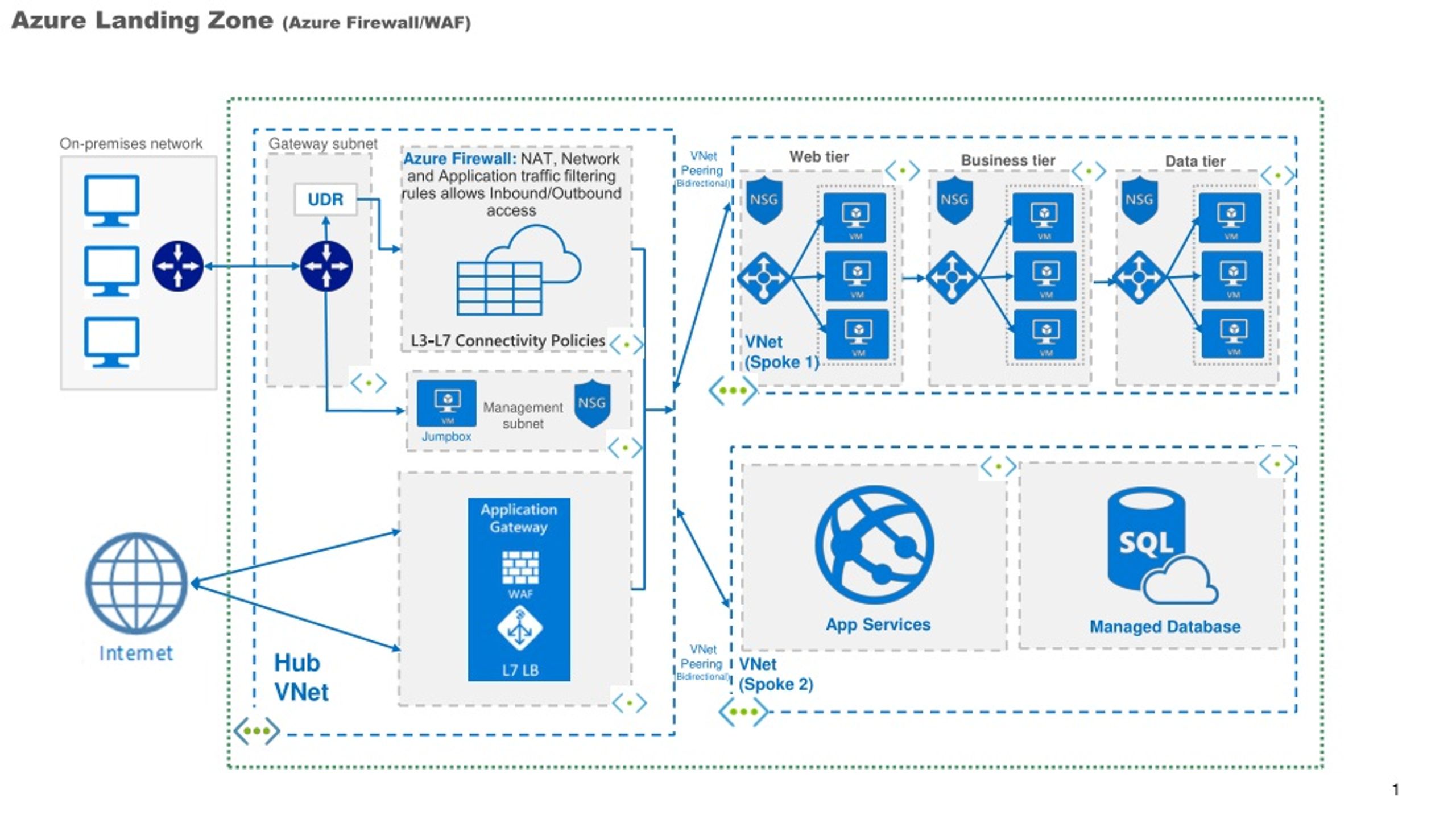
What is Azure Application Gateway WAF?
