What is Azure Virtual Desktop and Why Connect?
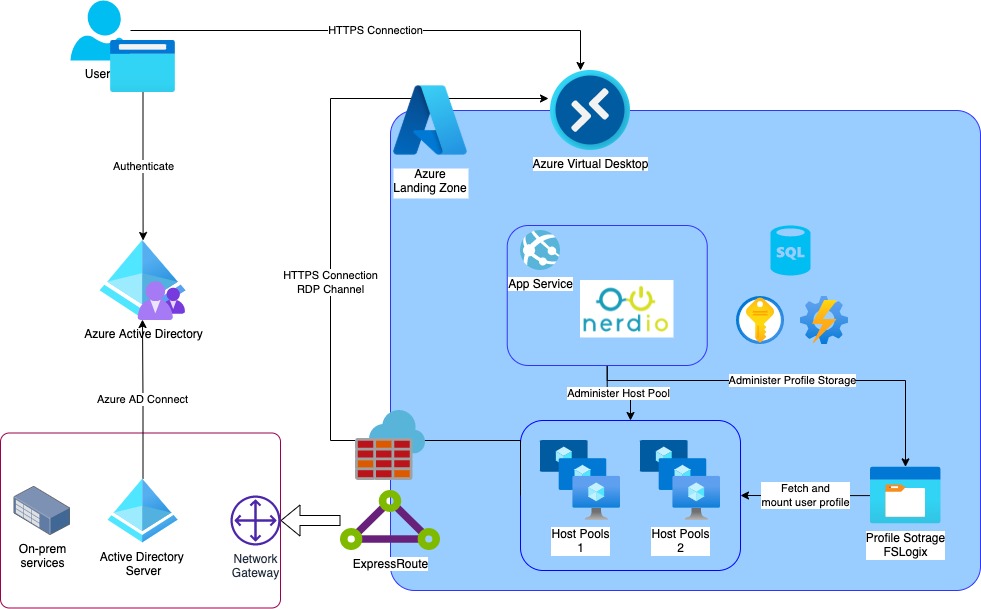
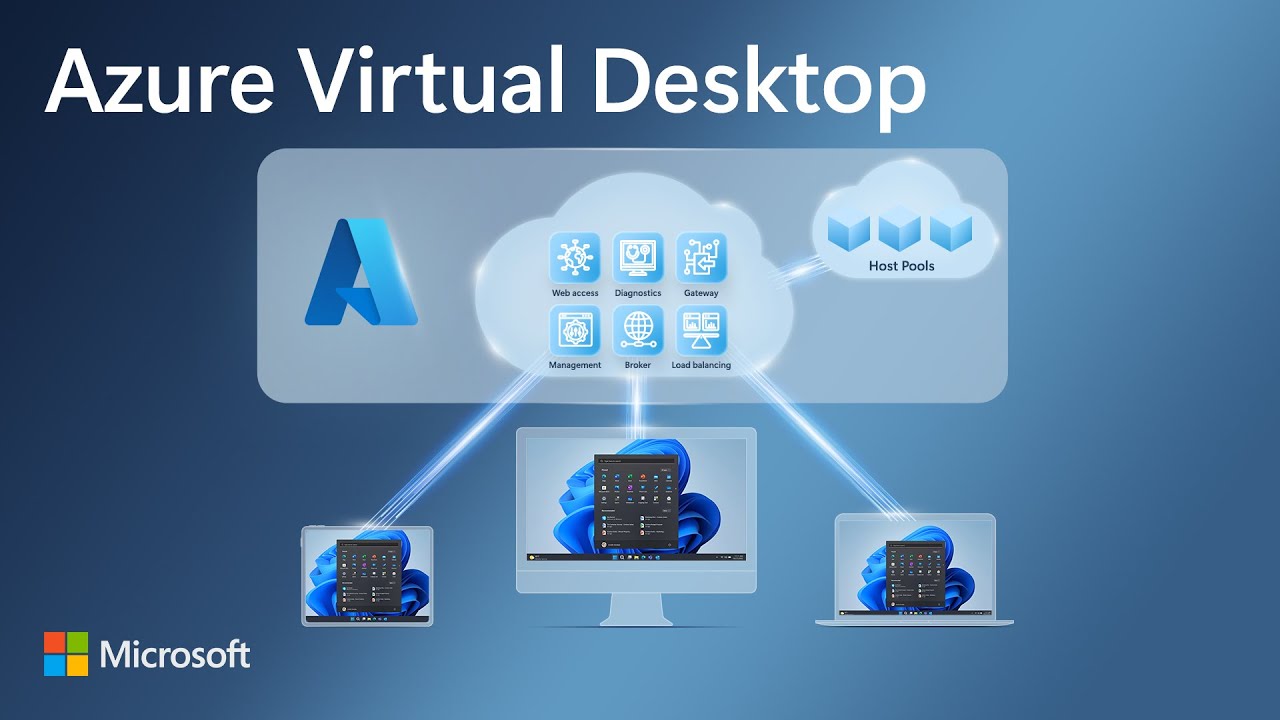
Azure Virtual Desktop is a cloud-based virtualization service provided by Microsoft. It enables users to access remote desktops and applications securely from various devices, including Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and even HTML5 web clients. This flexibility allows organizations to empower their workforces with seamless access to corporate resources, regardless of location or device.
Connecting to Azure Virtual Desktop offers numerous benefits, such as increased flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. Users can work from anywhere, accessing their desktops and applications with an internet connection. Organizations can scale their desktop and application environments up or down based on demand, without the need for significant capital investments in hardware. Additionally, Azure Virtual Desktop can help reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) by consolidating infrastructure, streamlining management, and optimizing licensing costs.
Prerequisites for Connecting to Azure Virtual Desktop
Before connecting to Azure Virtual Desktop, ensure you meet the following prerequisites:
- A compatible device: Desktops, laptops, and mobile devices running Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, or any HTML5-compatible web browser can access Azure Virtual Desktop.
- Supported operating system: Ensure your device runs a supported operating system, such as Windows 10, Windows 11, or macOS. For mobile devices, use the Microsoft Remote Desktop app available on Google Play Store or Apple App Store.
- Active Azure subscription: To use Azure Virtual Desktop, you need an active Azure subscription. You can sign up for a free account to get started.
- Appropriate network and security configurations: Properly configure your network and security settings to ensure seamless connectivity and secure access to Azure Virtual Desktop. This includes setting up firewall rules, configuring network security groups, and enabling multi-factor authentication.
