What is Cloud Computing? Understanding the Basics
Cloud computing is a revolutionary technology that enables on-demand access to shared computing resources over the internet. These resources include servers, storage, databases, software, and analytics. Instead of managing these resources on-premises, organizations can now leverage cloud computing essentials to access and utilize them remotely, paying only for what they use and when they use it. This paradigm shift has led to significant cost savings, increased efficiency, and greater flexibility for businesses worldwide.
The three primary service models in cloud computing are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides users with virtualized computing resources, such as servers and storage, which they can manage and maintain. PaaS offers a platform for application development, testing, and deployment, handling the underlying infrastructure. SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Digital Transformation
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in digital transformation, empowering businesses to scale, adapt, and innovate at an unprecedented pace. By providing on-demand access to a virtually unlimited pool of computing resources, cloud computing essentials enable organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, customer needs, and competitive pressures.
One of the primary advantages of cloud computing is its ability to drive cost savings. Traditional on-premises IT infrastructures often require significant upfront capital investments and ongoing maintenance costs. Cloud computing, on the other hand, allows businesses to pay only for the resources they consume, reducing total cost of ownership and freeing up resources for other strategic initiatives.
Cloud computing also fosters scalability and flexibility. Organizations can easily scale their computing resources up or down as needed, ensuring optimal performance during peak demand while minimizing waste during periods of low usage. Furthermore, cloud computing enables seamless integration with other digital tools and platforms, allowing businesses to create cohesive, end-to-end digital ecosystems that support agile, data-driven decision-making.
Real-life examples of cloud computing’s transformative power abound. For instance, Netflix, a leading entertainment streaming service, leverages cloud computing to deliver high-quality content to millions of users worldwide. By utilizing AWS’s scalable infrastructure, Netflix can handle spikes in demand, ensure rapid content delivery, and continuously innovate to stay ahead of the competition.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly enhance an organization’s IT capabilities. Among these advantages are on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service. Together, these benefits form the foundation of cloud computing essentials and contribute to its transformative impact on modern IT infrastructure.
On-demand self-service allows users to quickly and easily provision computing resources, such as servers, storage, and applications, without requiring human interaction with the service provider. This empowers businesses to respond swiftly to changing demands and opportunities, fostering agility and innovation.
Broad network access is another critical benefit of cloud computing. Users can access cloud services via standard mechanisms, such as web browsers and mobile devices, ensuring seamless integration with existing IT environments and enabling true location-independent computing.
Resource pooling is the practice of combining computing resources from multiple users, allowing them to share and utilize these resources as needed. Cloud computing providers dynamically allocate and reallocate resources to meet user demand, ensuring optimal utilization and cost savings.
Rapid elasticity is the ability of cloud computing resources to scale up or down quickly and efficiently in response to changing demands. This enables businesses to match their computing resources to their needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost management.
Measured service is the practice of monitoring and controlling the usage of cloud computing resources, allowing users to pay only for what they consume. This transparency and cost predictability are essential for businesses seeking to optimize their IT budgets and achieve maximum value from their cloud investments.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Model
Choosing the right cloud service model is crucial for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of cloud computing essentials. The three primary service models—IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS—each offer distinct advantages and trade-offs, and understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides users with virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet. IaaS allows businesses to maintain control over their operating systems, applications, and data while offloading the management of physical infrastructure to the cloud provider. This model is ideal for organizations seeking flexibility, scalability, and cost savings without sacrificing control and customization.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS offers a platform for application development, testing, and deployment, handling the underlying infrastructure and allowing businesses to focus on building and delivering software. PaaS provides a complete development and deployment environment, including databases, middleware, and operating systems, enabling rapid application development and iteration. This model is best suited for organizations looking to accelerate their software development lifecycle and reduce the time and resources required to manage infrastructure.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. SaaS applications are typically subscription-based, providing businesses with predictable costs and easy access to the latest software features and updates. This model is ideal for organizations seeking to minimize the time, resources, and expertise required to manage and maintain software applications, allowing them to focus on their core business functions.
