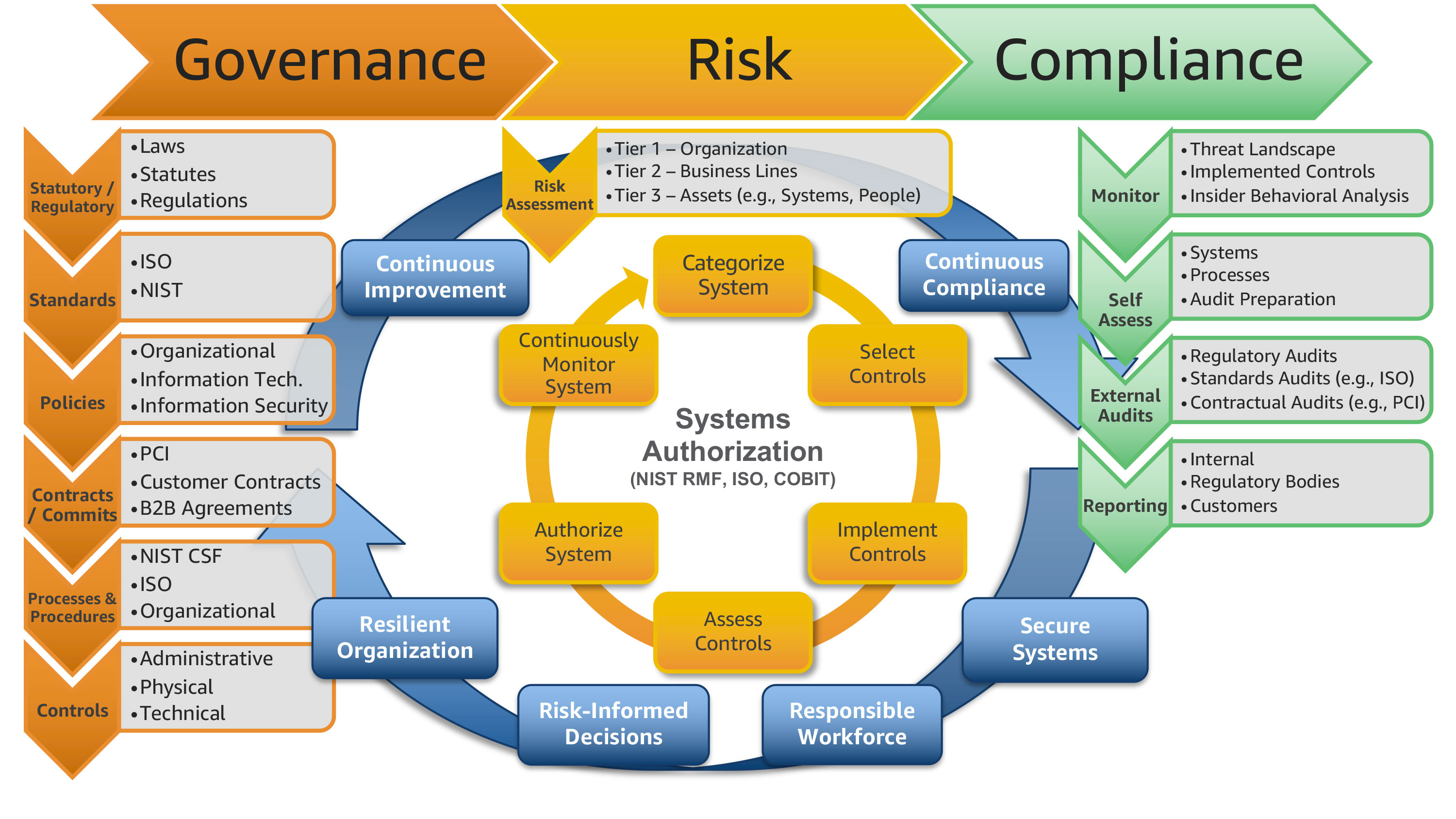
Understanding Sovereignty in Cloud Computing
In the era of cloud computing, sovereignty refers to an organization’s ability to maintain control over its data and comply with regulatory requirements while leveraging cloud services. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure to store and process sensitive information, the need for robust cloud architectures that prioritize sovereignty and compliance has become paramount. This section will delve into the concept of sovereignty in cloud computing, its challenges, and the importance of addressing these issues in cloud architectures.