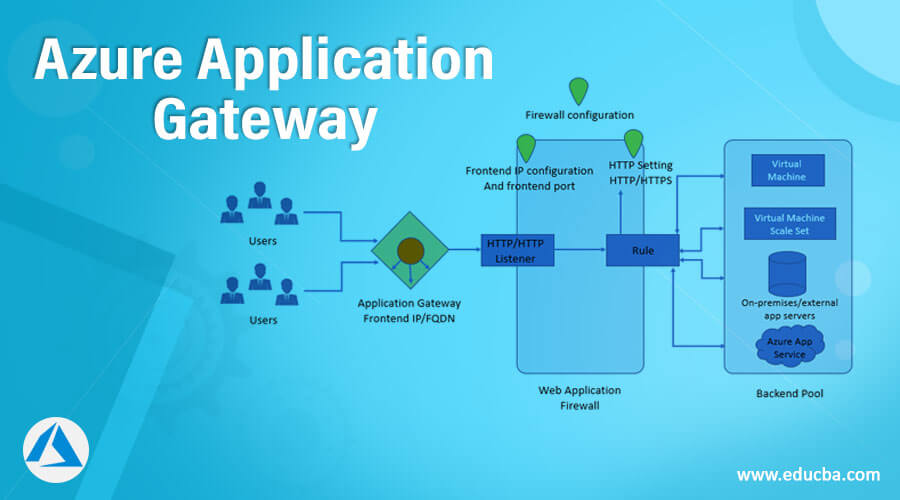
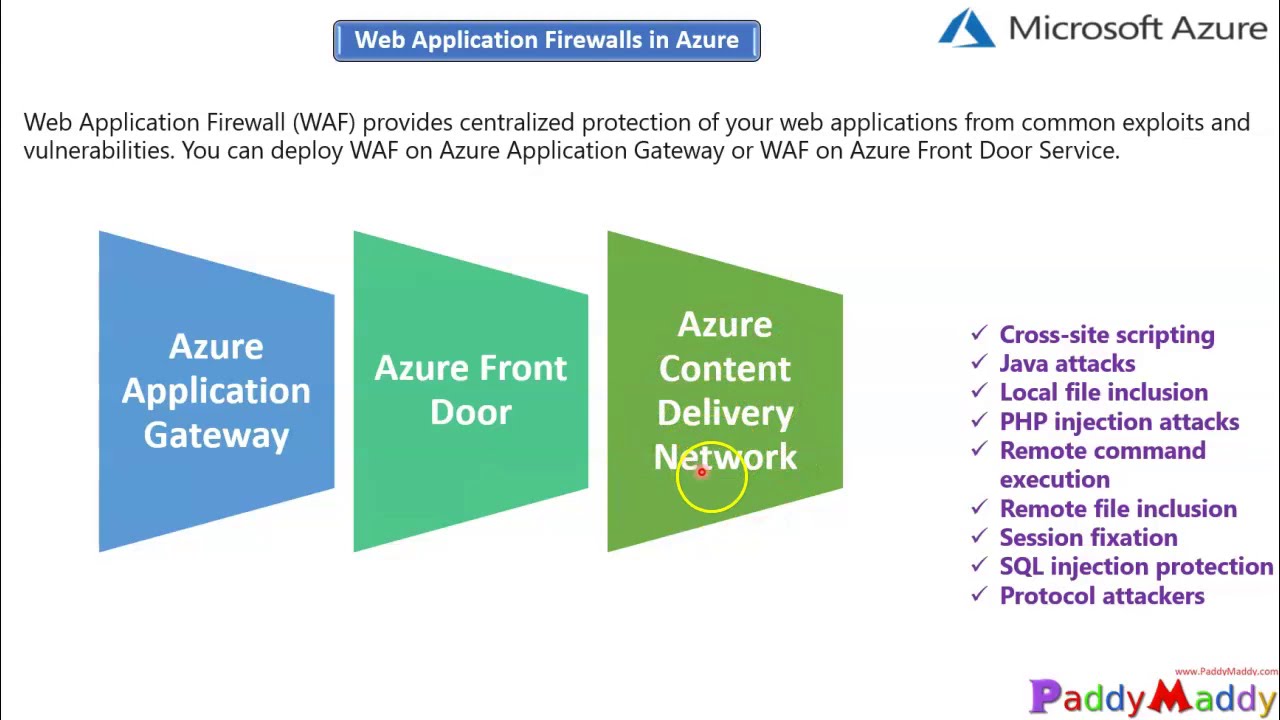
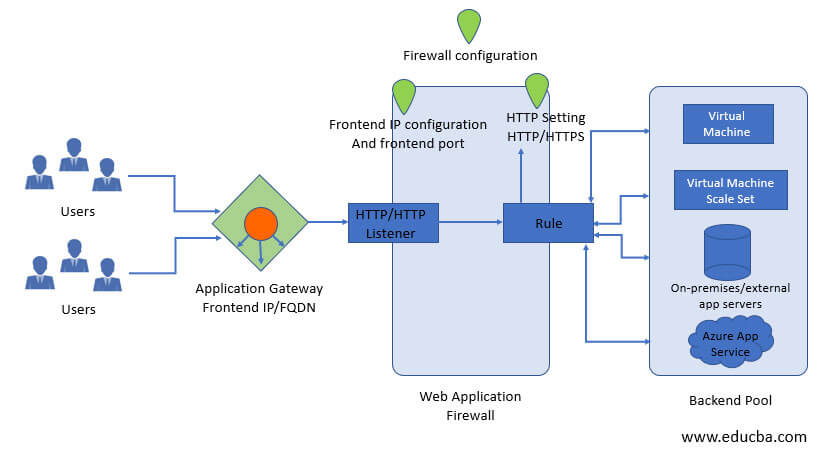
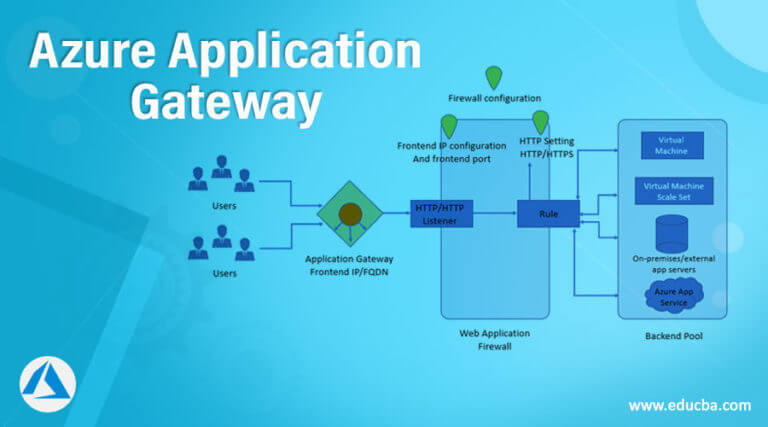
Azure Application Gateway WAF (Web Application Firewall) is a cloud-based security service that helps protect web applications from common web exploits and attacks. It is a layer 7 load balancer that provides centralized management, customizable rules, and integration with other Azure services. Unlike traditional firewalls, Azure Application Gateway WAF is specifically designed to secure web applications and provide advanced security features such as OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) Core Rule Set (CRS) support, bot protection, and rate limiting.
In a cloud-based environment, Azure Application Gateway WAF plays a critical role in securing web applications by providing a centralized point of control and management for security policies. It enables organizations to implement consistent security policies across their web applications, regardless of where they are hosted. With its advanced security features and integration with other Azure services, Azure Application Gateway WAF is a powerful tool for securing web applications in the cloud.
Key Features and Benefits of Azure Application Gateway WAF
Azure Application Gateway WAF offers a wide range of features and benefits that make it an ideal solution for securing web applications in the cloud. One of its key features is centralized management, which enables organizations to manage security policies and rules for all their web applications from a single location. This not only simplifies management but also ensures consistent security policies across all web applications.
