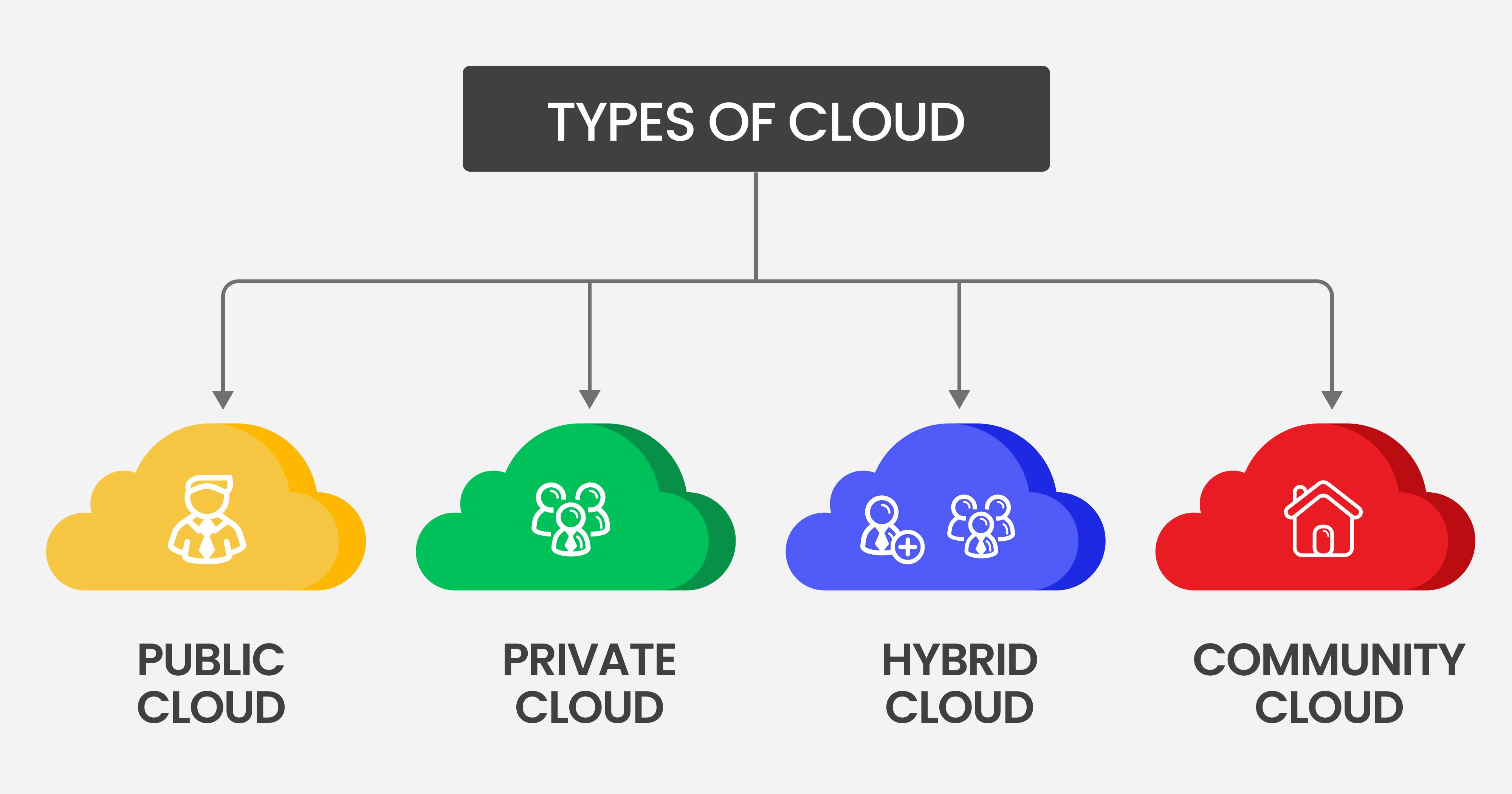
What is Cloud Computing?
