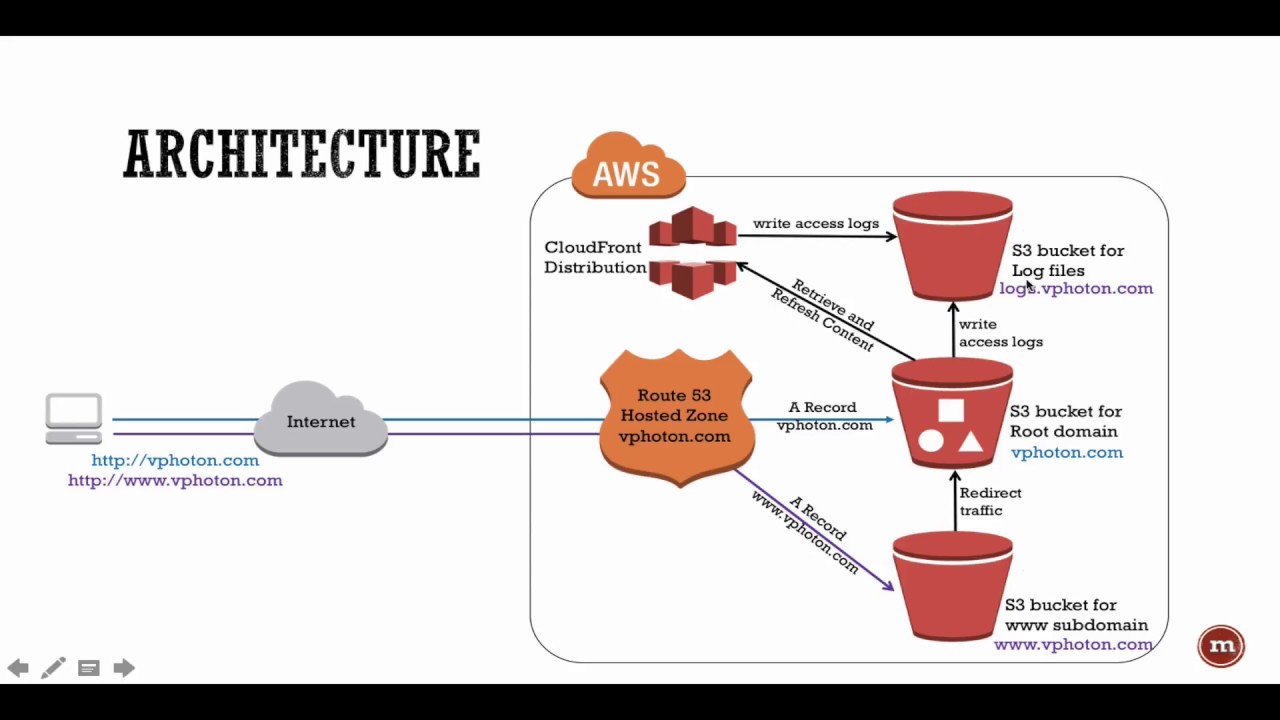
What is an S3 Bucket in AWS?
An S3 bucket in AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a scalable and secure object storage solution that allows users to store, manage, and access data in a highly flexible and durable manner. As a part of Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service), S3 buckets can accommodate various data types, including text, images, videos, and application files. This makes them suitable for a wide range of use cases, such as backup and archiving, data warehousing, and media hosting.
Key Features and Benefits of S3 Buckets
Amazon S3 buckets offer a wide range of features and benefits that make them an ideal choice for object storage in AWS. Some of the key features include:
- Versioning: This feature allows users to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object in their bucket, enabling data recovery and maintaining previous iterations of objects.
- Lifecycle Policies: S3 buckets support lifecycle policies, which automate the transitioning and deletion of objects based on age, access frequency, and storage class. This helps optimize storage costs and ensures data is stored according to its lifecycle needs.
- Cross-Region Replication: S3 buckets can be configured to automatically replicate objects to other AWS regions, providing data durability, disaster recovery, and low-latency access to data across the globe.
- Access Control Options: S3 buckets offer various access control options, such as bucket policies, access control lists (ACLs), and Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies, ensuring secure and controlled access to stored data.
These features contribute to several benefits for users, such as:
- Data Durability: S3 buckets provide 99.999999999% durability, ensuring data is protected against failures and losses.
