Understanding Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and Their Importance
Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) are fundamental components of modern cloud computing architectures. A VPC is a logically isolated network environment within a public cloud, allowing users to define and manage their network resources, such as subnets, IP addresses, route tables, and network gateways. By creating a VPC, users can benefit from enhanced security, control, and customization.
Connecting VPCs is essential for organizations seeking to achieve increased scalability, resource sharing, and disaster recovery. By connecting VPCs, businesses can seamlessly extend their network infrastructure across different regions, cloud providers, or even on-premises environments. This enables the creation of hybrid or multi-cloud architectures, which can lead to improved performance, cost savings, and business continuity.
When discussing the concept of “connect vpc,” it is crucial to consider various connection methods available, such as VPC peering, VPN connections, and Direct Connect. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations, making it essential to understand their functionality and use cases. By carefully evaluating these factors, organizations can make informed decisions about which connection method best suits their specific needs and requirements.
The Need to Connect VPCs: Linking Networks for Scalability and Flexibility
Connecting Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) is essential for businesses seeking to achieve increased scalability, resource sharing, and disaster recovery. By connecting VPCs, organizations can extend their network infrastructure across different regions, cloud providers, or even on-premises environments. This enables the creation of hybrid or multi-cloud architectures, which can lead to improved performance, cost savings, and business continuity.
Connecting VPCs is particularly important in several scenarios:
- Scalability: As businesses grow, they may need to expand their cloud infrastructure to accommodate increased traffic and resource demands. Connecting VPCs allows organizations to distribute workloads across multiple regions or cloud providers, ensuring optimal performance and availability.
- Resource sharing: Connecting VPCs enables resource sharing between different departments, teams, or business units within an organization. This can help reduce costs and improve collaboration by allowing teams to access shared resources, such as databases, storage, and applications.
- Disaster recovery: In the event of a disaster or service disruption, connecting VPCs can help ensure business continuity by allowing organizations to quickly failover to a secondary site or cloud provider. This can help minimize downtime, protect data, and maintain critical business functions.
- Regulatory compliance: In some cases, businesses may be required to maintain data residency in specific geographic locations due to regulatory requirements. Connecting VPCs can help organizations meet these requirements by allowing them to maintain separate VPCs in different regions while still providing secure, low-latency access to shared resources.
When considering how to “connect vpc,” it is essential to evaluate the various connection methods available, such as VPC peering, VPN connections, and Direct Connect. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations, making it crucial to understand their functionality and use cases. By carefully weighing these factors, organizations can make informed decisions about which connection method best suits their specific needs and requirements.
How to Connect VPCs: Exploring Different Connection Methods
Connecting Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) can be achieved through various methods, each with its unique advantages and limitations. The three primary methods for connecting VPCs are VPC peering, VPN connections, and Direct Connect.
VPC Peering
VPC peering is a method for connecting two VPCs within the same cloud provider. This connection allows resources in both VPCs to communicate with each other as if they were in the same network. VPC peering offers several advantages, such as low-latency connections, private IP address communication, and the ability to route traffic directly between peered VPCs.
VPN Connections
VPN connections enable secure communication between VPCs across different cloud providers or on-premises environments. VPN connections can be established using third-party VPN gateways or cloud provider-managed VPN services. This method is ideal for organizations seeking to create hybrid or multi-cloud architectures while maintaining strong security and privacy.