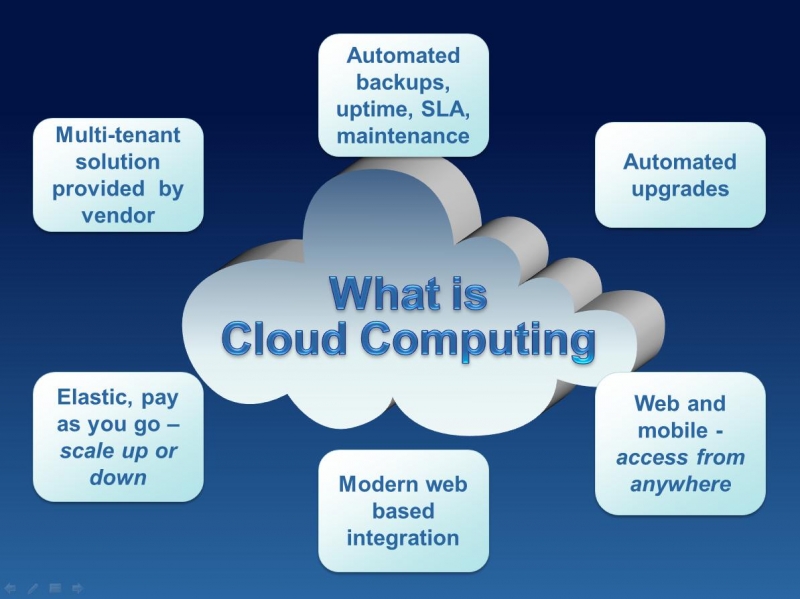
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing resources—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. You can think of cloud computing as the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. Cloud computing allows businesses and individuals to use shared computing resources rather than building, operating, and maintaining their own infrastructure and services in-house. This sharing of resources is what makes cloud computing a cost-effective and efficient solution for many organizations.
One of the key benefits of cloud computing is its ability to provide cost savings. By using shared resources, organizations can reduce the costs associated with building and maintaining their own infrastructure. Additionally, cloud computing offers scalability, allowing organizations to easily increase or decrease their computing resources as needed. This flexibility can lead to significant cost savings, as organizations only pay for the resources they use.
Another major advantage of cloud computing is its accessibility. With cloud computing, users can access their computing resources and data from anywhere with an Internet connection. This accessibility allows for increased collaboration and productivity, as team members can work together from remote locations.
In summary, cloud computing is a delivery model for computing services that offers cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. By using shared resources and paying only for what they use, organizations can reduce their IT costs and increase their flexibility. Additionally, cloud computing’s accessibility allows for increased collaboration and productivity.
The Different Cloud Services Available
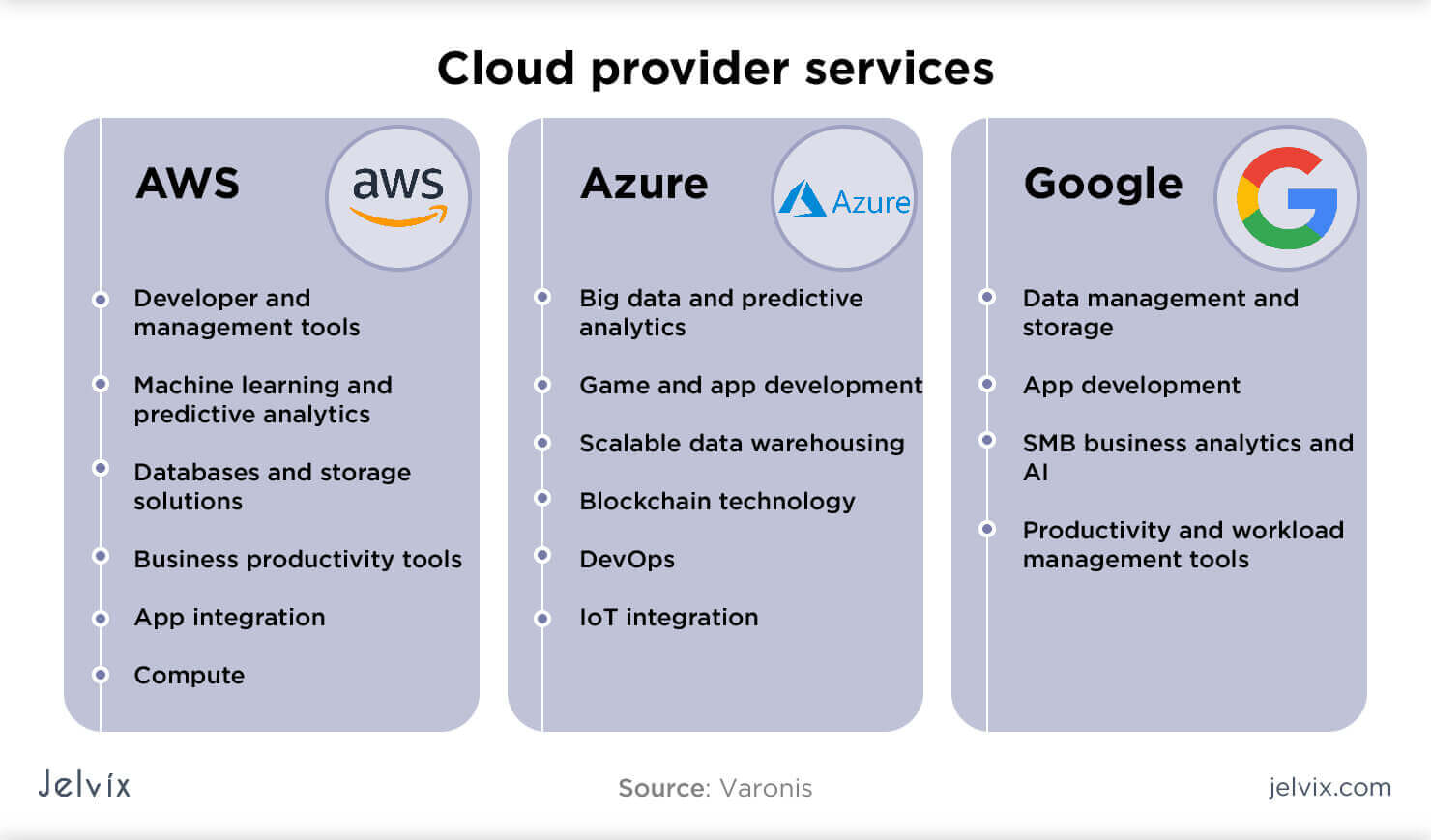
Cloud services can be categorized into three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each type of cloud service offers different levels of control, management, and functionality. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) refers to the delivery of computing infrastructure—such as servers, storage, and networking—over the Internet. With IaaS, organizations can rent computing resources on a pay-per-use basis, allowing them to scale up or down as needed. IaaS is often used by organizations that want to maintain control over their computing resources, but do not want to build and maintain their own infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) refers to the delivery of a platform for developing, running, and managing applications. With PaaS, organizations can focus on building and deploying their applications, without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS is often used by organizations that want to develop and deploy applications quickly, without having