- Cost Optimization: With features like versioning and lifecycle policies, users can minimize storage costs and ensure data is stored efficiently.
- Enhanced Security: Access control options and encryption capabilities enable users to secure their data and meet compliance requirements.
How to Create an S3 Bucket in AWS
Creating an S3 bucket in AWS is a straightforward process that can be accomplished through the AWS Management Console. Follow these steps to create your first S3 bucket:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to the S3 service.
- Click on the “Create bucket” button, which will open the “Create bucket” page.
- Enter a unique and descriptive name for your bucket, ensuring it adheres to the naming requirements and does not conflict with existing bucket names.
- Select a region for your bucket from the dropdown menu. This will determine the physical location where your data is stored.
- Configure additional settings as needed, such as versioning, server-side encryption, and access control options. These settings can be modified later if required.
- Review your settings and click “Create bucket” to finalize the process.
When creating an S3 bucket, consider the following best practices:
- Use a unique and meaningful name for your bucket.
- Select a region that is geographically close to your users to minimize latency.
- Enable versioning to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object in your bucket.
- Implement access control options, such as bucket policies and IAM policies, to secure your data and control access.
- Monitor and log activities related to your bucket to track changes and ensure security.
Best Practices for Managing S3 Buckets
Effective management of S3 buckets is crucial for optimizing performance, cost, and security. Here are some tips and strategies to help you manage your S3 buckets:
- Monitoring and Logging: Regularly monitor your S3 buckets for any unusual activity or trends. Enable logging to track access and modifications to your buckets. AWS CloudTrail and Amazon S3 Server Access Logging are valuable tools for monitoring and logging purposes.
- Data Encryption: Protect your data by using encryption techniques such as server-side encryption (SSE), client-side encryption, or client-side master keys (SSE-C) managed by AWS Key Management Service (KMS). Encryption ensures that your data remains secure, even when stored in the cloud.
- Access Management: Implement strict access control policies to prevent unauthorized access to your S3 buckets. Use IAM roles, policies, and bucket policies to manage access to your data. Regularly review and update these policies to ensure they are up-to-date and aligned with your security requirements.
- Lifecycle Management: Implement lifecycle policies to automatically transition or delete objects based on their age, access frequency, or storage class. This helps optimize storage costs and ensures data is stored according to its lifecycle needs.
- Versioning Management: Enable versioning to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object in your bucket. However, be aware that versioning may increase storage costs, so regularly monitor and manage your versions to avoid unnecessary expenses.
By following these best practices, you can effectively manage your S3 buckets, ensuring optimal performance, cost, and security. Regularly review and update your management strategies to stay current with the latest AWS features and updates.
Use Cases for S3 Buckets in AWS
Amazon S3 buckets offer a wide range of use cases, making them an essential component of many AWS-based solutions. Here are some real-world examples of how S3 buckets can be utilized:
Website Hosting
S3 buckets can be used to host static websites, providing a simple, cost-effective, and scalable solution. By storing HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and media files in an S3 bucket, you can serve your website to users across the globe with low latency and high availability.
Data Analytics
S3 buckets can serve as a centralized data lake for storing and processing large volumes of structured and unstructured data. With services like AWS Glue, Amazon Athena, and Amazon Redshift, you can easily analyze and gain insights from your data, making data-driven decisions more accessible and efficient.
Machine Learning
S3 buckets can be used as storage for machine learning models, datasets, and training materials. AWS machine learning services, such as Amazon SageMaker and Amazon Rekognition, can directly access data stored in S3 buckets, streamlining the machine learning workflow and enabling faster model development and deployment.
Backup and Archiving
S3 buckets can be used as a secure and durable storage solution for backup and archiving purposes. With features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication, you can ensure data durability, cost optimization, and regulatory compliance for your backup and archiving needs.
Media Hosting
S3 buckets can be used to store, manage, and distribute digital media content, such as images, videos, and audio files. With AWS Elemental MediaConvert, AWS Elemental MediaLive, and AWS Elemental MediaPackage, you can easily transcode, package, and deliver media content to various devices and platforms.
By understanding these use cases, you can leverage the full potential of S3 buckets in AWS and create efficient, secure, and scalable solutions for your data storage and management needs.