When selecting a cloud service model, organizations should consider factors such as control, customization, resource management, and cost. IaaS offers the most control and customization but requires more resources to manage. PaaS simplifies infrastructure management while enabling rapid application development, and SaaS reduces the burden of software management but offers limited control and customization. By carefully evaluating their needs and constraints, businesses can choose the cloud service model that best aligns with their strategic objectives and IT requirements.
Top Infrastructure Providers and Their Offerings
When it comes to cloud computing, several major infrastructure providers offer a wide range of services and solutions designed to meet the diverse needs of businesses worldwide. This section provides an overview of the top cloud infrastructure providers, comparing their services, pricing, and unique selling points.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the leading cloud infrastructure provider, offering a vast array of services, including computing, storage, databases, and analytics. AWS boasts an extensive global network of data centers, ensuring low-latency connections and high availability. Its pay-as-you-go pricing model and flexible service options make AWS an attractive choice for businesses of all sizes.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a robust cloud platform that offers services in computing, storage, networking, and analytics. Azure’s hybrid cloud capabilities, seamless integration with Microsoft products, and strong focus on security make it an ideal choice for businesses already using Microsoft technologies. Azure also supports various programming languages and frameworks, catering to a wide range of developer preferences.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a powerful and scalable cloud infrastructure provider that offers services in computing, storage, networking, and machine learning. GCP is renowned for its innovative technologies, such as Kubernetes and TensorFlow, and its commitment to open-source software. Its global network, competitive pricing, and focus on sustainability make GCP an appealing option for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud is a full-stack cloud platform that provides services in computing, storage, networking, and AI. IBM Cloud’s expertise in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics sets it apart from other providers. Its focus on security, compliance, and hybrid cloud solutions makes IBM Cloud an excellent choice for businesses operating in highly regulated industries.
When selecting a cloud infrastructure provider, businesses should consider factors such as service offerings, pricing, performance, security, and support. By carefully evaluating their needs and constraints, organizations can choose the provider that best aligns with their strategic objectives and IT requirements, ultimately harnessing the full potential of cloud computing essentials.
How to Migrate to the Cloud: Best Practices
Migrating to the cloud can offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, increased scalability, and enhanced agility. However, the process of moving IT infrastructure and applications to the cloud requires careful planning and execution. This section provides a step-by-step guide for migrating to the cloud, covering assessment, planning, migration, and optimization. Additionally, we’ll discuss best practices and potential challenges to help ensure a successful transition.
Step 1: Assessment
Begin by evaluating your current IT infrastructure, applications, and data to determine which components are suitable for migration. Identify business objectives, performance requirements, and security constraints. This assessment will help you establish a solid foundation for your cloud migration strategy.
Step 2: Planning
Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the timeline, resources, and milestones required to execute the migration. Consider factors such as application dependencies, data migration strategies, and the selection of a cloud service provider. Ensure that your plan aligns with your business objectives and IT requirements.
Step 3: Migration
Execute the migration according to your plan, carefully monitoring the process to ensure a smooth transition. Implement appropriate security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect your data and systems during the migration. Address any issues or discrepancies as they arise, and maintain open communication with all stakeholders to keep them informed of the migration’s progress.
Step 4: Optimization
Once the migration is complete, focus on optimizing your cloud environment to maximize its benefits. Implement cost management strategies, such as reserved instances or spot instances, to control cloud spending. Continuously monitor and analyze performance metrics to identify opportunities for improvement and ensure that your cloud infrastructure meets your evolving business needs.
Best Practices
When migrating to the cloud, consider the following best practices:
- Collaborate with stakeholders to ensure a shared understanding of the migration’s objectives, benefits, and challenges.
- Choose a cloud service provider that aligns with your business needs, IT requirements, and budget.
- Implement a robust testing strategy to validate the functionality and performance of your applications and data in the cloud environment.
- Establish a disaster recovery and business continuity plan to minimize downtime and data loss in the event of a disruption.
