The Emergence of Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS), a subsidiary of the e-commerce giant Amazon, has become a cornerstone in the realm of cloud computing. AWS offers a wide array of services, including on-demand computing resources, storage, and APIs for government agencies, companies, and individuals. Although the precise inception date of AWS remains undisclosed, it is widely believed to have originated between 2004 and 2
Early Developments and Offerings
As Amazon Web Services (AWS) took its first steps in the cloud computing landscape, it introduced several groundbreaking services that would significantly impact the industry. Simple Queue Service (SQS) and Simple Storage Service (S3) were among the earliest offerings, launched in 2004 and 2006, respectively.
Simple Queue Service (SQS), a fully managed message queuing service, marked AWS’s entry into the cloud computing space. SQS enables developers to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. By providing a reliable and scalable messaging solution, SQS has played a pivotal role in simplifying application development and maintenance.
In 2006, AWS unveiled Simple Storage Service (S3), an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. S3 has become a fundamental building block for countless applications, websites, and storage solutions, empowering developers and businesses to store, manage, and serve files and data at a massive scale. The introduction of S3 further solidified AWS’s position as a trailblazer in the cloud computing market.
These early developments from AWS have significantly shaped the cloud computing landscape, paving the way for a new era of on-demand, scalable, and secure computing resources.
Expansion and Maturation of AWS
Since its inception, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has experienced remarkable growth and evolution, expanding its service offerings and catering to diverse industries and use cases. AWS has continuously matured, offering a wide range of tools, features, and capabilities to meet the ever-changing demands of the cloud computing market.
Throughout the years, AWS has made several significant acquisitions and established strategic partnerships that have contributed to its growth. For instance, in 2012, AWS acquired the mobile and web application platform, Go.com, to enhance its mobile services portfolio. In 2015, AWS partnered with Accenture, a leading global professional services company, to deliver robust cloud services and solutions to enterprises worldwide.
AWS has also expanded its service offerings to include machine learning, artificial intelligence, analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). For example, Amazon SageMaker, a fully managed service that provides developers and data scientists with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning models quickly, was launched in 2017. AWS also offers AWS IoT Core, a managed cloud service that lets connected devices easily and securely interact with cloud applications and other devices.
By consistently adding new services and features, AWS has solidified its position as a leading cloud computing provider, catering to a wide array of industries and use cases.
AWS’s Global Impact and Market Dominance
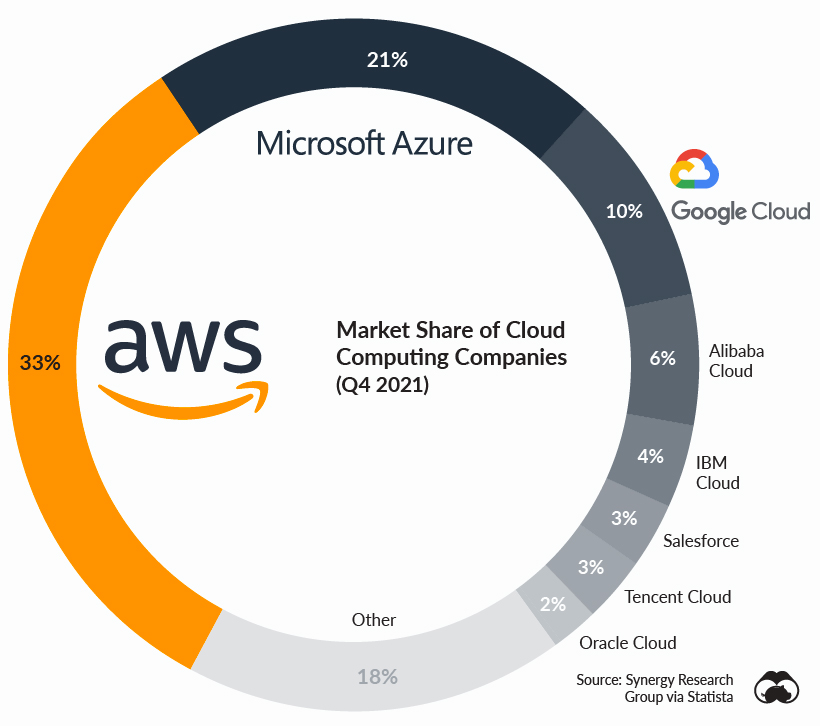
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has established itself as a dominant force in the global cloud computing market, demonstrating significant influence and leadership in the industry. According to a recent Synergy Research Group report, AWS holds the largest market share in cloud infrastructure services, accounting for over 30% of the global market.
AWS’s extensive service portfolio, robust security features, and commitment to innovation have attracted a diverse range of customers, from individual developers and startups to large enterprises and government agencies. Notable AWS customers include Netflix, Airbnb, and the National Football League (NFL), which rely on AWS for various computing needs, such as data storage, application hosting, and machine learning.
“AWS has been a game-changer for our business,” says John Ciancutti, Vice President of Engineering at Netflix. “Their platform has allowed us to scale quickly and efficiently, ensuring that we can deliver high-quality streaming content to our millions of users worldwide.”