Comparing S3 Buckets with Other AWS Storage Services
Amazon S3 buckets are just one of many storage solutions offered by AWS. Understanding the differences in performance, cost, and use cases between S3 buckets and other AWS storage services can help you choose the right storage solution for your needs. Here’s a comparison of S3 buckets with Amazon EBS, Amazon EFS, and Amazon FSx:
Amazon S3 vs. Amazon EBS
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) provides block-level storage for Amazon EC2 instances, while Amazon S3 offers object storage for various data types and use cases. EBS is designed for use with EC2 instances and provides low-latency, high-throughput storage for applications that require frequent read/write access, such as databases and boot volumes. In contrast, S3 is ideal for storing large volumes of data, such as backups, archives, and media content, and offers features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication.
Amazon S3 vs. Amazon EFS
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) provides a scalable, fully-managed network file system for use with EC2 instances and on-premises resources. EFS is designed for use with applications that require a shared file system, such as content management systems, web servers, and home directories. S3, on the other hand, is an object storage solution that offers a simple web interface for storing and retrieving data. While EFS provides a shared file system, S3 offers features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication, making it a better choice for backup, archiving, and media hosting use cases.
Amazon S3 vs. Amazon FSx
Amazon FSx provides fully-managed file systems that are compatible with popular file systems, such as Windows Server, Lustre, and OpenZFS. FSx is designed for use with applications that require high-performance, shared file systems, such as high-performance computing (HPC), machine learning, and media and entertainment workloads. S3, however, is an object storage solution that offers a simple web interface for storing and retrieving data. While FSx provides high-performance shared file systems, S3 offers features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication, making it a better choice for backup, archiving, and media hosting use cases.
By understanding the differences between S3 buckets and other AWS storage services, you can choose the right storage solution for your needs and ensure optimal performance, cost, and security for your data storage and management requirements.
Troubleshooting Common S3 Bucket Issues
Amazon S3 buckets are a reliable and secure storage solution, but users may occasionally encounter issues that require troubleshooting. Here are some common S3 bucket issues and their solutions:
Access Denied Errors
Access denied errors can occur when a user doesn’t have the necessary permissions to access an S3 bucket. To resolve this issue, ensure that the user has the required IAM policies, bucket policies, or ACLs that grant access to the S3 bucket. You can also use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to create and manage users, groups, and permissions for accessing S3 resources.
Bucket Listing Limitations
By default, the AWS S3 console limits the number of buckets displayed in the bucket list to 1000. To view all of your buckets, you can use the AWS CLI, SDKs, or the S3 API. Additionally, you can use the console’s “Next token” feature to navigate through multiple pages of bucket listings.
Versioning Conflicts
Versioning conflicts can occur when two or more users attempt to upload a file with the same name to the same S3 bucket. To resolve this issue, you can use versioning to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object in your bucket. You can also use lifecycle policies to automatically manage older versions of objects and delete them based on a specified retention period.
By understanding these common S3 bucket issues and their solutions, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve any problems that may arise, ensuring optimal performance, cost, and security for your data storage and management needs.
Staying Up-to-Date with S3 Bucket Innovations
Amazon S3 is a constantly evolving storage solution, with new features and updates released regularly. Staying informed about the latest innovations can help you optimize your S3 bucket performance, cost, and security. Here are some valuable resources for learning and networking:
AWS Documentation
The official AWS documentation is a comprehensive resource for learning about S3 buckets and other AWS services. The documentation includes user guides, API references, and tutorials that cover a wide range of topics, from getting started with S3 to advanced features and best practices.
AWS Blogs
The AWS blogs are a great resource for staying up-to-date with the latest S3 bucket features and updates. The blogs cover a wide range of topics, from new service launches and feature updates to best practices and customer stories. You can subscribe to the AWS Blogs to receive notifications about new posts and updates.
AWS Forums
The AWS forums are a community-driven resource where you can ask questions, share knowledge, and connect with other AWS users. The forums cover a wide range of topics, from getting started with AWS to advanced features and troubleshooting. You can join the S3 bucket forum to ask questions and get answers from other AWS users and experts.
By staying informed about the latest S3 bucket innovations and updates, you can ensure that you are using the most up-to-date and secure storage solution for your data storage and management needs. Additionally, by participating in the AWS community, you can learn from other users, share your knowledge, and contribute to the development of S3 buckets and other AWS services.