- Regularly review and update your cloud security policies to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Potential Challenges
Be aware of the following potential challenges when migrating to the cloud:
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Integration with existing systems and applications
- Ensuring compliance with industry regulations
- Managing cloud costs and avoiding overspending
- Addressing staff skills gaps and training needs
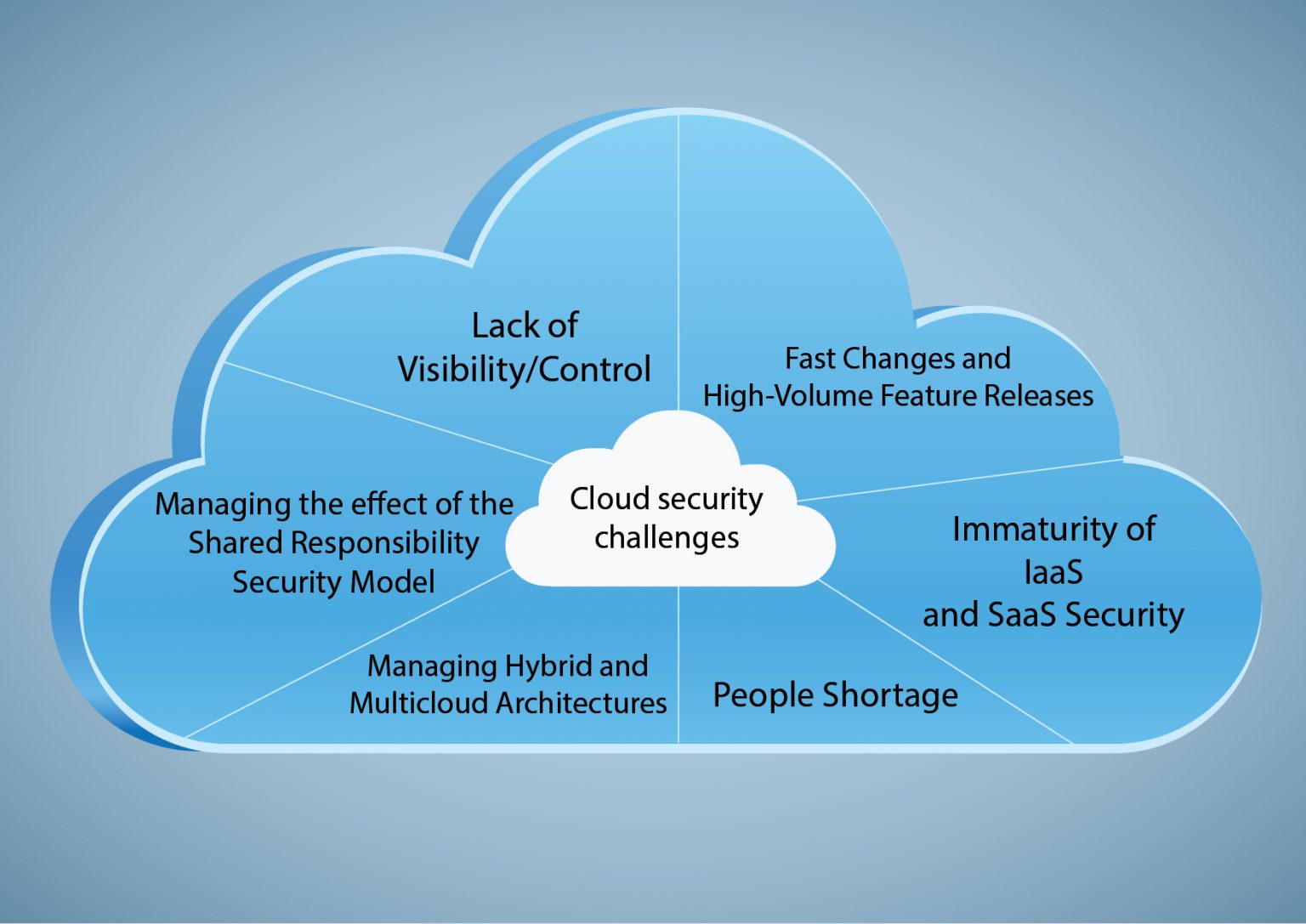
Ensuring Security and Compliance in the Cloud: Tips and Strategies
As cloud computing becomes increasingly popular, organizations must address essential security and compliance considerations to protect their data and systems. This section offers practical tips and strategies for ensuring security and compliance when adopting cloud computing essentials.