Direct Connect
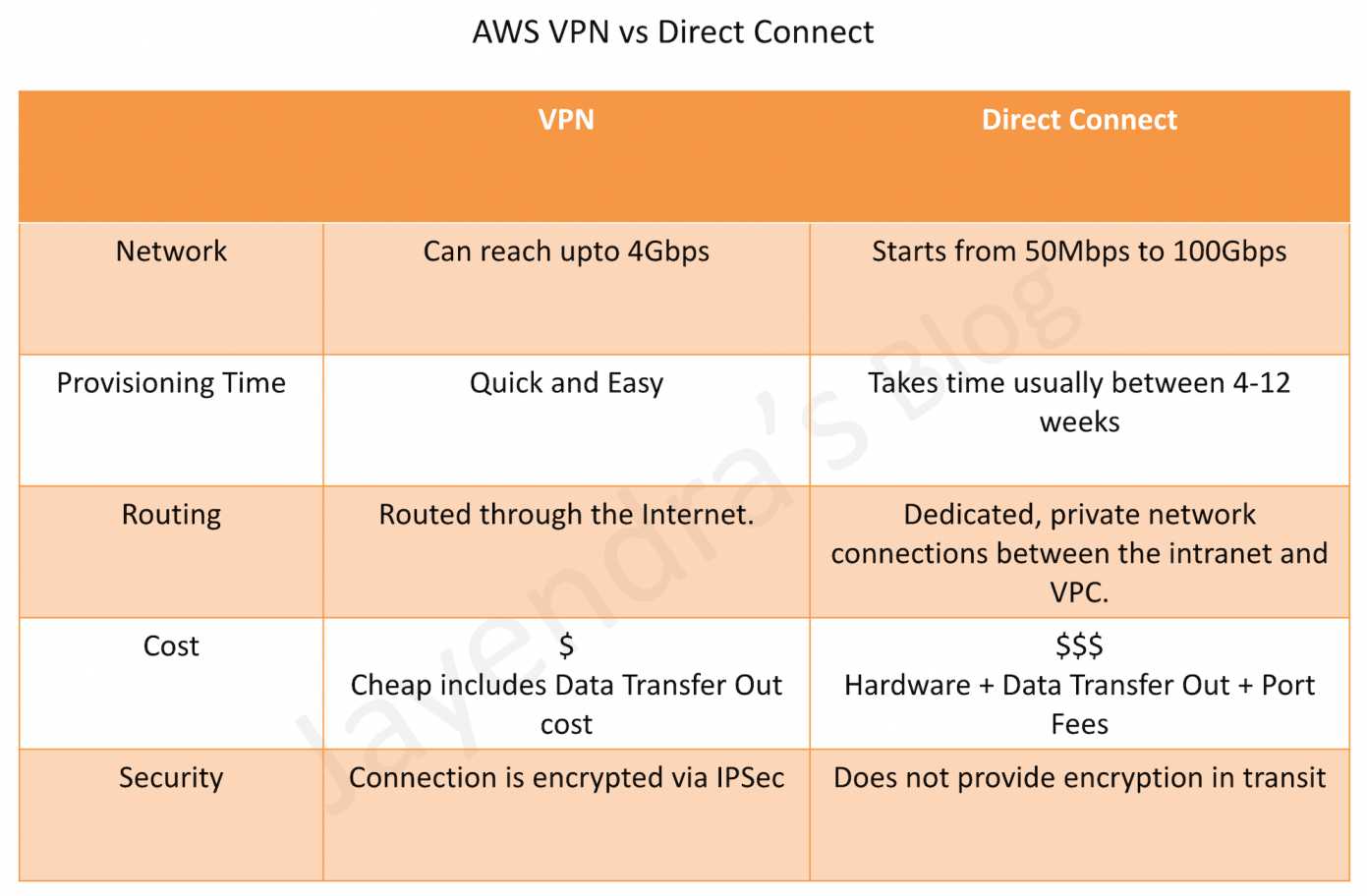
Direct Connect is a dedicated network connection between a user’s on-premises infrastructure and a cloud provider’s network. This method offers improved performance and security compared to VPN connections, as it provides a dedicated, private connection with lower latency and higher bandwidth. However, Direct Connect may be more expensive and complex to set up than other connection methods.
When deciding how to “connect vpc,” it is essential to consider factors such as performance, security, cost, and ease of implementation. Each organization’s specific needs and requirements will influence the best connection method for their use case. By understanding the functionality and use cases of each method, businesses can make informed decisions and effectively link their VPCs for enhanced scalability, resource sharing, and disaster recovery.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kM7zunMeBg8
VPC Peering: Connecting VPCs Within the Same Cloud Provider
VPC peering is a method for connecting two Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) within the same cloud provider. This connection allows resources in both VPCs to communicate with each other as if they were in the same network, offering several advantages such as low-latency connections, private IP address communication, and the ability to route traffic directly between peered VPCs.
Advantages of VPC Peering
VPC peering provides several benefits, including:
- Low-latency connections: Since the VPCs are connected within the same cloud provider, data transfer between peered VPCs can be faster and more efficient than other connection methods.
- Private IP address communication: Resources in peered VPCs can communicate using private IP addresses, ensuring secure and private data transfer.
- Direct routing: Traffic between peered VPCs can be routed directly, reducing the need for additional network hops and improving overall performance.
Limitations of VPC Peering
Despite its advantages, VPC peering has some limitations, such as:
- Same cloud provider: VPC peering is only available within the same cloud provider, meaning it cannot be used to connect VPCs across different cloud providers or on-premises environments.