to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS) refers to the delivery of software applications over the Internet. With SaaS, organizations can access and use software applications—such as email, customer relationship management (CRM), and human resources (HR)—without having to install and run the software on their own computers. SaaS is often used by organizations that want to use software applications without having to manage the underlying infrastructure.
When choosing a cloud service, it is important to consider the organization’s needs and requirements. IaaS is often used by organizations that want to maintain control over their computing resources, while PaaS is often used by organizations that want to develop and deploy applications quickly. SaaS, on the other hand, is often used by organizations that want to use software applications without having to manage the underlying infrastructure.
In summary, cloud services can be categorized into three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each type of cloud service offers different levels of control, management, and functionality. By understanding the differences between these services and their use cases, organizations can choose the right cloud service to meet their needs and requirements.
Benefits of Cloud Services
Cloud services offer a number of benefits to businesses and organizations, including increased security, reduced maintenance, and improved collaboration. One of the key benefits of cloud services is increased security. Cloud service providers have the resources and expertise to implement robust security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption. These security measures help to protect sensitive data and applications from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Another benefit of cloud services is reduced maintenance. With cloud services, organizations no longer have to worry about maintaining their own computing infrastructure. Instead, the cloud service provider is responsible for maintaining the infrastructure, freeing up organizations to focus on their core business activities.
Cloud services also offer improved collaboration. With cloud services, team members can access and share data and applications from anywhere with an Internet connection. This accessibility allows for increased collaboration and productivity, as team members can work together from remote locations.
In addition to these benefits, cloud services also offer cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. By using shared resources and paying only for what they use, organizations can reduce their IT costs and increase their flexibility. Additionally, cloud computing allows for easy scaling of resources, allowing organizations to quickly and easily increase or decrease their computing resources as needed.