Another important feature of Azure Application Gateway WAF is customizable rules. With customizable rules, organizations can create and implement rules that are tailored to their specific security needs. This allows them to fine-tune their security policies and ensure that they are effectively protecting their web applications against the latest threats.
Azure Application Gateway WAF also offers integration with other Azure services, such as Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center. This integration enables organizations to monitor and manage their web application security policies in real-time, as well as receive alerts and notifications when potential security threats are detected. Additionally, Azure Application Gateway WAF supports integration with third-party security tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, providing even more advanced security capabilities.
Overall, Azure Application Gateway WAF offers a powerful set of features and benefits for securing web applications in the cloud. Its centralized management, customizable rules, and integration with other Azure services make it a flexible and effective solution for protecting web applications against a wide range of threats.
How to Configure Azure Application Gateway WAF
Configuring Azure Application Gateway WAF is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to configure Azure Application Gateway WAF:
Step 1: Create a New Application Gateway
To create a new Application Gateway, navigate to the Azure portal and select “Create a resource.” Search for “Application Gateway” and click “Create.” Fill in the required fields, including the name, SKU, tier, and resource group. Once you’ve filled in all the required fields, click “Create” to create the new Application Gateway.
Step 2: Add Listeners and Backend Pools
Once the Application Gateway has been created, the next step is to add listeners and backend pools. Listeners are used to listen for incoming traffic, while backend pools are used to route traffic to the appropriate backend servers. To add a listener, navigate to the Application Gateway and click “Add listener.” Fill in the required fields, including the listener name, frontend IP address, and protocol. Once you’ve filled in all the required fields, click “Add” to create the new listener. To add a backend pool, navigate to the Application Gateway and click “Add backend pool.” Fill in the required fields, including the backend pool name and backend targets. Once you’ve filled in all the required fields, click “Add” to create the new backend pool.
Step 3: Configure WAF Settings
Once the listeners and backend pools have been configured, the next step is to configure WAF settings. To configure WAF settings, navigate to the Application Gateway and click “WAF.” Fill in the required fields, including the WAF mode, action, and rules. Once you’ve filled in all the required fields, click “Save” to save the WAF settings.
Step 4: Monitor Activity
After the Application Gateway has been configured, it’s important to monitor activity to ensure that it’s working correctly. To monitor activity, navigate to the Application Gateway and click “Monitoring.” From here, you can view metrics such as requests, responses, and response times. You can also set up alerts to notify you when potential security threats are detected.
By following these steps, you can easily configure Azure Application Gateway WAF and start securing your web applications in the cloud. Remember to regularly update rules, monitor traffic, and integrate with other security tools to ensure that your web applications are protected against the latest threats.
Best Practices for Implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF
Implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF can help organizations secure their web applications and protect against common web exploits and attacks. However, to ensure that Azure Application Gateway WAF is implemented effectively, it’s important to follow best practices. Here are some best practices for implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF:
Regularly Update Rules
One of the most important best practices for implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF is to regularly update rules. Azure Application Gateway WAF includes a set of preconfigured rules that are designed to protect against common web exploits and attacks. However, new threats emerge constantly, so it’s important to regularly update rules to ensure that they are effective against the latest threats.
Monitor Traffic
Another important best practice for implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF is to monitor traffic. By monitoring traffic, organizations can identify potential security threats and take action to mitigate them. Azure Application Gateway WAF includes a range of monitoring and logging features that can help organizations monitor traffic and identify potential security threats.
Integrate with Other Security Tools
Integrating Azure Application Gateway WAF with other security tools can help organizations enhance their security posture. For example, organizations can integrate Azure Application Gateway WAF with Azure Security Center to receive security alerts and notifications. They can also integrate Azure Application Gateway WAF with third-party security tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, to provide even more advanced security capabilities.
Test and Validate Configuration
Before deploying Azure Application Gateway WAF in a production environment, it’s important to test and validate the configuration. This can help ensure that Azure Application Gateway WAF is configured correctly and that it is effective in protecting against web exploits and attacks. Organizations can use Azure Application Gateway WAF’s testing and validation features to simulate traffic and validate the configuration.