Understanding Cloud Security Responsibilities
Both cloud service providers and customers share security responsibilities in a cloud environment. While providers secure the underlying infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing their applications, data, and access controls. Clearly understanding these responsibilities is crucial for maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Implementing Strong Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is essential for securing your cloud resources. Utilize multi-factor authentication, least privilege access, and role-based access control to limit unauthorized access and mitigate the risk of data breaches. Regularly review and update access controls to ensure they remain effective and up-to-date.
Encrypting Data at Rest and in Transit
Encrypt data both at rest and in transit to protect sensitive information and maintain confidentiality. Use encryption algorithms and protocols, such as AES and TLS, to secure data and ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Monitoring and Logging Cloud Activities
Monitor and log cloud activities to detect and respond to security threats in real-time. Utilize cloud-native monitoring tools and third-party solutions to track user activities, resource usage, and potential security incidents. Regularly review logs and alerts to identify and address suspicious behavior or vulnerabilities.
Regularly Assessing Security and Compliance
Regularly assess your cloud security and compliance posture to ensure ongoing protection and adherence to industry standards and regulations. Utilize security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to identify and remediate potential weaknesses and maintain a secure cloud environment.
Establishing a Cloud Security Policy
Develop and implement a comprehensive cloud security policy that outlines roles, responsibilities, and best practices for securing your cloud resources. Ensure that all stakeholders are aware of and adhere to the policy, and regularly review and update it to address emerging threats and changing business needs.
Choosing a Secure Cloud Service Provider
Select a cloud service provider with a strong commitment to security and compliance. Look for providers that offer robust security features, adhere to industry standards and regulations, and provide transparency into their security practices and policies.
Providing Security Awareness Training
Provide regular security awareness training to all employees to ensure they understand the importance of cloud security and their role in protecting your organization’s data and systems. Training should cover topics such as strong passwords, phishing awareness, and secure data handling practices.
The Future of Cloud Computing: Trends and Predictions
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. As cloud computing continues to evolve, several emerging trends and predictions are shaping the future of this transformative technology. This section explores the most significant trends and predictions in cloud computing essentials, offering insights into the innovations and opportunities that lie ahead.
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency, and improving performance for IoT devices and applications. By combining edge computing with cloud computing, organizations can create more efficient, secure, and responsive systems that cater to the growing demands of IoT and edge devices.
Serverless Architecture
Serverless architecture enables developers to build and deploy applications without managing servers, allowing them to focus on code and functionality. This model offers numerous benefits, including reduced operational overhead, increased scalability, and faster time-to-market for applications and services.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming increasingly integrated into cloud computing environments, enabling organizations to harness the power of data-driven insights and automation. By leveraging AI and ML in the cloud, businesses can improve decision-making, streamline operations, and create more personalized user experiences.