Cloud sovereignty is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various aspects of data management, including data protection, data localization, and data access. Organizations must ensure that their cloud architectures align with regulatory requirements and industry best practices to maintain control over their data and protect their digital sovereignty. Failure to do so can result in legal and financial consequences, as well as reputational damage.
The challenges associated with cloud sovereignty are numerous and complex. For instance, data protection regulations vary across jurisdictions, making it difficult for organizations to ensure compliance when storing and processing data across multiple regions. Additionally, the dynamic nature of cloud environments can make it challenging to maintain consistent security policies and access controls.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that considers various strategies and best practices. By prioritizing cloud sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures, organizations can ensure the secure and responsible use of cloud services while maintaining control over their data and protecting their digital sovereignty.

Key Components of Compliance in Cloud Architectures
In cloud computing, maintaining compliance is a critical aspect of ensuring cloud sovereignty. Compliance involves adhering to regulatory requirements and industry best practices related to data protection, access control, and audit trails. This section will outline the essential components of compliance in cloud architectures and their role in ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Data Protection
Data protection is a fundamental component of cloud compliance, encompassing various measures to safeguard sensitive information. These measures include encryption, access controls, and backup and disaster recovery strategies. Encryption ensures that data remains confidential during transmission and storage, while access controls limit who can access and modify data. Backup and disaster recovery strategies ensure that data remains available and recoverable in the event of a disaster or data loss.
Access Control
Access control is another critical component of cloud compliance, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information. Access controls can be implemented through various mechanisms, such as user authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), and access control lists (ACLs). User authentication verifies the identity of users before granting access to resources. RBAC restricts access based on a user’s role within an organization, while ACLs define access rights for specific users or groups.
Audit Trails
Audit trails are essential for maintaining compliance in cloud architectures, providing a record of user activity and system events. Audit trails can be used to detect and respond to security incidents, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and identify areas for improvement in security policies and procedures. Logging services, such as AWS CloudTrail and Azure Monitor, can be used to generate audit trails in cloud environments.
By prioritizing these key components of compliance in cloud architectures, organizations can ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and industry best practices while maintaining control over their data and protecting their digital sovereignty.
Strategies for Achieving Sovereignty in Cloud Architectures
In cloud computing, achieving sovereignty is a critical concern for organizations seeking to maintain control over their data and comply with regulatory requirements. This section will explore various strategies for achieving sovereignty in cloud architectures, including data localization, private cloud deployments, and hybrid cloud solutions. We will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and provide real-world examples.
Data Localization
Data localization involves storing and processing data within a specific geographic region to comply with regulatory requirements and ensure data sovereignty. This approach can provide several benefits, including reduced latency, improved performance, and increased control over data. However, data localization can also limit the scalability and flexibility of cloud architectures and increase costs due to the need for multiple data centers.
Private Cloud Deployments
Private cloud deployments involve building and managing a dedicated cloud infrastructure for an organization’s exclusive use. This approach can provide several benefits, including increased control over data, improved security, and customizable infrastructure. However, private cloud deployments can also be expensive to build and maintain, requiring significant resources and expertise.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Hybrid cloud solutions involve integrating private and public cloud infrastructures to create a flexible and scalable cloud architecture. This approach can provide several benefits, including improved cost efficiency, increased scalability, and the ability to leverage the strengths of both private and public clouds. However, hybrid cloud solutions can also introduce complexity and require careful management to ensure data sovereignty and regulatory compliance.
In summary, achieving sovereignty in cloud architectures requires careful consideration of various strategies, including data localization, private cloud deployments, and hybrid cloud solutions. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, and organizations must carefully evaluate their specific needs and regulatory requirements to determine the best approach for their cloud architecture.
Implementing Compliance Measures in Cloud Architectures
In cloud computing, implementing compliance measures is essential for maintaining control over data and ensuring regulatory compliance. This section will offer practical guidance on implementing compliance measures in cloud architectures, including the use of encryption, access management tools, and logging services. We will also address common challenges and provide solutions for maintaining compliance in a dynamic cloud environment.
Encryption
Encryption is a critical security measure for protecting data in transit and at rest. Organizations can use encryption to ensure that data is only accessible to authorized users and to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. In cloud architectures, encryption can be implemented using various methods, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption, and can be applied to data both in transit and at rest.