Implement a Layered Security Approach
Finally, implementing a layered security approach is an important best practice for implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF. By implementing a layered security approach, organizations can ensure that they are protected against a wide range of threats. For example, they can implement network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), in addition to Azure Application Gateway WAF. This can help ensure that they are protected against both network-level threats and application-level threats.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure that they are implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF effectively and that they are protecting their web applications against a wide range of threats. Remember to regularly update rules, monitor traffic, integrate with other security tools, test and validate configuration, and implement a layered security approach to ensure that your web applications are protected against the latest threats.
Real-World Examples of Azure Application Gateway WAF
Azure Application Gateway WAF is a powerful tool for securing web applications in the cloud. But don’t just take our word for it – here are some real-world examples of Azure Application Gateway WAF in action:
Case Study: Global Retailer
A global retailer was looking for a way to secure their web applications against common web exploits and attacks. They turned to Azure Application Gateway WAF and were able to implement a centralized security solution that protected all their web applications. By using Azure Application Gateway WAF’s customizable rules, they were able to tailor their security policies to their specific needs. And by integrating Azure Application Gateway WAF with Azure Security Center, they were able to receive security alerts and notifications in real-time.
Testimonial: Healthcare Provider
“Azure Application Gateway WAF has been a game-changer for our organization,” said the IT security manager at a healthcare provider. “We were able to implement a secure web application gateway in just a few clicks, and the customizable rules allowed us to fine-tune our security policies to our specific needs. Plus, the integration with other Azure services has made it easy to monitor and manage our web application security.”
Case Study: Financial Services Firm
A financial services firm was looking for a way to secure their web applications against sophisticated attacks. They turned to Azure Application Gateway WAF and were able to implement a layered security solution that included network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS), in addition to Azure Application Gateway WAF. By using Azure Application Gateway WAF’s preconfigured rules, they were able to protect against common web exploits and attacks. And by regularly updating rules, they were able to ensure that they were protected against the latest threats.
These are just a few examples of how organizations are using Azure Application Gateway WAF to secure their web applications in the cloud. By implementing Azure Application Gateway WAF, organizations can protect against common web exploits and attacks, implement a layered security approach, and ensure that their web applications are secure in a cloud-based environment.
Comparing Azure Application Gateway WAF to Other WAF Solutions
When it comes to securing web applications, there are a variety of WAF (Web Application Firewall) solutions available. However, Azure Application Gateway WAF stands out from the crowd with its unique features and benefits. Here’s a comparison of Azure Application Gateway WAF to other WAF solutions:
Centralized Management
One of the key benefits of Azure Application Gateway WAF is centralized management. With Azure Application Gateway WAF, organizations can manage their web application security policies from a single location. This is in contrast to other WAF solutions, which may require organizations to manage security policies on a per-application basis. With centralized management, organizations can ensure that their web applications are consistently protected against web exploits and attacks.
Customizable Rules
Another benefit of Azure Application Gateway WAF is customizable rules. Azure Application Gateway WAF includes a set of preconfigured rules that are designed to protect against common web exploits and attacks. However, organizations can also create their own custom rules to tailor their security policies to their specific needs. This is in contrast to other WAF solutions, which may not offer the same level of customization.
Integration with Other Azure Services
Azure Application Gateway WAF integrates seamlessly with other Azure services, such as Azure Monitor and Azure Security Center. This integration provides organizations with advanced monitoring and logging capabilities, as well as real-time security alerts and notifications. In contrast, other WAF solutions may not offer the same level of integration with cloud-based services.
Potential Drawbacks
While Azure Application Gateway WAF offers many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider. For example, Azure Application Gateway WAF may have a steeper learning curve compared to other WAF solutions. Additionally, organizations may need to invest in additional training and resources to effectively manage and configure Azure Application Gateway WAF.