- Transitive peering: Transitive peering (chaining multiple VPC peering connections together) is not supported, which can limit scalability in certain scenarios.
Step-by-Step Configuration Process
To set up VPC peering, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the VPC dashboard in your cloud provider’s console.
- Select the VPC you want to peer and choose the “Peering Connections” option.
- Create a new peering connection and specify the target VPC and peering details.
- Accept the peering request from the target VPC’s owner (if applicable).
- Update the route tables in both VPCs to allow traffic to flow between the peered networks.
- Test the connection to ensure resources in both VPCs can communicate as expected.
Use Cases for VPC Peering
VPC peering is an ideal solution for scenarios such as:
- Sharing resources between different departments or teams within an organization.
- Creating separate VPCs for development, testing, and production environments.
- Connecting VPCs in different regions for improved performance and disaster recovery.
VPN Connections: Linking VPCs Across Cloud Providers or On-Premises Environments
Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections enable secure communication between Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) across different cloud providers or on-premises environments. VPN connections can be established using third-party VPN gateways or cloud provider-managed VPN services, offering organizations flexibility and strong security when creating hybrid or multi-cloud architectures.
Using Third-Party VPN Gateways
Third-party VPN gateways allow organizations to leverage their existing VPN infrastructure when connecting VPCs. This approach offers several benefits, such as using familiar VPN technologies, maintaining control over VPN configurations, and potentially reducing costs. However, managing VPN connections independently may increase operational overhead and require more in-house expertise.
Cloud Provider-Managed VPN Services
Cloud provider-managed VPN services simplify the process of setting up and managing VPN connections between VPCs. These services typically include pre-configured VPN gateways, automated key management, and easy-to-use interfaces for managing VPN connections. While this approach may be easier to implement, it may also limit customization options and introduce vendor lock-in.
Pros and Cons of VPN Connections
VPN connections offer several advantages, including:
- Strong security: VPN connections encrypt data in transit, ensuring secure communication between VPCs.
- Flexibility: VPN connections can be established between VPCs in different cloud providers or on-premises environments.
- Cost-effective: VPN connections may be more cost-effective than other connection methods, especially when using existing VPN infrastructure.
However, VPN connections also have some limitations, such as:
- Performance: VPN connections may introduce additional latency due to encryption and decryption processes.
- Complexity: Managing VPN connections, especially when using third-party gateways, can be complex and require specialized knowledge.
Use Cases for VPN Connections
VPN connections are an ideal solution for scenarios such as:
- Creating hybrid or multi-cloud architectures that require secure communication between VPCs.
- Connecting on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based VPCs for data migration, backup, or disaster recovery purposes.
- Extending an organization’s existing VPN infrastructure to the cloud.
Direct Connect: Dedicated Connections for Improved Performance and Security
Direct Connect is a service offered by cloud providers that enables organizations to establish a dedicated network connection between their on-premises infrastructure and the cloud provider’s network. This method offers improved performance and security compared to VPN connections, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking to create robust, high-performance connections between their Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs).
Benefits of Direct Connect
Direct Connect offers several advantages, including:
- Improved performance: Dedicated connections provide lower latency and higher bandwidth than VPN connections, ensuring optimal performance for data-intensive applications.
- Enhanced security: Direct Connect establishes a private connection, bypassing the public internet and reducing the risk of data breaches or cyber attacks.
- Cost-effective: Direct Connect can reduce data transfer costs by offering lower pricing for data transferred over dedicated connections compared to internet-based data transfer.
How to Configure Direct Connect
To set up Direct Connect, follow these general steps:
- Order a Direct Connect connection from your cloud provider.
- Establish a cross-connect between your on-premises network and the cloud provider’s network.
- Configure the Direct Connect connection settings, such as VLANs and BGP parameters.
- Update your on-premises and cloud-based route tables to route traffic through the Direct Connect connection.
- Test the connection to ensure resources in both environments can communicate as expected.
Comparing Direct Connect to Other Connection Methods
When comparing Direct Connect to other connection methods, consider the following factors:
- Performance: Direct Connect offers improved performance over VPN connections due to dedicated bandwidth and lower latency.
- Security: Direct Connect provides enhanced security by establishing a private connection between on-premises and cloud-based resources.
- Cost: Direct Connect may be more expensive to set up and maintain than VPN connections, but it can reduce data transfer costs in the long run.
- Ease of implementation: Direct Connect can be more complex to configure than VPN connections, requiring specialized knowledge and resources.
Use Cases for Direct Connect
Direct Connect is an ideal solution for scenarios such as:
- Migrating large amounts of data to the cloud.