By meeting these prerequisites, you can ensure a smooth and secure connection to Azure Virtual Desktop, allowing you to access your remote desktops and applications from anywhere, at any time.
How to Connect to Azure Virtual Desktop: Step-by-Step Instructions
To connect to Azure Virtual Desktop, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the Azure Portal using your Azure account.
- Navigate to the Virtual Desktop service and create a new host pool or select an existing one.
- Install the Remote Desktop client on your device or use the Windows Virtual Desktop client for web access.
- Configure the Remote Desktop client with the necessary details, such as the host pool name, resource address, and your Azure AD credentials.
- Launch the remote desktop session and start accessing your applications and desktops securely.
For detailed instructions, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Connecting to Azure Virtual Desktop may sometimes encounter issues, such as authentication errors, network latency, and firewall restrictions. Here are some solutions and workarounds to help you maintain a stable connection:
-
Authentication Errors
Ensure you are using the correct Azure AD credentials and that your account has the necessary permissions. If issues persist, try resetting your password or contact your Azure administrator.
-
Network Latency
Optimize your network connection by adjusting display settings, such as reducing color depth and resolution. Additionally, leverage Azure’s global network of data centers to minimize latency and improve responsiveness.
-
Firewall Restrictions
Configure your firewall to allow traffic from Azure Virtual Desktop. This includes allowing traffic on TCP port 3389 for Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and any other required ports for your specific use case.
For more information on troubleshooting common connection issues, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
Securing Your Connection to Azure Virtual Desktop
To ensure a secure connection to Azure Virtual Desktop, follow these best practices:
-
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide at least two forms of authentication. Enable MFA for your Azure AD accounts to protect against unauthorized access.