Overall, Azure Application Gateway WAF is a powerful WAF solution that offers centralized management, customizable rules, and integration with other Azure services. While there are some potential drawbacks to consider, Azure Application Gateway WAF is an excellent choice for organizations looking to secure their web applications in a cloud-based environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Azure Application Gateway WAF
While Azure Application Gateway WAF is a powerful tool for securing web applications, there are some common issues that may arise when implementing and managing the service. Here are some solutions for troubleshooting and resolving these issues:
Issue: High CPU Utilization
If you notice that your Azure Application Gateway WAF is experiencing high CPU utilization, it may be due to a misconfiguration or a high volume of traffic. To troubleshoot this issue, check your WAF’s rules and configurations to ensure that they are optimized for performance. You may also want to consider scaling up your WAF to handle the increased traffic.
Issue: False Positives
False positives can occur when your WAF blocks legitimate traffic due to a misconfiguration or overly aggressive rules. To troubleshoot this issue, review your WAF’s rules and configurations to ensure that they are not too restrictive. You may also want to consider implementing custom rules to fine-tune your WAF’s security policies.
Issue: Slow Response Times
Slow response times can occur when your WAF is experiencing high traffic volumes or when it is performing complex security checks. To troubleshoot this issue, review your WAF’s configurations and rules to ensure that they are optimized for performance. You may also want to consider implementing caching or other performance optimization techniques to improve response times.
Issue: Inconsistent Behavior Across WAF Instances
If you notice inconsistent behavior across different instances of your WAF, it may be due to misconfigurations or differences in the underlying infrastructure. To troubleshoot this issue, review the configurations and infrastructure for each instance of your WAF to ensure that they are consistent. You may also want to consider implementing infrastructure as code (IaC) techniques to ensure consistency across all instances of your WAF.
By following these solutions for troubleshooting common issues with Azure Application Gateway WAF, you can ensure that your web applications are consistently protected against web exploits and attacks. Remember to regularly monitor your WAF’s activity and performance to identify and resolve any issues as quickly as possible.
The Future of Azure Application Gateway WAF
As web applications continue to be a target for cyber attacks, the need for effective security solutions is more important than ever. Azure Application Gateway WAF is a powerful tool for securing web applications in a cloud-based environment, and it is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of organizations. Here are some upcoming features and enhancements to look out for in the future of Azure Application Gateway WAF:
Integration with Azure Security Center
Azure Security Center is a cloud-native security solution that provides organizations with threat protection across their entire infrastructure. In the future, Azure Application Gateway WAF will integrate more closely with Azure Security Center, providing even more advanced security capabilities. This integration will enable organizations to centrally manage their web application security policies and receive real-time security alerts and notifications.
Advanced Machine Learning Capabilities
Azure Application Gateway WAF already includes preconfigured rules that are designed to protect against common web exploits and attacks. However, in the future, it will also include advanced machine learning capabilities that can detect and block sophisticated attacks that traditional rules may miss. These machine learning capabilities will be able to learn from past attacks and adapt to new threats as they emerge.
Enhanced Performance and Scalability
As web applications continue to grow in complexity and traffic volume, the need for enhanced performance and scalability is more important than ever. In the future, Azure Application Gateway WAF will include enhancements that will enable it to handle even higher traffic volumes and provide even faster response times. These enhancements will include improved caching capabilities, advanced traffic management features, and enhanced load balancing capabilities.
Integration with Other Azure Services
Azure Application Gateway WAF is already integrated with a variety of other Azure services, such as Azure Monitor and Azure Key Vault. In the future, it will integrate even more closely with other Azure services, providing organizations with even more advanced security capabilities. For example, it may integrate with Azure Active Directory for identity and access management, or with Azure Event Grid for real-time event-based communication.
Overall, the future of Azure Application Gateway WAF is bright, with upcoming features and enhancements that will provide even more advanced security capabilities, enhanced performance and scalability, and closer integration with other Azure services. By staying up-to-date with the latest developments in Azure Application Gateway WAF, organizations can ensure that their web applications are consistently protected against web exploits and attacks.