In summary, cloud services offer a number of benefits to businesses and organizations, including increased security, reduced maintenance, and improved collaboration. By using shared resources and paying only for what they use, organizations can reduce their IT costs and increase their flexibility. Additionally, cloud computing allows for easy scaling of resources, allowing organizations to quickly and easily increase or decrease their computing resources as needed.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider
Choosing the right cloud service provider is an important decision for any business or organization. With so many cloud service providers to choose from, it can be difficult to know where to start. Here are some tips on how to select the right cloud service provider:
Define your needs and requirements. Before selecting a cloud service provider, it is important to define your needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the type of cloud service you need (IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS), the amount of computing resources you require, and any specific features or functionality you need.
Consider cost. Cost is an important factor to consider when choosing a cloud service provider. Be sure to compare the prices of different providers, taking into consideration any additional costs (such as data transfer fees) that may apply.
Evaluate reliability. Reliability is another important factor to consider when choosing a cloud service provider. Look for providers that offer uptime guarantees and have a proven track record of reliability.
Assess support. Support is an important consideration when choosing a cloud service provider. Look for providers that offer 24/7 support and have a reputation for providing excellent customer service.
Research security. Security is a top concern for many businesses and organizations when it comes to cloud computing. Be sure to research the security measures offered by different cloud service providers, and choose a provider that has a strong focus on security.
Consider scalability. Scalability is an important factor to consider when choosing a cloud service provider. Look for providers that offer the ability to easily scale up or down as needed, to ensure that you have the right amount of computing resources at all times.
Evaluate integration. Integration is another important factor to consider when choosing a cloud service provider. Look for providers that offer easy integration with your existing systems and applications.
Read reviews and case studies. Reading reviews and case studies can provide valuable insights into the experiences of other businesses and organizations with different cloud service providers.
In summary, choosing the right cloud service provider is an important decision for any business or organization. By considering factors such as cost, reliability, support, security, scalability, integration, and reviews, you can select a provider that meets your needs and requirements.
Real-World Applications of Cloud Services
Cloud services have become increasingly popular in recent years, with businesses and organizations of all sizes implementing them to improve their operations and reduce costs. Here are some real-world examples of businesses and organizations that have successfully implemented cloud services:
Netflix: Netflix is a leading streaming service that uses cloud services to deliver content to its millions of subscribers. By using cloud services, Netflix has been able to scale its operations and improve its reliability, while also reducing its costs.
Amazon: Amazon is one of the largest retailers in the world, and it uses cloud services to power its e-commerce platform and other services. By using cloud services, Amazon has been able to improve its scalability and flexibility, while also reducing its IT costs.
The City of Los Angeles: The City of Los Angeles has implemented cloud services to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of its operations. By using cloud services, the city has been able to reduce its IT costs, improve its disaster recovery capabilities, and enhance its cybersecurity.
The American Red Cross: The American Red Cross uses cloud services to support its disaster response efforts. By using cloud services, the American Red Cross has been able to improve its ability to quickly and effectively respond to disasters, while also reducing its costs.
GE Healthcare: GE Healthcare uses cloud services to support its medical imaging and other healthcare technologies. By using cloud services, GE Healthcare has been able to improve the reliability and performance of its technologies, while also reducing its costs.
In each of these examples, cloud services have provided significant benefits to the business or organization. By improving scalability, reliability, and flexibility, while also reducing costs, cloud services have become an essential tool for modern businesses and organizations.
How to Migrate to Cloud Services
Migrating to cloud services can provide numerous benefits for businesses and organizations, including cost savings, increased scalability, and improved accessibility. However, the migration process can be complex and time-consuming, and it is important to plan and execute the migration carefully to ensure a smooth transition. Here are the steps involved in migrating to cloud services:
Planning: The first step in migrating to cloud services is to plan the migration. This includes identifying the applications and data that will be migrated, as well as the cloud service provider that will be used. It is important to consider factors such as cost, reliability, and support when selecting a cloud service provider.
Preparation: Once the planning phase is complete, the next step is to prepare for the migration. This includes configuring the cloud environment, setting up user accounts, and testing the migration process. It is also important to ensure that all data and applications are backed up and that any necessary updates or patches are applied.