-
Implement Network Security Groups
Configure network security groups to control inbound and outbound traffic to your Azure Virtual Desktop resources. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures only approved traffic reaches your resources.
-
Configure Conditional Access Policies
Conditional access policies allow you to control access to Azure Virtual Desktop based on specific conditions, such as user location, device, and application. Implement these policies to enhance security and reduce the risk of data breaches.
-
Adhere to Microsoft’s Security Recommendations and Guidelines
Microsoft provides comprehensive security recommendations and guidelines for Azure Virtual Desktop. Stay up-to-date with these guidelines and follow best practices to ensure a secure connection.
For more information on securing your connection to Azure Virtual Desktop, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
Optimizing Performance for Azure Virtual Desktop Connections
To ensure optimal performance when connecting to Azure Virtual Desktop, consider the following tips and strategies:
-
Adjust Display Settings
Adjusting display settings, such as color depth and resolution, can help minimize latency and improve responsiveness. Lower settings may reduce the visual quality but can significantly improve performance on less powerful devices.
-
Use Quality of Service (QoS) Policies
QoS policies help prioritize network traffic and ensure that critical applications, such as Azure Virtual Desktop, receive the necessary bandwidth. Implement QoS policies to maintain consistent performance and prevent network congestion.
-
Leverage Azure’s Global Network of Data Centers
Azure’s global network of data centers allows you to place your Azure Virtual Desktop resources closer to your users, reducing latency and improving performance. Consider the location of your users and resources when setting up your Azure Virtual Desktop environment.
-
Monitor and Adjust Resource Allocation
Monitor the resource usage of your Azure Virtual Desktop environment and adjust resource allocation as needed. Adding or removing resources can help maintain optimal performance and minimize costs.
For more information on optimizing performance for Azure Virtual Desktop connections, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
Monitoring and Managing Azure Virtual Desktop Connections
Monitoring and managing Azure Virtual Desktop connections is crucial for ensuring seamless connectivity for end-users. Azure provides several built-in tools, such as Azure Monitor and Azure Log Analytics, to help administrators track usage, diagnose issues, and maintain optimal performance.
-
Azure Monitor
Azure Monitor collects data from various sources, including Azure Virtual Desktop, and provides a centralized location for monitoring and managing your resources. With Azure Monitor, you can:
- Create custom alerts and notifications based on specific conditions or thresholds.
- Visualize performance metrics and trends using charts and graphs.
- Integrate with Azure Log Analytics for deeper analysis and troubleshooting.
-
Azure Log Analytics
Azure Log Analytics is a powerful tool for analyzing and troubleshooting log data from various sources, including Azure Virtual Desktop. With Azure Log Analytics, you can:
- Search and analyze log data to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
- Create custom queries and visualizations to gain insights into your Azure Virtual Desktop environment.
- Integrate with Azure Monitor for real-time alerting and notifications.
For more information on monitoring and managing Azure Virtual Desktop connections, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.
Exploring Advanced Features and Scenarios for Azure Virtual Desktop
Azure Virtual Desktop offers several advanced features and scenarios that can help organizations maximize their investment and streamline their virtualization efforts. Here are a few examples:
-
Using Windows 10 Multi-Session
Windows 10 Multi-Session is a new deployment option for Azure Virtual Desktop that allows multiple concurrent users to connect to a single Windows 10 virtual machine. This option can help reduce costs and simplify management by allowing organizations to use a single image for multiple users.
-
Integrating with Microsoft 365
Azure Virtual Desktop integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365, allowing users to access their familiar Office applications and data from anywhere. This integration can help improve productivity and collaboration, especially for organizations with remote or distributed workforces.
-
Deploying Applications with Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Templates
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates provide a way to automate the deployment and configuration of Azure Virtual Desktop resources. By using ARM templates, organizations can ensure consistent and repeatable deployments, reduce errors, and save time.
To learn more about these and other advanced features and scenarios for Azure Virtual Desktop, refer to the official Microsoft documentation.