Access Management Tools
Access management tools are essential for controlling access to cloud resources and ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data. Access management tools can include identity and access management (IAM) solutions, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and access control lists (ACLs). By implementing access management tools, organizations can ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and cloud resources.
Logging Services
Logging services are essential for monitoring cloud architectures and detecting potential security threats. By implementing logging services, organizations can track user activity, monitor system performance, and detect potential security threats. Logging services can include cloud-specific logging solutions, such as AWS CloudTrail and Azure Monitor, or third-party logging solutions.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Implementing compliance measures in cloud architectures can be challenging due to the dynamic and complex nature of cloud environments. Common challenges include managing access to cloud resources, ensuring data protection, and maintaining regulatory compliance. To address these challenges, organizations can implement access management tools, encryption, and logging services, and can establish clear policies and procedures for managing cloud resources and data.
In summary, implementing compliance measures in cloud architectures requires careful consideration of various security measures, including encryption, access management tools, and logging services. By addressing common challenges and establishing clear policies and procedures, organizations can maintain control over data and ensure regulatory compliance in a dynamic cloud environment.
How to Balance Sovereignty and Compliance with Cloud Service Providers
When selecting a cloud service provider (CSP), it is crucial to ensure that the provider can support an organization’s sovereignty and compliance requirements. This section will discuss the importance of selecting the right CSP and establishing a strong partnership to ensure sovereignty and compliance. We will also explore key considerations when evaluating CSPs, such as data protection policies, certifications, and contractual terms.
Data Protection Policies
Organizations must ensure that their CSP has robust data protection policies in place. These policies should include encryption, access controls, and data backup and recovery procedures. Additionally, organizations should ensure that their CSP complies with relevant data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Certifications
CSPs should hold relevant certifications to demonstrate their commitment to security and compliance. These certifications may include ISO 27001, SOC 2, or PCI DSS. Organizations should ensure that their CSP holds the necessary certifications to meet their specific compliance requirements.
Contractual Terms
Organizations should carefully review the contractual terms of their agreement with their CSP. These terms should include provisions for data ownership, data protection, and data breach notification. Additionally, organizations should ensure that their CSP provides adequate service level agreements (SLAs) and disaster recovery plans.
Establishing a Strong Partnership
Establishing a strong partnership with a CSP is essential for ensuring sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures. Organizations should work closely with their CSP to ensure that their cloud environment meets their specific compliance requirements. This partnership should include regular communication, collaboration, and review of security and compliance measures.
In summary, selecting the right CSP and establishing a strong partnership is critical for ensuring sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures. Organizations should carefully evaluate CSPs based on data protection policies, certifications, and contractual terms. By working closely with their CSP, organizations can ensure that their cloud environment meets their specific compliance requirements and maintains control over their data.
Monitoring and Auditing Cloud Architectures for Sovereignty and Compliance
Continuous monitoring and auditing are essential for maintaining sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures. These processes help organizations ensure that their cloud environment adheres to regulatory requirements and industry best practices. In this section, we will provide an overview of available tools and best practices for monitoring and auditing cloud services, including third-party solutions and CSP-specific offerings.
Monitoring Tools
Monitoring tools can help organizations track and analyze cloud activity, detect anomalies, and identify potential security threats. These tools may include log management systems, security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, and cloud-specific monitoring services. Organizations should ensure that their monitoring tools provide real-time alerts, customizable dashboards, and integration with other security and compliance tools.
Auditing Best Practices
Regular audits are essential for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices. Organizations should establish a formal auditing process that includes the following best practices:
- Define clear audit objectives and scope.
- Identify relevant regulations and industry standards.
- Develop audit checklists and procedures.
- Assign qualified personnel to conduct the audit.
- Document audit findings and recommendations.
- Implement corrective actions and verify their effectiveness.
CSP-Specific Offerings
Many CSPs offer monitoring and auditing services that can help organizations ensure sovereignty and compliance in their cloud environment. These services may include compliance reports, security assessments, and activity monitoring. Organizations should carefully review the features and limitations of these services and ensure that they align with their specific compliance requirements.
Third-Party Solutions
Third-party monitoring and auditing solutions can provide organizations with additional visibility and control over their cloud environment. These solutions may include cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools, and cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs). Organizations should carefully evaluate these solutions based on their specific compliance requirements and ensure that they provide adequate coverage and integration with other security and compliance tools.