- Running data-intensive applications that require high-bandwidth, low-latency connections.
- Establishing a secure connection between on-premises and cloud-based resources for disaster recovery or business continuity purposes.
Selecting the Right Connection Method: Factors to Consider
When connecting Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), organizations must consider various factors to determine the best connection method for their specific needs. Performance, security, cost, and ease of implementation are crucial aspects to evaluate when choosing between VPC peering, VPN connections, and Direct Connect.
Performance
Performance is a critical factor when connecting VPCs. Organizations should consider the following performance aspects:
- Latency: Direct Connect and VPC peering typically offer lower latency than VPN connections due to dedicated connections and private communication.
- Bandwidth: Direct Connect provides dedicated bandwidth, while VPN connections share bandwidth with other internet traffic. Ensure the chosen connection method offers sufficient bandwidth for your workloads.
Security
Security is another essential factor when connecting VPCs. Consider the following security aspects:
- Encryption: VPN connections encrypt data in transit, while Direct Connect and VPC peering do not (unless specifically configured). Evaluate the need for encryption based on your data sensitivity and compliance requirements.
- Access control: Implement strong access control policies to ensure only authorized users and resources can access your VPCs.
Cost
Cost is a significant factor when selecting a connection method. Consider the following cost aspects:
- Setup fees: Direct Connect may have higher setup fees than VPN connections or VPC peering.
- Data transfer costs: Evaluate the cost of data transfer over each connection method. Direct Connect and VPC peering may offer lower data transfer costs than VPN connections.
- Maintenance fees: Consider the ongoing costs of maintaining each connection method.
Ease of Implementation
Ease of implementation is an important factor when connecting VPCs. Consider the following ease of implementation aspects:
- Complexity: Direct Connect can be more complex to set up and manage than VPN connections or VPC peering.
- Expertise: Evaluate the in-house expertise required to implement and maintain each connection method.
Real-Life Scenarios and Examples
Consider the following scenarios and examples to help illustrate the decision-making process:
- Scenario: A company wants to connect two VPCs within the same cloud provider for increased scalability and resource sharing. Solution: VPC peering would be the ideal solution due to its simplicity, low cost, and low latency.
- Scenario: A company needs to connect a VPC to an on-premises environment for disaster recovery purposes. Solution: Direct Connect would be the best option due to its dedicated bandwidth, low latency, and enhanced security.
- Scenario: A company wants to connect VPCs across different cloud providers for increased flexibility and resource sharing. Solution: VPN connections would be the ideal solution, as they offer encryption, flexibility, and compatibility with various cloud providers.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Connected VPCs: Ensuring Optimal Performance
Monitoring and troubleshooting connected Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) is essential for maintaining high availability and performance. Various tools and best practices can help ensure optimal performance across connected VPCs. This section discusses best practices for monitoring and troubleshooting connected VPCs, including the use of cloud provider-specific tools and third-party monitoring solutions.
Cloud Provider-Specific Tools
Most cloud providers offer built-in monitoring and troubleshooting tools for VPC connections. These tools can help you:
- Monitor network performance, latency, and bandwidth usage.
- Identify and diagnose connectivity issues.
- Track resource utilization and allocation.
- Receive alerts and notifications for performance degradation or connectivity issues.
Third-Party Monitoring Solutions
Third-party monitoring solutions can complement cloud provider-specific tools by offering additional features and capabilities, such as:
- Cross-platform compatibility: Monitor and troubleshoot connections between VPCs across different cloud providers and on-premises environments.
- Advanced analytics: Analyze performance data to identify trends, patterns, and potential issues.
- Customizable alerts: Set up custom alerts based on specific performance metrics and thresholds.
- Integration with existing tools: Integrate with existing monitoring, ticketing, and incident management systems.
Best Practices for Monitoring and Troubleshooting Connected VPCs
Follow these best practices to ensure optimal performance and minimize connectivity issues:
- Regularly monitor performance metrics: Track latency, bandwidth usage, and other relevant metrics to identify potential issues before they impact your applications.
- Establish baselines: Understand normal performance levels for your VPC connections to quickly identify anomalies and potential issues.
- Implement proactive alerting: Set up alerts and notifications for performance degradation or connectivity issues to minimize downtime and maintain high availability.
- Perform regular health checks: Schedule regular health checks for your VPC connections to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Document and test troubleshooting procedures: Develop and test troubleshooting procedures to minimize downtime and ensure a consistent response to connectivity issues.