In addition to its strong customer base, AWS has a vast global footprint, with 81 Availability Zones across 25 geographic regions and 199 points of presence. This extensive infrastructure enables AWS to provide low-latency, high-availability services to customers worldwide, further solidifying its position as a global leader in cloud computing.
How Amazon Web Services Continues to Evolve
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has consistently demonstrated its commitment to innovation and continuous improvement. In recent years, AWS has introduced numerous updates, announcements, and trends that showcase its ongoing evolution in the cloud computing space.
In 2021, AWS announced the general availability of Amazon Braket, a fully managed quantum computing service that enables scientists, researchers, and developers to experiment with computers from quantum hardware providers. This development highlights AWS’s dedication to pushing the boundaries of technology and advancing the field of quantum computing.
In addition to exploring emerging technologies, AWS has also expanded its service offerings in existing domains. For instance, in 2020, AWS introduced AWS Outposts, a hybrid cloud solution that allows customers to run AWS compute and storage services on-premises, providing a seamless connection between on-premises infrastructure and the AWS Global Infrastructure.
Moreover, AWS has made significant strides in enhancing its machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities. In 2019, AWS launched Amazon SageMaker Studio, a fully integrated development environment for machine learning, providing data scientists and developers with a single, web-based visual interface to manage, build, train, and deploy machine learning models.
By staying at the forefront of innovation and continuously refining its services, AWS ensures that it remains a leading player in the ever-evolving cloud computing landscape.
Navigating AWS’s Comprehensive Service Portfolio
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a vast and continually expanding array of services, making it essential for users to strategically navigate the portfolio. Here are some tips for selecting the right services for specific needs and staying updated on new offerings and features:
- Identify your requirements: Clearly define your organization’s needs and objectives before exploring AWS services. This approach will help you focus on relevant offerings and avoid being overwhelmed by the extensive portfolio.
- Explore the AWS Management Console: The AWS Management Console provides a user-friendly interface for managing services and discovering new features. Regularly browsing the console can help you stay informed about updates and potential benefits for your organization.
- Leverage AWS documentation and resources: AWS provides comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and guides for each service. Utilize these resources to understand the capabilities and limitations of each offering, as well as to learn best practices for implementation and management.
- Follow AWS news and announcements: Stay updated on AWS news and announcements by subscribing to AWS blogs, newsletters, and social media channels. AWS re:Invent, the company’s annual conference, is also an excellent source of information on new services, features, and trends.
- Engage with the AWS community: Join AWS user groups, forums, and webinars to connect with other users, share experiences, and learn from experts. Participating in the AWS community can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions about service selection and utilization.
By following these tips, you can effectively navigate AWS’s comprehensive service portfolio and ensure that you’re making the most of the platform’s capabilities for your organization.
Assessing AWS’s Role in Your Organization
When considering Amazon Web Services (AWS) for your organization, evaluating several factors is crucial to ensuring a successful implementation. Key aspects to assess include cost, scalability, security, and integration with existing systems:
- Cost: AWS operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can result in significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. However, it’s essential to monitor usage and optimize costs by utilizing AWS cost management tools and best practices.
- Scalability: One of the primary benefits of AWS is its ability to scale resources up or down on demand. This elasticity enables organizations to handle fluctuating workloads and accommodate growth without the need for significant capital investments.
- Security: AWS offers robust security features, including encryption, access control, and compliance with various industry standards. However, it’s crucial to configure these features correctly and follow security best practices to protect your data and infrastructure.
- Integration with existing systems: Assessing the compatibility of AWS services with your current systems and processes is essential. AWS provides various tools and APIs to facilitate integration, but it’s essential to plan and execute a smooth migration strategy to minimize disruptions.
By carefully evaluating these factors, organizations can determine whether AWS is the right choice for their specific needs and objectives.
Preparing for AWS Adoption and Migration
Transitioning to Amazon Web Services (AWS) can offer numerous benefits, but it’s essential to approach the migration process strategically. By following best practices and addressing potential challenges, organizations can ensure a successful transition to AWS:
- Assess readiness: Evaluate your organization’s current IT infrastructure, applications, and processes to identify areas that require improvement or modification before migration. This assessment will help ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
- Plan and prioritize: Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the sequence and timeline for moving workloads to AWS. Prioritize applications and services based on business needs, dependencies, and complexity.
- Choose the right migration tools: AWS provides various tools and services, such as AWS Server Migration Service, AWS Database Migration Service, and AWS Application Discovery Service, to simplify the migration process. Select the appropriate tools based on your specific requirements and use cases.
- Optimize costs: AWS operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can result in significant cost savings. However, it’s crucial to monitor usage and optimize costs by utilizing AWS cost management tools and best practices.
- Ensure security and compliance: Implement robust security measures and ensure compliance with industry standards during the migration process. Utilize AWS security features, such as Identity and Access Management (IAM), Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and Security Groups, to protect your infrastructure and data.
- Test and validate: Thoroughly test and validate the migrated applications and services to ensure they function correctly and meet performance expectations. Address any issues before deploying them in a production environment.
By following these best practices, organizations can successfully adopt AWS and leverage its extensive capabilities to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.