Execution: The next step is to execute the migration. This involves transferring the data and applications to the cloud environment and configuring them for use in the cloud. It is important to monitor the migration process closely to ensure that it is completed successfully and to address any issues that may arise.
Testing: After the migration is complete, it is important to test the applications and data in the cloud environment to ensure that they are functioning properly. This includes testing connectivity, performance, and security.
Optimization: Once the migration is complete and the applications and data are functioning properly, the next step is to optimize the cloud environment. This includes configuring settings for performance, security, and cost, and monitoring the environment to ensure that it is running efficiently.
In summary, migrating to cloud services can provide numerous benefits, but it is important to plan and execute the migration carefully. By following the steps outlined above, businesses and organizations can ensure a smooth transition to the cloud and take advantage of the many benefits that cloud services have to offer.
Best Practices for Cloud Service Management
Cloud services offer numerous benefits for businesses and organizations, including cost savings, increased scalability, and improved accessibility. However, it is important to manage cloud services properly to ensure that they are running efficiently and securely. Here are some best practices for managing cloud services:
Regular backups: It is essential to perform regular backups of all data and applications in the cloud environment. This will ensure that data can be recovered in the event of a failure or outage.
Monitoring: It is important to monitor cloud services continuously to ensure that they are running efficiently and to detect any issues that may arise. This includes monitoring for security threats, performance issues, and other potential problems.
Optimization: Cloud services should be optimized for performance, security, and cost. This includes configuring settings for each of these areas and monitoring the environment to ensure that it is running efficiently.
Security: Security is a top concern for businesses and organizations using cloud services. It is important to implement strong security measures, such as firewalls, access controls, and encryption, to protect data and applications in the cloud.
User management: User management is an important aspect of cloud service management. It is important to ensure that only authorized users have access to cloud services and that access is granted on a need-to-know basis.
Compliance: Businesses and organizations using cloud services must ensure that they are in compliance with all relevant regulations and standards. This includes regulations related to data privacy, security, and other areas.
Disaster recovery: It is important to have a disaster recovery plan in place for cloud services. This plan should include procedures for recovering data and applications in the event of a failure or outage.
In summary, managing cloud services properly is essential for ensuring that they are running efficiently and securely. By following the best practices outlined above, businesses and organizations can maximize the benefits of cloud services and minimize the risks associated with them.
The Future of Cloud Computing and Cloud Services
Cloud computing and cloud services have revolutionized the way businesses and organizations operate, providing numerous benefits such as cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. As we look to the future, it is clear that cloud computing will continue to play a significant role in the way we use and manage technology. Here are some emerging trends and technologies in cloud computing and cloud services, and their potential impact on businesses and organizations:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are becoming increasingly important in cloud computing, with many businesses and organizations using these technologies to analyze data, automate processes, and make better decisions. In the future, we can expect to see even more advanced AI and ML capabilities in cloud services, providing businesses and organizations with even more powerful tools for data analysis and automation.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing
The IoT and edge computing are becoming increasingly important in cloud computing, with many businesses and organizations using these technologies to collect and analyze data from connected devices. In the future, we can expect to see even more advanced IoT and edge computing capabilities in cloud services, providing businesses and organizations with even more powerful tools for data collection and analysis.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a new approach to cloud computing that allows businesses and organizations to run applications and services without having to manage servers. In the future, we can expect to see even more advanced serverless computing capabilities in cloud services, providing businesses and organizations with even more flexibility and scalability.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Environments
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments are becoming increasingly common, with many businesses and organizations using multiple cloud providers and on-premises infrastructure to meet their needs. In the future, we can expect to see even more advanced multi-cloud and hybrid cloud capabilities in cloud services, providing businesses and organizations with even more flexibility and choice.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a new and emerging technology that has the potential to revolutionize cloud computing. With its ability to perform complex calculations much faster than traditional computers, quantum computing could provide businesses and organizations with even more powerful tools for data analysis and problem-solving.
In conclusion, the future of cloud computing and cloud services is bright, with emerging trends and technologies providing businesses and organizations with even more powerful tools for data analysis, automation, and problem-solving. By staying up-to-date with these trends and technologies, businesses and organizations can take advantage of the many benefits that cloud computing has to offer.