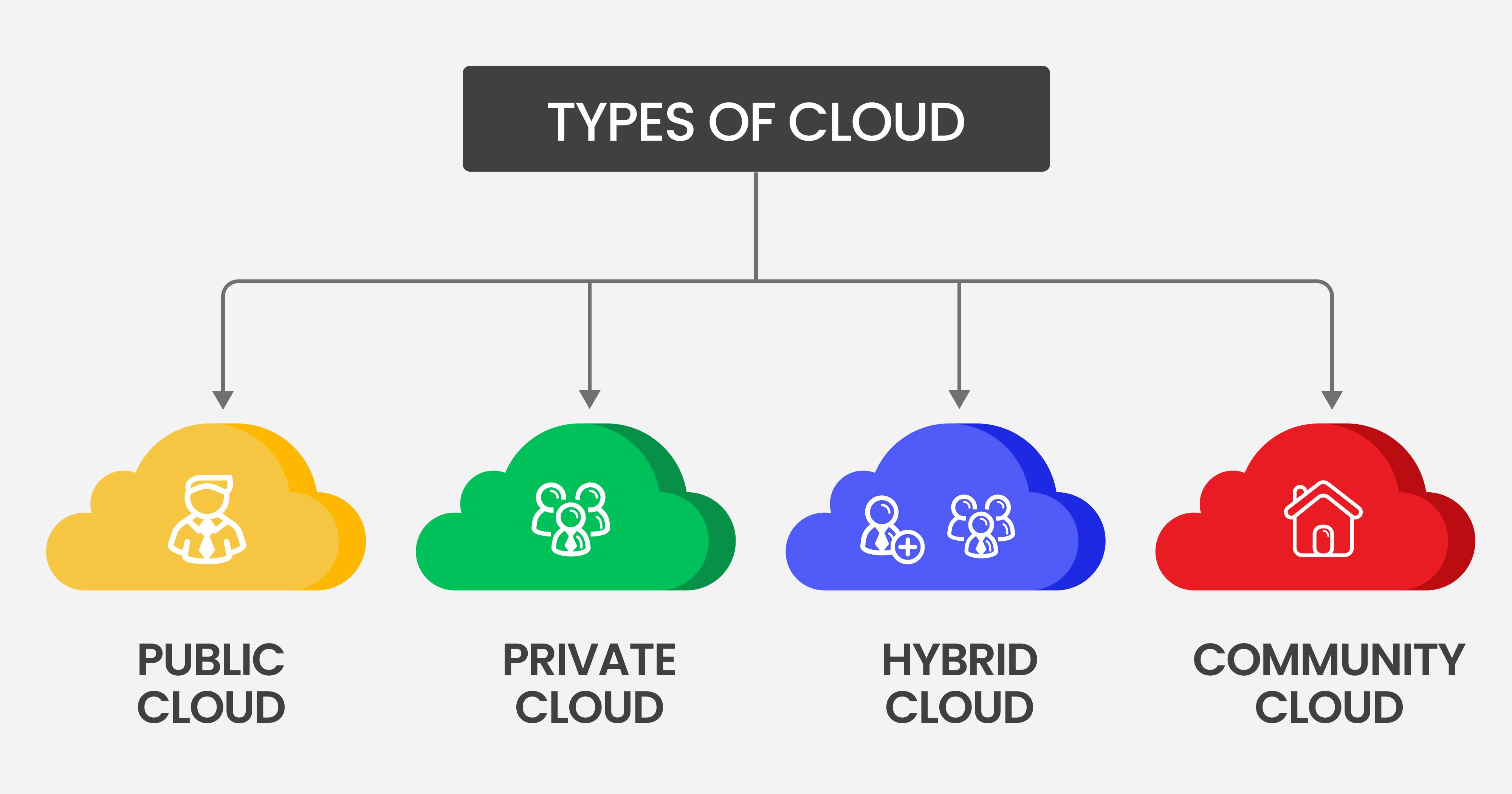
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
As organizations continue to adopt cloud computing, multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies are becoming more prevalent. These approaches enable businesses to leverage the unique strengths and capabilities of different cloud providers and platforms, creating a cohesive and flexible IT infrastructure that meets their specific needs and objectives.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is an emerging technology that promises to revolutionize cloud computing by offering unprecedented processing power and speed. While still in its infancy, quantum computing has the potential to solve complex problems and unlock new possibilities for businesses operating in various industries, including finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Computing
As environmental concerns become more pressing, cloud computing providers are focusing on sustainability and green initiatives to reduce their carbon footprint and promote eco-friendly practices. By adopting energy-efficient data centers, renewable energy sources, and other green technologies, cloud providers can contribute to a more sustainable future while still delivering high-performance computing resources.
Data Governance and Privacy
Data governance and privacy will continue to be essential considerations for organizations adopting cloud computing. As businesses grapple with increasingly complex data protection regulations and the growing threat of data breaches, cloud providers must offer robust data governance tools, encryption, and access controls to help businesses protect their sensitive information and maintain compliance.
The Evolution of Cloud Computing Essentials
The future of cloud computing is bright, with numerous trends and predictions shaping its evolution. By staying informed about these developments and adopting innovative cloud computing solutions, businesses can gain a competitive edge, streamline operations, and unlock new opportunities for growth and success.