In summary, continuous monitoring and auditing are essential for maintaining sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures. Organizations should use monitoring tools, follow auditing best practices, and consider CSP-specific offerings and third-party solutions to ensure that their cloud environment adheres to regulatory requirements and industry best practices. By implementing a comprehensive monitoring and auditing strategy, organizations can maintain control over their data and ensure compliance in a dynamic cloud environment.

Addressing Emerging Challenges in Cloud Sovereignty and Compliance
As cloud computing continues to evolve, organizations face new challenges in maintaining sovereignty and compliance in their cloud architectures. Two such challenges are the increasing adoption of multi-cloud environments and the rise of edge computing. In this section, we will discuss these challenges and offer strategies for addressing them.
Multi-Cloud Environments
Many organizations are adopting multi-cloud strategies to take advantage of the unique features and benefits offered by different cloud service providers (CSPs). However, managing multiple cloud environments can create new challenges in ensuring sovereignty and compliance. Organizations must ensure that data protection policies, access controls, and audit trails are consistent across all cloud environments. They must also be aware of any regulatory requirements that may apply to data stored in each cloud.
To address these challenges, organizations should consider implementing a centralized cloud management platform that provides visibility and control over all cloud environments. They should also establish clear policies and procedures for data protection, access control, and auditing that are consistent across all clouds. Additionally, organizations should consider using third-party monitoring and auditing solutions that can provide a unified view of their multi-cloud environment.
Edge Computing
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source, is becoming increasingly popular in IoT, AI, and other data-intensive applications. However, edge computing can create new challenges in ensuring sovereignty and compliance, as data may be processed and stored on devices outside of the organization’s control.
To address these challenges, organizations should establish clear policies and procedures for data protection, access control, and auditing at the edge. They should also consider using edge computing platforms that provide built-in security and compliance features. Additionally, organizations should consider using encryption and access management tools to ensure that data is protected both in transit and at rest.
In summary, the increasing adoption of multi-cloud and edge computing environments is creating new challenges in maintaining sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures. Organizations should consider implementing centralized cloud management platforms, establishing clear policies and procedures, and using third-party monitoring and auditing solutions to address these challenges. By taking a proactive approach to these emerging challenges, organizations can maintain control over their data and ensure regulatory compliance in these complex settings.

Future Trends and Best Practices for Sovereignty and Compliance in Cloud Architectures
As cloud computing continues to mature, organizations must stay informed about emerging trends and best practices to maintain sovereignty and compliance in their cloud architectures. In this section, we will discuss some of these trends and offer guidance on how to implement them effectively.
Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is a security model that assumes that all network traffic is untrusted, regardless of its origin. This model is particularly relevant in cloud environments, where data and applications are distributed across multiple cloud platforms and devices. By implementing Zero Trust Security, organizations can ensure that access to sensitive data and applications is granted only to authorized users and devices, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
To implement Zero Trust Security, organizations should consider using multi-factor authentication, access management tools, and encryption. They should also establish clear policies and procedures for access control and regularly review and update them to ensure they are effective and up-to-date.
Data Governance
Data governance is the process of managing the availability, usability, integrity, and security of data. In cloud environments, data governance is critical to ensuring that data is protected, accessible, and compliant with regulatory requirements. By implementing effective data governance practices, organizations can ensure that they have control over their data, even when it is stored and processed in the cloud.
To implement effective data governance, organizations should consider using data classification tools, data loss prevention solutions, and data catalogs. They should also establish clear policies and procedures for data management and regularly review and update them to ensure they are effective and up-to-date.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming increasingly important in cloud computing, enabling organizations to automate processes, improve efficiency, and gain insights from data. However, AI and ML also present new challenges in maintaining sovereignty and compliance, as they can be used to process and analyze sensitive data in new and unpredictable ways.
To address these challenges, organizations should consider using AI and ML models that are transparent, explainable, and auditable. They should also establish clear policies and procedures for AI and ML development and deployment and ensure that they are compliant with regulatory requirements.
In conclusion, maintaining sovereignty and compliance in cloud architectures requires a proactive and ongoing approach. Organizations must stay informed about emerging trends and best practices and implement them effectively to ensure that their data is protected, accessible, and compliant with regulatory requirements. By implementing Zero Trust Security, effective data governance practices, and transparent and explainable AI and ML models, organizations can maintain control over their data and ensure regulatory compliance in complex cloud environments.